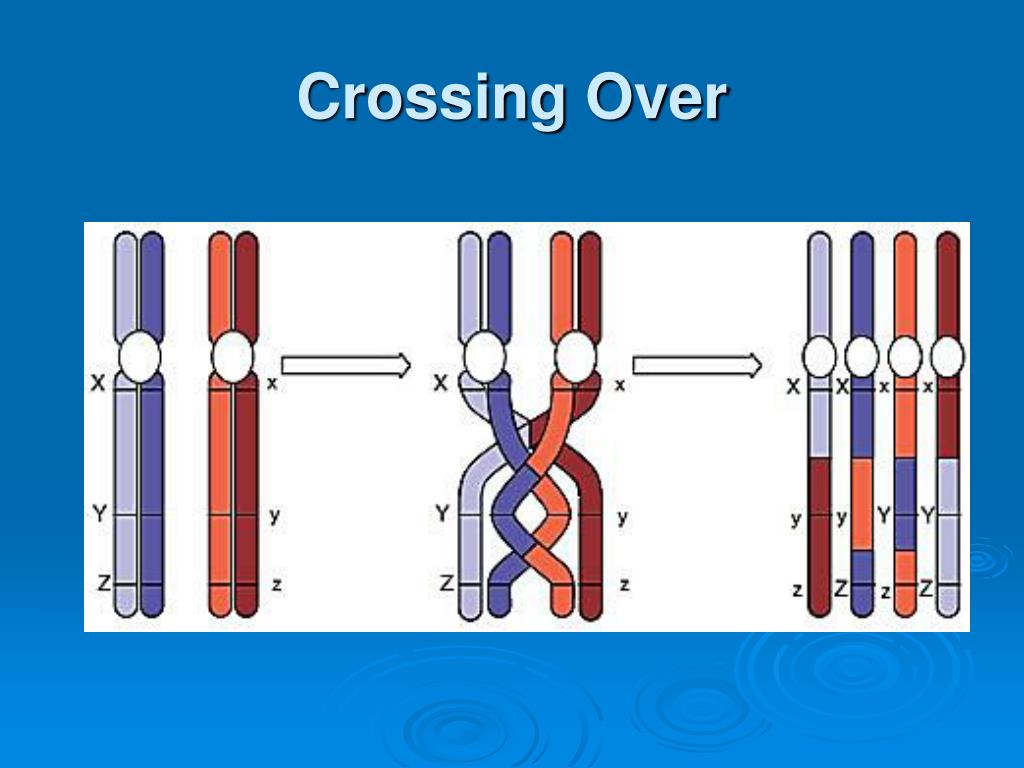
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells. Each diploid cell contains two copies of every chromosome, one derived from the maternal gamete and the other from the paternal gamete. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers to the exchange of DNA between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during the development of egg and sperm cells (meiosis).

Linkage and (Part 1) Chromosomal Theory, Linkage
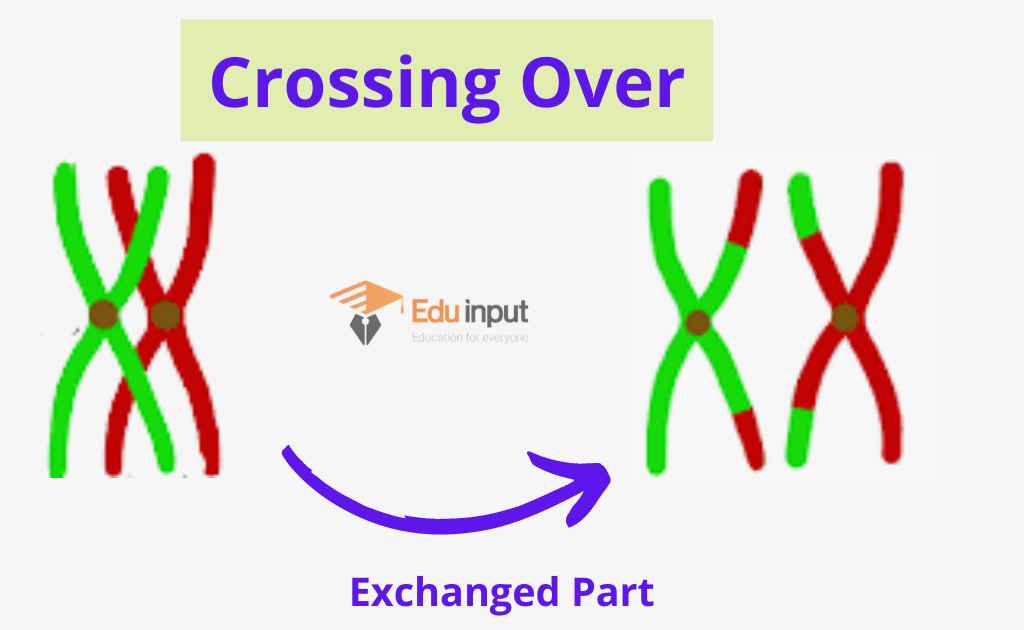
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes ' non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. : an interchange of genes or segments between homologous chromosomes Word History First Known Use 1912, in the meaning defined above Time Traveler The first known use of crossing-over was in 1912 See more words from the same year Dictionary Entries Near crossing-over crossing guard crossing-over cross-interrogate See More Nearby Entries Crossing-over occurs when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis I. The closer together two genes are on a chromosome, the less likely their alleles will be separated by crossing-over. At the following link, you can watch an animation showing how genes on the same chromosome may be separated by crossing-over:www. Crossing-Over. Crossing-over occurs during prophase I, and it is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Recall during prophase I, homologous chromosomes line up in pairs, gene-for-gene down their entire length, forming a configuration with four chromatids, known as a tetrad. At this point, the.
PPT Biology EOC REVIEW PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
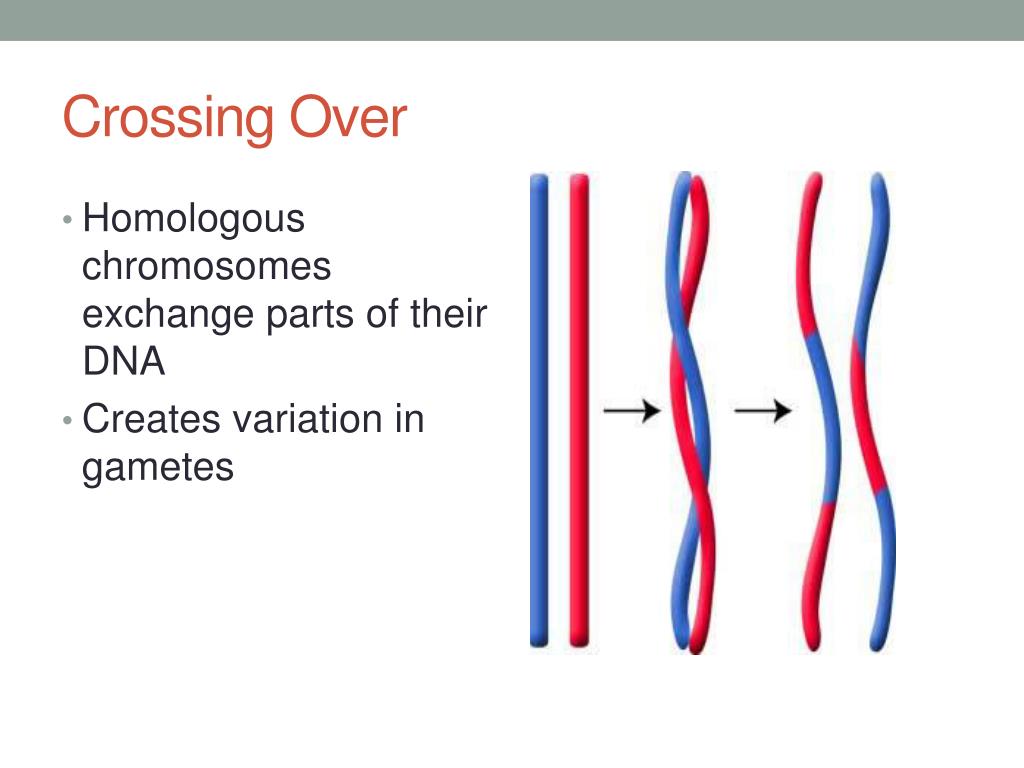
This process, in which homologous chromosomes trade parts, is called crossing over. It's helped along by a protein structure called the synaptonemal complex that holds the homologues together. Crossing over, or recombination, is the exchange of chromosome segments between nonsister chromatids in meiosis. Crossing over creates new combinations of genes in the gametes that are not found in either parent, contributing to genetic diversity. Homologues and Chromatids All body cells are diploid, meaning they contain pairs of each chromosome. Crossing over allows alleles on DNA molecules to change positions from one homologous chromosome segment to another. Genetic recombination is responsible for genetic diversity in a species or population. For an example of crossing over, you can think of two pieces of foot-long rope lying on a table, lined up next to each other. noun A process occurring during meiosis wherein homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of their genetic material More Info on Chromosomal Crossover Chromosomal crossover occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
PPT Biology EOC Review PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. During crossing over, part of one chromosome is exchanged with another. The result is a hybrid chromosome with a unique pattern of genetic material. Geneticists define "crossing over" as a process by which a pair of chromosomes aligns closely to each other and swap segments of DNA-containing genes during replication. Crossing over is also known as genetic recombination. DNA Replication There are two different DNA replication processes that occur in plants and animals.
Crossing over is the process of swapping DNA sequences between the chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes. This process occurs during the prophase of meiosis I. When did the chromosomes. Crossing over is a process that happens during meiosis and results in genetic variation in gametes. It happens between prophase and metaphase. Pairs of homologous chromosomes lined up next to each other touch at the same loci on each. These points of contact are called chiasmata.
What is Crossing Over?Definition, Mechanism, and Frequency
Quiz Course 40K views Genes on the Same Chromosome are Linked He first decides to mate the white, fire-breathing hamster with a true-breeding brown hamster. At the F1 generation, as expected, he. The process of crossing over was used in genetic mapping to understand the order of genes on a chromosome, and to determine the distance between them. This works on the basis that if two genes are present far apart on the chromosome, the frequency of crossing over between the two will be greater.




