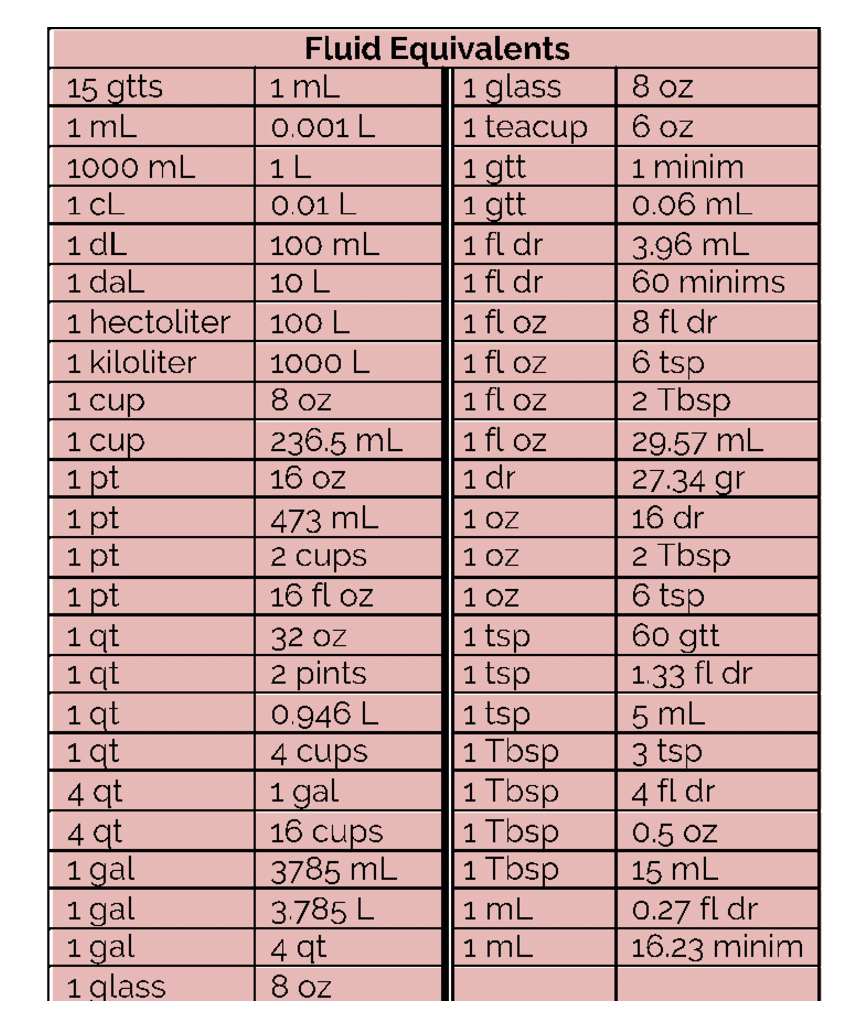
Step 1: What do I need? What unit of measurement do you need? Write this on the right of your paper. Step 2: What is the order? What does the order or prescription say? Write this on the left of the paper. Step 3: What conversion do I need to use? Does the question give any conversion? What conversion does the medication give? Here are the most useful ones: Converting lb to kg and kg to lb lb = kg × 2.2 kg = lb ÷ 2.2 Converting mL to L and L to mL mL = L × 1,000 L = mL ÷ 1,000 Converting mg to g, g to mg, mg to mcg, and mcg to mg mg = g × 1,000 g = mg ÷ 1,000 mcg = mg × 1,000
Nursing Dosage Med Math Calculations
Here are the most commonly used abbreviations when preparing drugs: Routes IM - Intramuscular IO - Intraosseous IV - Intravenous IVP - Intravenous Push ID - Intradermal IN - Intranasal IP - Intraperitoneal IT - Intrathecal IVPB - Intravenous piggyback p.o - By mouth SC / SubQ - Subcutaneous SL - Sublingual top. - Topical vag. - Vaginally Practicing dosage calculations and learning from your mistakes is the secret to success on the test - and patient safety. High-yield videos, thousands of practice questions, multiple self-assessment tests, and more. NCLEX-RN. NCLEX-PN. Learn how to answer nursing dosage calculations quickly and accurately with easy-to-follow tips, formulas, and. How many mL will you need to administer a 0.5 mg dose? Subcutaneous Dose Heparin 7500 units subcutaneous every 12 hours is ordered. The pharmacy provides a heparin vial with a concentration of 5000 units/mL. How many mL will you need to administer 7500 units? General Tips: Check that your answer makes sense clinically. Triple check your work. In preparation for a key nursing course, Principles and Applications in Nursing Technologies all students must enter with a core knowledge of medication dosage calculation.

Printable Nursing Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet
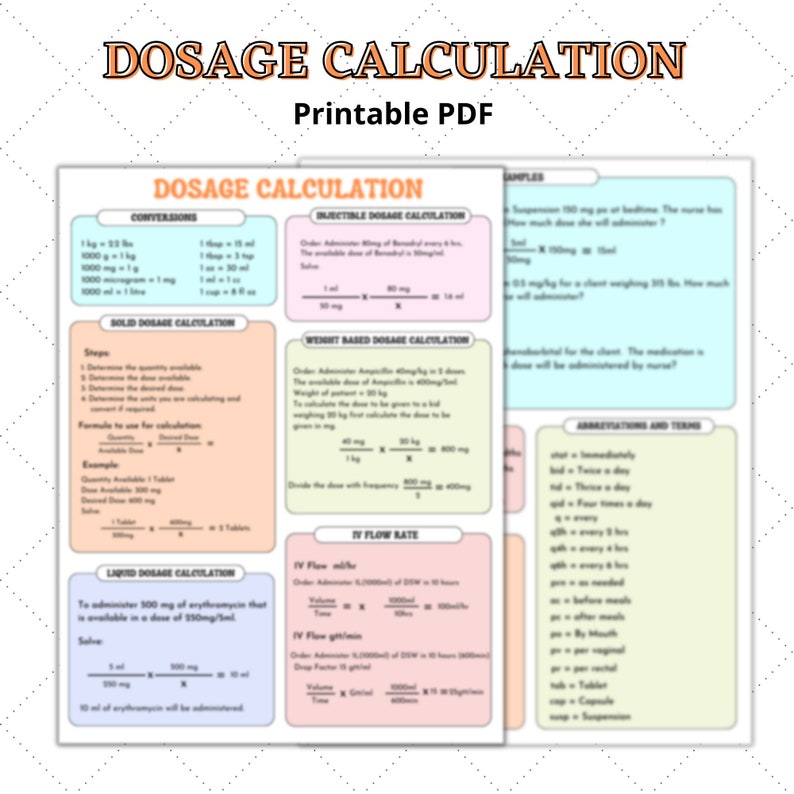
This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions Oral Liquid Medications Capsules and Tablets IV Boluses Calculating medication dosages, ensuring adequate fluid balances, and other treatment parameters - unit conversions are an essential mathematical tool in clinical nursing practice. A failure to accurately convert units can lead to medical errors with potentially serious or even fatal consequences. Linear Measure: ft. = 12 in. in. = 2.54 cm 39.4 in. = 1 m m = 1000 mm km = 1000 m Abbreviations for Units: lb - pound kg - kilogram g - gram mg - milligram ft - foot in. - inch m - meter Times amount.". (Dose ordered ÷ dose available) x amount. So you take whatever dose the physician ordered, divide it by whatever you have available, and multiply that times the amount that the med comes in. Example 1: The physician has ordered 2.5 grams and the medication comes in 500 mg/tab.

Dosage Calculation Cheat Sheet in 2021 Nursing school notes, Medical school essentials
This is a printable metric table for dosage and calculation quizzes. Print this metric table off of your printer and have it handy while you watch the video series. The metric table is in Microsoft docx format. Simply click the picture below to access the metric table. To watch Video Dosage & Calculation Tutorials you can view them here: This package is designed to assist the nurse to become competent in making drug calculations and can also be used as a reference guide. It owes much to the work of Darrel Baker (at the University Hospital of Wales), but has been significantly reduced in size in order to make it both manageable and less daunting.
How many mL should be administered per day? For this oral dosage problem, you have to find out how many mL of tetracycline the patient will get when the doctor has ordered 150 mg and the syrup has 50 mg/ml. This problem is set up and calculated as shown below. 150 mg: x mL = 50 mg: 1 mL. 50 x = 150. X = 150/50 = 3 mL. 5.4 Equivalencies. The nurse performs a variety of calculations in the clinical setting including intake and output conversions, weight conversions, dosages, volumes, and rates. The metric system is typically used when documenting and performing calculations in the clinical setting. Dosages may be calculated and converted into micrograms (mcg.
Printable Nursing Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet Printable Word Searches
40 Nursing Bullets: Pediatric Nursing Reviewer. Extend and further strengthen your knowledge about the concepts of Pediatric Nursing with these 40 Nursing Bullets. These Nursing Bullets are bite-sized information that are easy to absorb and best read during your reviews for NCLEX or the board exams. Fundamentals of Nursing , Nursing Pharmacology. Cheat Sheet Nursing Dosage Conversion Chart. 1 kilogram = 2.2 pound (lb) 1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams = 15 grains (gr) 0.6 gram = 600 milligrams = 10 grains. Professionally written to guarantee your satisfaction. = 30 ml cup = 250 ml l = 1000 ml ml = 1 cc abbreviations for units: Your email address will not be published.




