Term. 2 types: Dense regular collagenous CT: -In tendons and ligaments, covers skeletal muscles. -very tough made of mostly straight parallel collagen fibers, not very many cells. -Provides firm attachment, conducts pull of muscle, reduces friction. Dense regular elastic CT: -Between vertebrae and in vocal cords. Concept Map: Connective Tissues Complete the Part A Concept Map to describe the types of connective tissue found in the body Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Click the card to flip 👆 Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 74 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat mstackss69 Top creator on Quizlet Students also viewed

Connective Tissue Tissue Biology, Cell Biology, Adipose Tissue, School
As its name implies, "connective tissue" is a term given to several body tissues that connect, support, and help bind other tissues. While the various connective tissues of the body are diverse, they share numerous structural and functional features that explain why they are subsumed into a single tissue category. Samples of Tissue Maps created by students These are sample concept maps created by anatomy students studying the four types of tissues. Instructions required them to include at least two bits of information about each tissue type. In the samples below, the four main tissue types are respresented: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle. Concept Review. Connective tissue is a heterogeneous tissue class with assorted cell shapes and tissue architecture. Structurally, all connective tissues contain cells that are embedded in an extracellular matrix stabilized by proteins. The chemical nature and physical layout of the extracellular matrix and proteins vary enormously among. 1. Start with your center concept - TISSUES OF THE BODY 2. Draw 4 arrows connecting to the four types of tissues found in the body. 3. From each tissue type, draw arrows (varies in number) to related types 4. For each you want to include linked concepts that describe the tissue type, indicate where it is located, and any additional related terms

Connective Tissue Concept Map
Connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues in the body. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ECM). However connective tissue differs from other types in that its cells are loosely, rather than tightly, packed. 1. cells fit tightly together and neighboring cells are bound together at many points by specialized cell junctions (desmosomes & tight junctions) 2. one free unattached surface or edge (apical surface) 3. lower surface rests on a basement membrane (secreted by the epithelial cells and the connective tissue cells abut the epithelium) 41.3.1: Animal Tissues. The development of a fertilized egg into a newborn child requires an average of 41 rounds of mitosis ( 241 = 2.2 ×1012 2 41 = 2.2 × 10 12 ). During this period, the cells produced by mitosis enter different pathways of differentiation; some becoming blood cells, some muscle cells, and so on. Connective tissue is one of this basics tissue types of the frame. More its name implies, "connective tissue" is a notion given to several body pattern that connect, support, and get bind different tissues. While the assorted connectivity tissues of the body are diverse, they stock numerous structur both functional features which explain why they become subsumed at a only tissue category.
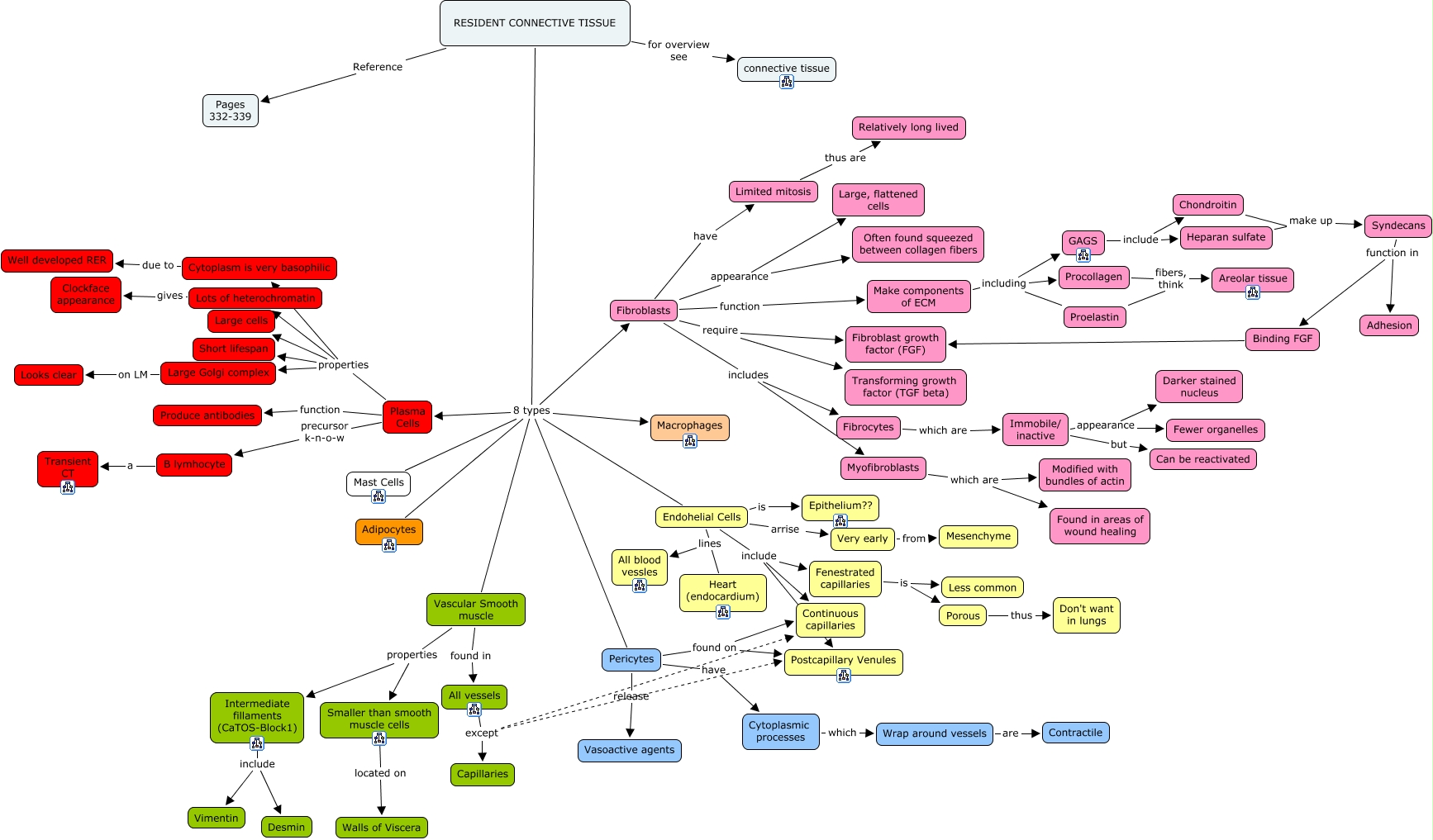
08. Resident Connective tissue
The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Connective tissues in the body region have a mesoderm origin, while in the head region neural crest also contributes to these tissues. This topic is also covered in musculoskeletal ( Tendon Development ), integumentary ( Integumentary Development) and endocrine development ( Adipose Tissue ). Blood is a liquid connective tissue (More? Blood.
Connective Tissue by Paige Salwei 1. Bone: hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fivers with blood vessels; supports & protects, provides levers for muscles, stores calcium & other minerals 1.1. Compact 1.2. Spongy 2. Blood: red & white blood cells in a fluid matrix; transport respiratory gases/nutrients/ wastes; found in blood. Connective Tissue - Catherine Joe. Function to: allows the tissue to sustain tension exerted from many different directions. Functions to: withstand pulling forces and often binds body parts together, as parts of tendons and ligaments. Found in ligaments and tendons (connections between bones)
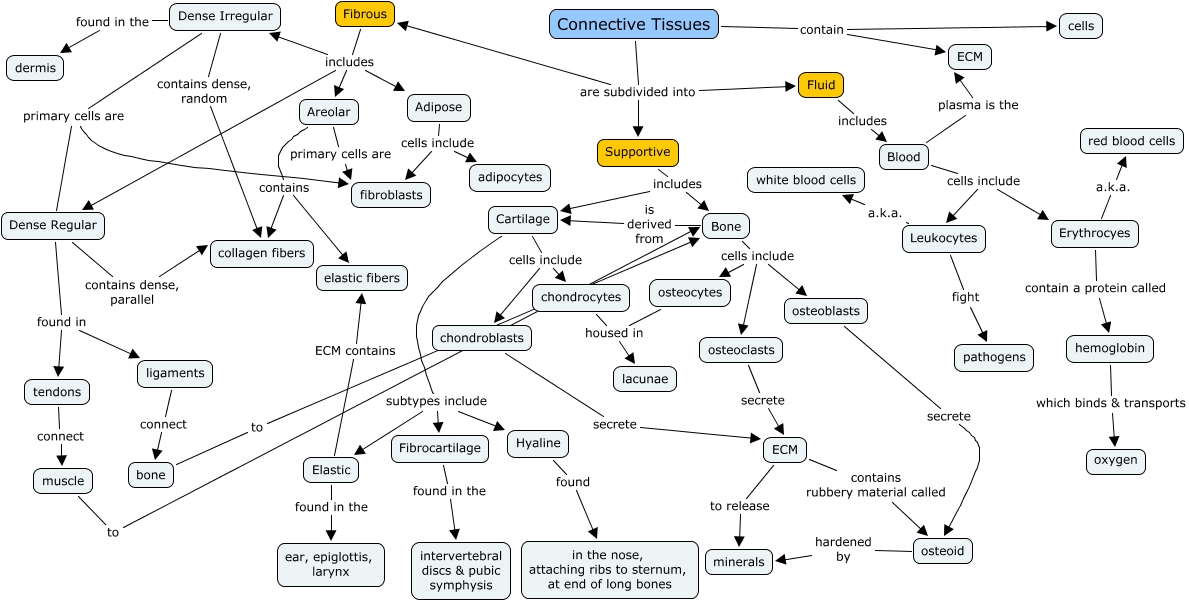
Connective Tissue Concept Map World Of Light Map
Tissues Concept Map 353 1 Learn about Prezi Fri Oct 21 2016 Outline 42 frames Reader view Connective Tissue Epithelial Cells that cover the body surfaces or lines a body cavity. The connective tissue functions to support the body (skeletal) and bind all types of tissues together. 18 terms hannah7_m Preview Mastering A&P CH 5 Integumentary System 45 terms D91607_J62112 Preview Terms in this set (14) Connective Tissue - Found everywhere in the body - Includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues - Functions: - Binds body tissues together - Supports the body - Provides protection Ground Substance


