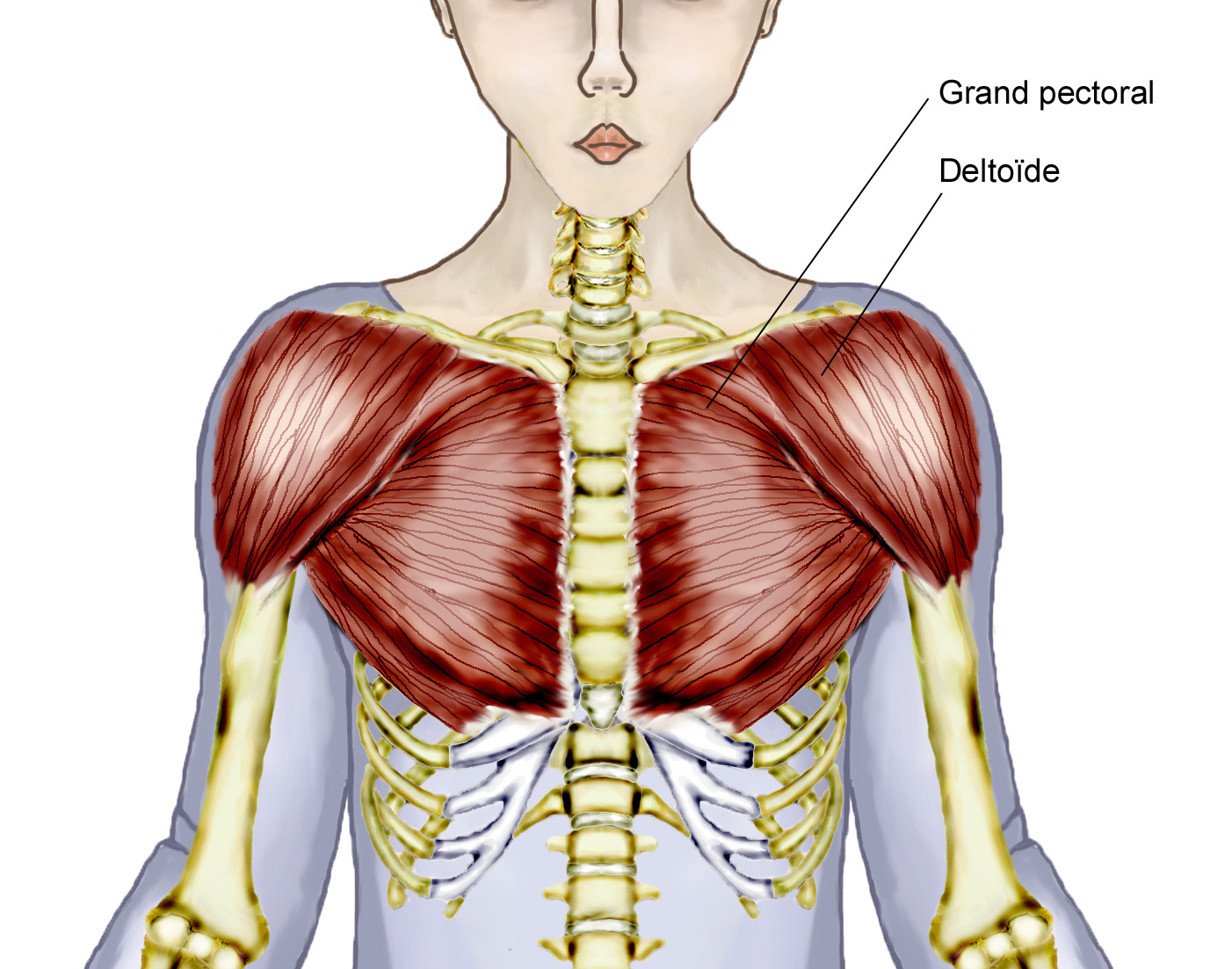
Muscles The dominant muscle in the upper chest is the pectoralis major. This large fan-shaped muscle stretches from the armpit up to the collarbone and down across the lower chest region. | Your Takeaways There's a reason gym rats all over the world celebrate "International Chest Day" every Monday. For physique-minded, stringer-tank-clad gym bros and "how much ya bench?" strength.
Overview Of Chest Muscles
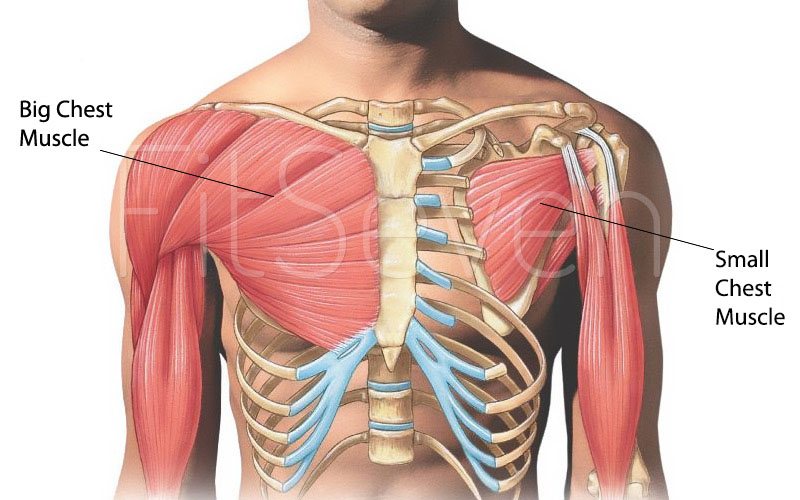
It contains four muscles that exert a force on the upper limb: the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior and subclavius. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the muscles of the pectoral region - their attachments, actions and innervation. Pectoralis Major Last updated on March 4, 2022 The chest anatomy includes the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor and the serratus anterior. Learn about each of these muscles, their locations, functional anatomy and exercises for them. This page provides an overview of the chest muscle group. Muscular System Muscles Muscles The major muscle in the chest is the pectoralis major. This large fan-shaped muscle stretches from the armpit up to the collarbone and down across the. Your pectoralis major—your biggest chest muscle —has three sub-heads: the clavicular head, the sternal head, and the abdominal head. These heads are important to know because they can be specifically trained through particular movements.
Chest Muscles Diagram / Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Male Biceps Photograph
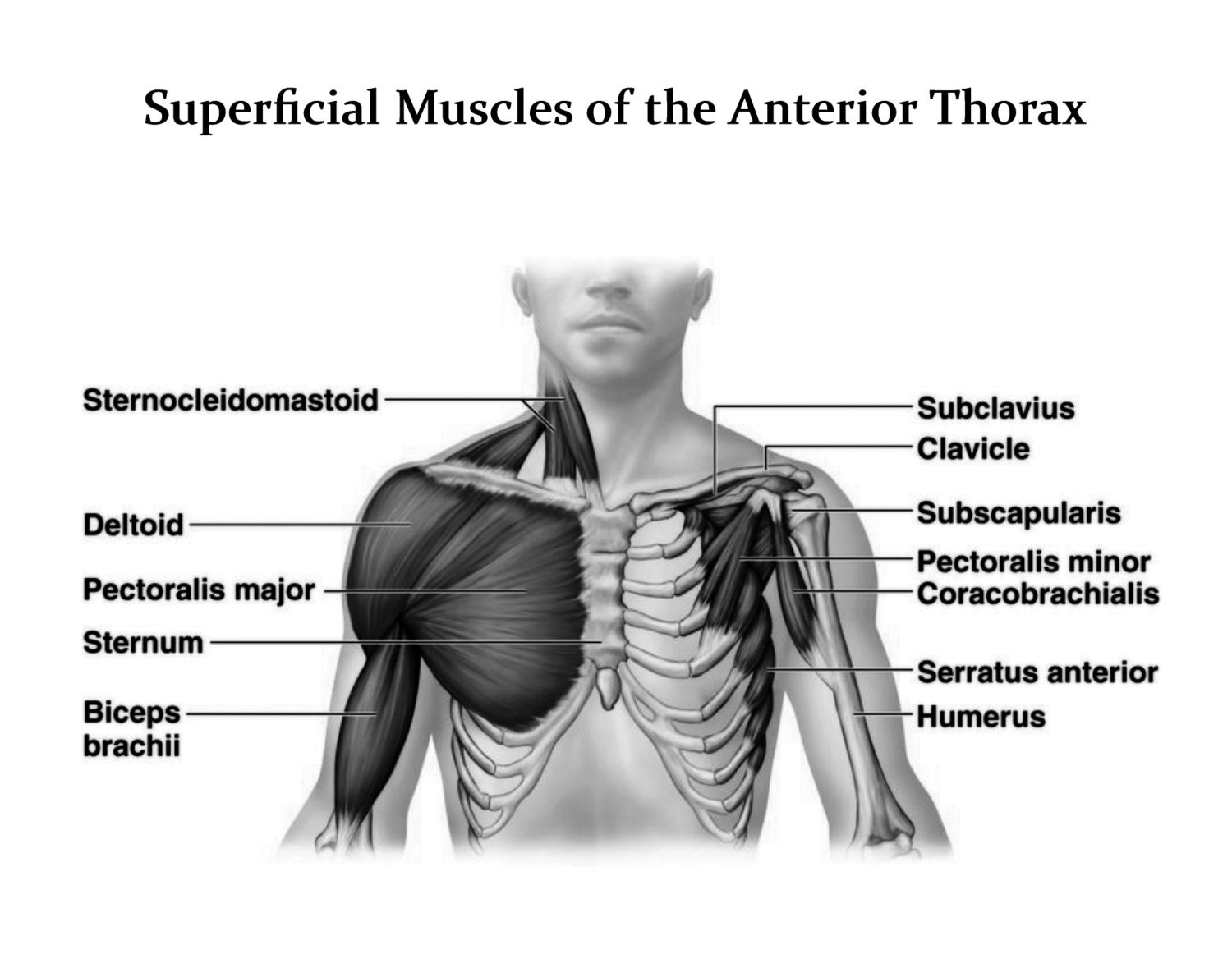
Anatomy Explorer Abdominal Head of Pectoralis Major Muscle Clavicular Head of Pectoralis Major Muscle Diaphragm Infraspinatus Muscle Intercostal Muscles Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Levator Scapulae Muscle Muscles of the Arm and Hand Muscles of the Head and Neck Pectoralis Major Muscle Pectoralis Minor Muscle Serratus Anterior Muscle Introduction The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. These muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. The main function of this chest muscle as a whole is the adduction and internal rotation of the arm in the shoulder joint. Acting independently, the clavicular part helps to flex the extended arm up to 90°, while the sternocostal part facilitates the extension of the flexed arm by pulling it downwards. The pectoral muscles are the group of skeletal muscles that connect the upper extremities to the anterior and lateral thoracic walls. Juxtaposed with the regional fascia, these muscles are responsible for moving the upper extremities in a wide range of motion.
Chest Muscle Anatomy Diagram / Chest Muscles Anatomy Chest Muscles
However, what is the anatomic definition or meaning of a 'chest'? The chest, properly called the thorax, is the superior part of the trunk located between the neck and abdomen. It consists of several components: Thoracic wall Several cavities Neurovasculature and lymphatics Internal organs Breasts There are five muscles that make up the thoracic cage; the intercostals (external, internal and innermost), subcostals, and transversus thoracis. These muscles act to change the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. There are some other muscles that do not comprise the thoracic wall, but do attach to it.
March 15, 2023 by Daniel Richter A broad and powerful chest is more than just a filler of your shirt. Strong chest muscles increase your physical performance in every athletic endeavor where you project force forward - whether you're throwing a ball, a punch, or pushing an opponent out of your way. Pectoral muscles (colloquially referred to as " pecs ") are the muscles that connect the front of the human chest with the bones of the upper arm and shoulder. This region contains four muscles that provide movements to the upper limbs or ribs. Deep muscles of the chest, including pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, and subclavius (Gray 1918)

Chest Muscle Anatomy Diagram Build Your Upper Body With CloseGrip
Printout. Rollover image shows the location of the major muscles of the chest, such as the pectoralis major, rectus abdominis, and external oblique. The trunk (torso) is the central part of the body to which the head and the limbs are attached. Except for the brain, the trunk houses all the vital organs of the human body. The torso muscles attach to the skeletal core of the trunk, and depending on their location are divided into two large groups: anterolateral muscles of the trunk.




