25/04/2023 28/10/2022 by Sonnet Poddar The cow leg anatomy consists of bones, muscles, nerves, and vessels. Bones are the hardest and main component of the cow leg structure. Again, the muscles are also essential as most vessels and nerves pass along or within them. Table of Contents Cow anatomy External body parts of a cow Little on terminologies of cow body Internal body parts of a cow Cow anatomy bones Bones of thoracic limb of a cow Bones from the hindlimb of a cow Cow skull anatomy Vertebrae of a cow Ribs and sternum anatomy of a cow Cow muscle anatomy Muscles of thoracic limb of a cow
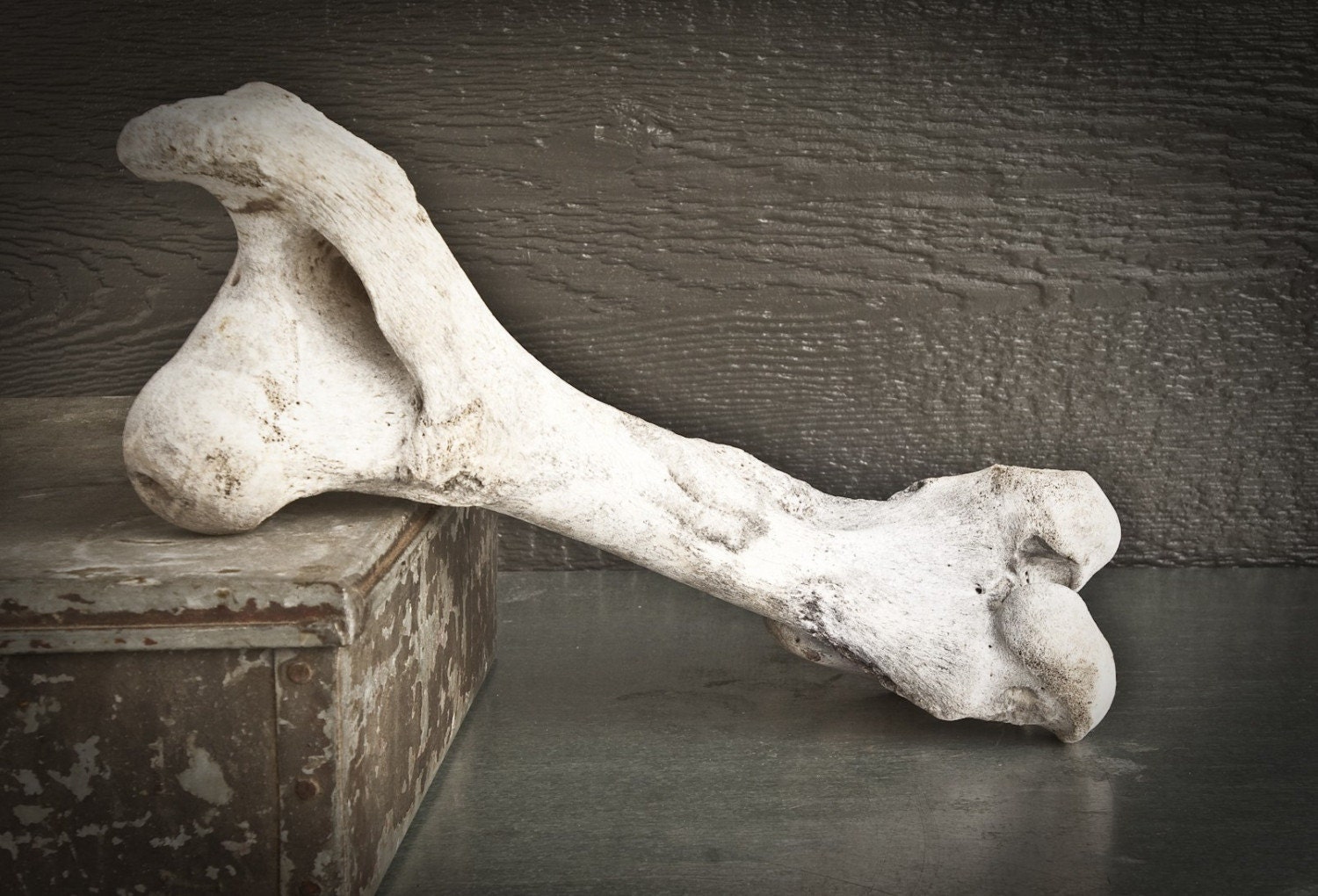
Bleached Cow Leg Bone
This veterinary anatomical atlas includes 27 scientific illustrations with a selection of labelled structures to understand and discover animal anatomy (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints and viscera). Positional and directional terms are also illustrated. Bovine Limb Anatomy. Home. 3D. Radiographic Projection. Tarsus (Left) Lateromedial (Juvenile) Dorsoplantar (Juvenile) Lateromedial (Mature) Dorsoplantar (Mature) Cow - Bones of the cranium Sacrum [Sacral vertebrae] - (Bull , Dorsal view) Bovine osteology : Thoracic skeleton, Ribs, Costal cartilage, Sternum Bones of the thoracic limb : Scapula, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Digital bones of the hand (Cow, Lateral view) Bull / Cow - Digital bones of the hand Veterinary anatomy - Coxal bone (Cow, Ventral view) Legs and Hooves Skin and Coat Unique Features Parts of A Cow | List Frequently Asked Questions Cows Let's start with the external body parts of a cow. A cow has many different parts, including the head, neck, legs, hooves, and tail. The head of a cow contains the mouth, nose, eyes, ears, and horns.
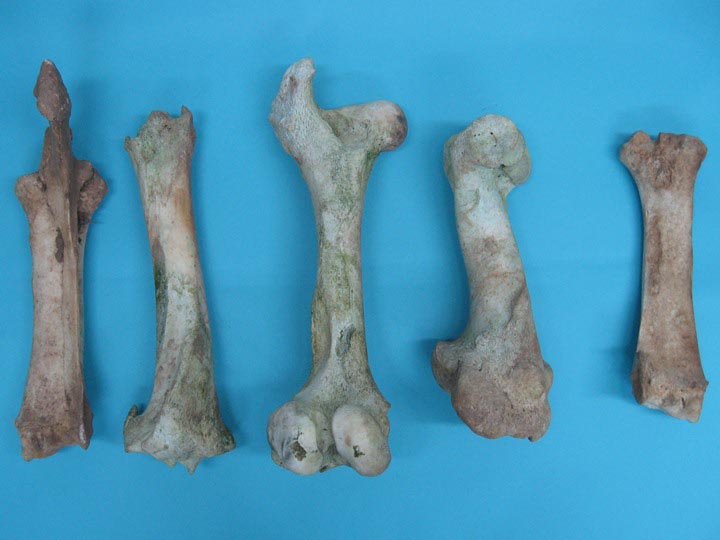
Cow Leg Bone
The shaft of the bone is then pointing up and back, toward the tail of the animal, to form the distinctive point of the hock in the cow's leg (no. 32 in the first diagram). The top of the bone is the attachment point for the large muscles of the lower leg. These are the gastrocnemius and soleus, (the 'calf muscles' in humans). The forelimbs of a cow consist of the humerus, radius, ulna, carpal bones, metacarpal bones, and phalanges. The humerus is the long bone situated between the scapula and the elbow joint. The radius and ulna are the bones that run from the elbow joint to the carpus or knee joint. In the front of the cow, from the front legs to the head, a diagram of the cow's skeletal system includes the cannon, knee joint, radius, sternum, elbow joint, ulna, humerus, shoulder joint, shoulder blade and eye socket. From the top of the head and along the top side of the cow, the skeletal system includes the horn cones, cervical. 1 Overview 2 Bones 2.1 Metacarpals and Metatarsals 2.2 Phalanges 3 Joints 3.1 Metacarpophalangeal/Fetlock Joint 3.2 Proximal Interphalangeal/Pastern Joint 3.3 Distal Interphalangeal/Coffin Joint 4 Musculature 4.1 Forelimb 4.2 Hindlimb 5 Vasculature 6 Innervation 7 The Bovine Claw 8 Webinars Overview Cattle are artiodactyl unguligrade animals.
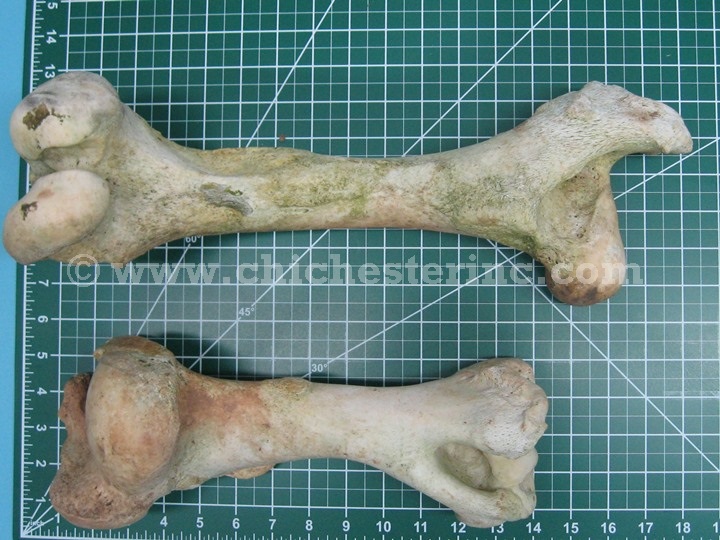
Cow Bones, Loose Cow Bones
Cattle muscles anatomy How many muscles does a cow have? Identification of forelimb muscles from the cow Muscles of the arm region of a cow Muscles of the forearm of the cow Muscles of the hindlimb of a cow Lateral muscles of the hip and thigh of a cow Cranial muscle of the cow's thigh Medial muscles of the cow's thigh Cow leg muscle anatomy There are six bones in each claw and each leg of a typical 600kg cow bears approximately 165kg (front legs) and 135kg (back legs). This is a significant amount of weight when you consider the relatively fine structure of a cow's leg compared to the rest of her body.
A side of beef is literally one side of the beef carcass that is split through the backbone. Each side is then halved between the 12th and 13th ribs. These sections are called the forequarter (front of the cow) and the hindquarter (back of the cow). In the cow the tuber coxae is visible and is readily palpable. The sacral tuber has two prominences; the cranial and caudal dorsal iliac spines. The iliac crest is thin and concave. The ileal wing is orientated in a vertical manner. Ischium The ischial tuberosity is triangular in shape. Femur

il_fullxfull.220623459.jpg (726×613) Animal Bison Pinterest
It is a synovial type of joint responsible for extension and flexion movements of the cattle's hind limb. I will describe the bony involvement and articulations of the cow's hock with their binding materials (ligaments). You will also find a short description of the muscles from this guide that are forming cattle's hock. Bovine Lameness and Podiatry Bovine Foot Anatomy Bones and joints While the cannon bone of a horse is MCIII or MTIII, in a cow it is a fused MCIII+IV or MTIII+IV. The fusion is present at the fetlock joint and above. Cattle do have the same bones and joints as horses below the fetlock but in duplicate form.



