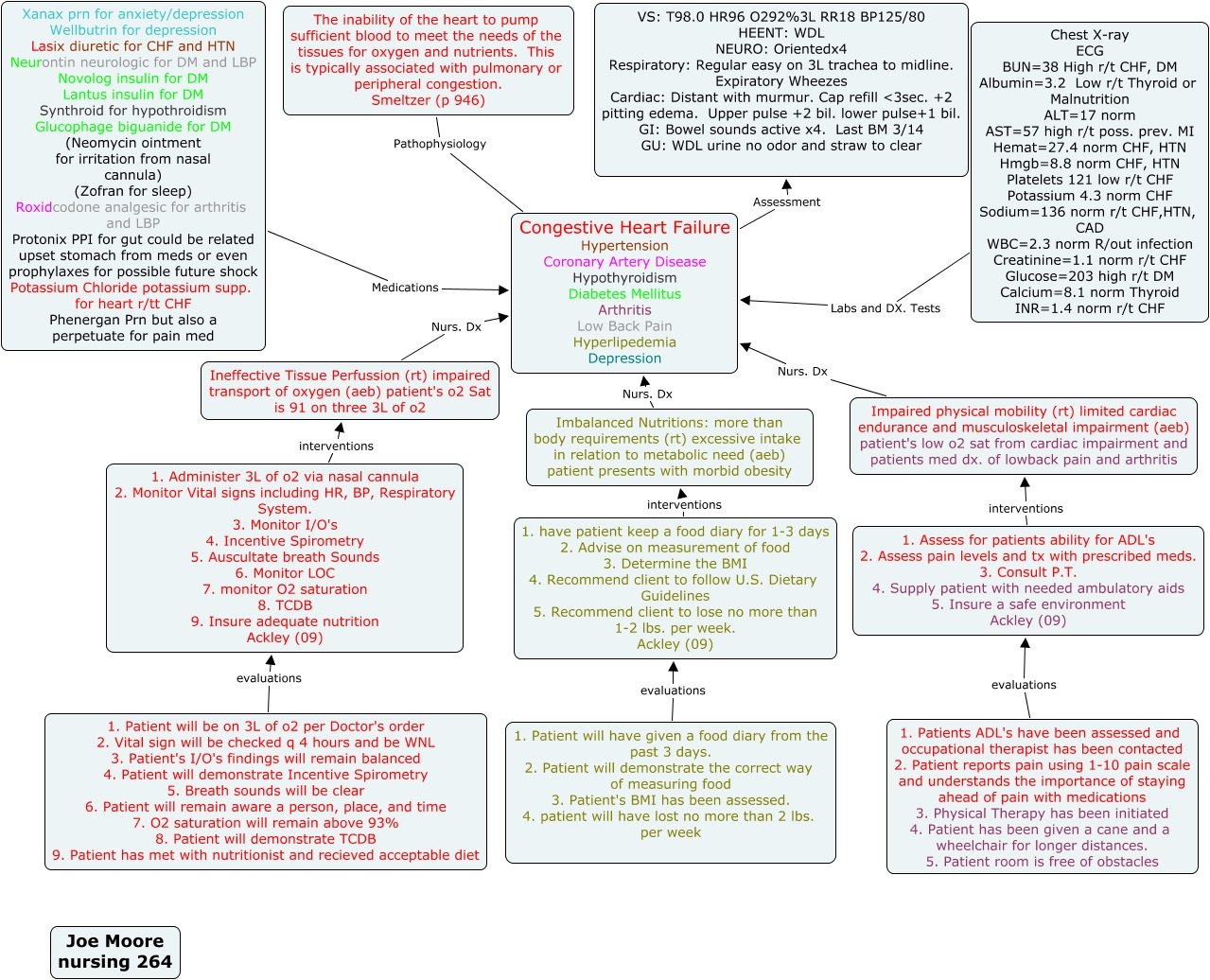
Congestion is one of the common features of heart failure, thus the term "congestive heart failure" is still used by many medical professionals. Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure Dyspnea ( shortness of breath) upon exertion or lying down Jugular vein distention (JVD) Fatigue and reduced ability to exercise Congestive heart failure (CHF), as defined by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), is "a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood."
CHF
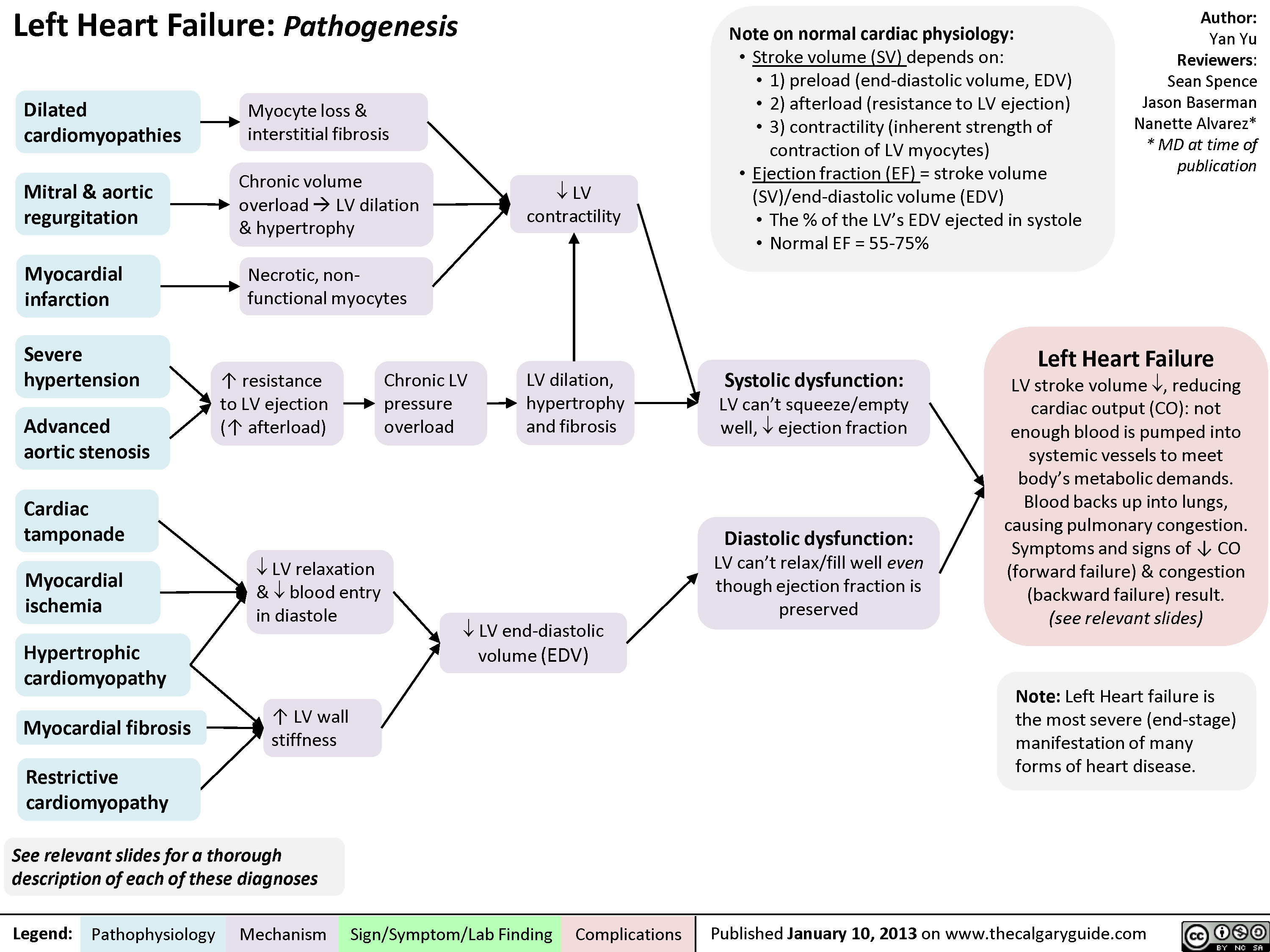
Heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from any functional or structural heart disorder, impairing ventricular filling or ejection of blood to the systemic circulation to meet the body's needs. Heart failure can be caused by several different diseases. R v L Heart Failure (Cheat Sheet) Outline Overview Concept maps Many types, variations, layouts Primary diagnosis Typically in center of maps Connects to Contributing factors Medications Labwork Patient education Nursing diagnoses Interventions Evaluations Nursing Points General Nursing diagnosis Activity intolerance Congestive heart failure is a long-term condition that happens when your heart can't pump blood well enough to give your body a normal supply. Blood and fluids collect in your lungs and legs over time. Medications and other treatments help manage symptoms like swelling. Congestive heart failure is life-limiting for many. Congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure that requires timely medical attention, although sometimes the two terms are used interchangeably. Your body depends on the heart's pumping action to deliver oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the body's cells. With heart failure, the weakened heart can't supply the cells with enough blood.
Congestive heart failure etiology and pathophysiology doctorvisit
Overview Concept maps Many types, variations, layouts Primary diagnosis Typically in center of maps Connects to Contributing factors Medications Labwork Patient education Nursing diagnoses Interventions Evaluations Nursing Points General Nursing diagnosis Activity intolerance Provide patient assistance with self-care Abstract. Heart failure is an epidemic disease which affects about 1% to 2% of the population worldwide. Both, the etiology and phenotype of heart failure differ largely. Following a cardiac injury (e.g., myocardial infarction, increased preload or afterload) cellular, structural and neurohumoral modulations occur that affect the phenotype. Overview Concept maps Many types, variations, layouts Primary diagnosis Typically in center of maps Connects to Contributing factors Medications Labwork Patient education Nursing diagnoses Interventions Evaluations Nursing Points General Nursing diagnosis Activity intolerance Provide patient assistance with self-care Abstract. Chronic heart failure (CHF) remains the only cardiovascular disease with an increasing hospitalization burden and an ongoing drain on health care expenditures. The prevalence of CHF increases with advancing life span, with diastolic heart failure predominating in the elderly population. Primary prevention of coronary artery disease.

Congestive Heart Failure 1 Concept Map ! Heart Failure Physiology
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) • A weakened heart condition that causes fluid buildup in the feet, arms, lungs, and other organs. • Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, arrhythmias, and edema. • Treatments include medications, heart surgery, or transplantation. • Involves Cardiology, Surgery. Symptoms. Congestive heart failure (CHF), also simply called heart failure, is a chronic condition in which the heart progressively becomes weaker and less efficient at pumping blood around the body. Heart failure impacts about 6.5 million people in the United States, and it's one of the most common reasons older adults get admitted to the.
A person usually has no symptoms of HF at this stage but may experience symptoms of their chronic conditions, including: shortness of breath. difficulty breathing. swelling in the hands, feet, and. Overview Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle doesn't pump blood as well as it should. When this happens, blood often backs up and fluid can build up in the lungs, causing shortness of breath. Certain heart conditions gradually leave the heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump blood properly.

Right Heart Failure Calgary Guide Pathophysiology nursing
Updated on May 19, 2022 By Marianne Belleza, R.N. Learn about the nursing care management of patients with heart failure. What is Heart Failure? Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is recognized as a clinical syndrome characterized by signs and symptoms of fluid overload or of inadequate tissue perfusion. Dr. Steven Jones. Congestive heart failure (also called heart failure) is a serious condition in which the heart doesn't pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesn't mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract.



