What's my mouth's function? Your mouth supports many daily functions, including: Breathing. Talking. Chewing. Tasting. Swallowing. Eating. Drinking. Mouth function in digestive system Your mouth is where digestion begins. When you chew food, your salivary glands make saliva (spit). Saliva helps break down starches in the foods you eat. The chief structures of the mouth are the teeth, which tear and grind ingested food into small pieces that are suitable for digestion; the tongue, which positions and mixes food and also carries sensory receptors for taste; and the palate, which separates the mouth from the nasal cavity, allowing separate passages for air and for food.

Oral cavity anatomy with educational labeled structure vector illustration
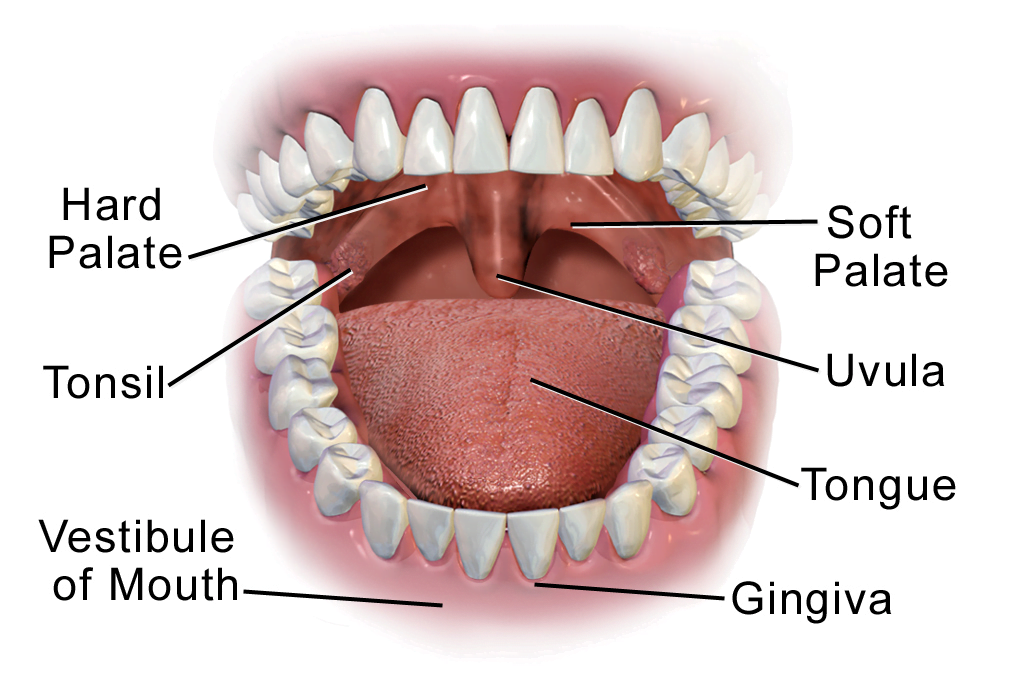
The cavity is separated into anterior and posterior parts by the dental arches (or teeth): the anterior oral vestibule sits anteriorly to the teeth and behind the lips, whilst the oral cavity proper describes the area behind the teeth. The Mouth: Anatomy and 3D Illustrations The Mouth By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: Feb 16, 2022 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom Anatomy Explorer Apex of Tongue Body of Tongue Epiglottis Esophagus Filiform Papillae Foliate Papillae Fungiform Papillae Gingiva (Gums) Glottis Hard Palate Lateral Glossoepiglottic Fold Lingual Glands Lingual Tonsils In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). A closed human mouth. The lips come together to close the opening of the mouth, forming a line between the upper and lower lip. In facial expression, this mouth line is iconically shaped like an up-open parabola in a smile, and like a down-open parabola in a frown.
Mouth and Stomach Part 2 and 3 of the 5 Phases of Digestion
The oral cavity, or more commonly known as the mouth or buccal cavity, serves as the first portion of the digestive system. It consists of several different anatomically different aspects that work together effectively and efficiently to perform several functions. These aspects include the lips, tongue, palate, and teeth. Although a small compartment, the oral cavity is a unique and complex. Mouth Mouth A molar tooth is located in the posterior (back) section of the mouth. It is found in most mammals that use their posterior teeth to grind food. Twelve molars are usually present. This e-Anatomy module contains 110 illustrations on the oral cavity, the mouth, the tongue and the salivary glands. These fully annotated anatomical illustrations are presented as a comprehensive atlas of the oral cavity, specially designed for medical students, medicine residents and healthcare professionals. Material and methods The inside of the mouth is lined with mucous membranes. When healthy, the lining of the mouth (oral mucosa) ranges in color from reddish pink to gradations of brown or black.

Labelled Human Mouth / Mouth Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors
The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). The structures of the mouth are illustrated in. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper. Structure of Human Mouth. The mouth contains some of the strongest muscles in the human body. One of these muscles is the tongue. The tongue is the pound for pound strongest muscle a human possesses. It is also the only muscle that is only attached at one end. Looking inside the mouth we can see the following: Lips. Lips form the border of our.
Mouth Proper The mouth proper lies posteriorly to the vestibule. It is bordered by a roof, a floor, and the cheeks. The tongue fills a large proportion of the cavity of the mouth proper. Roof The roof of the mouth proper consists of the hard and soft palates. The hard palate is found anteriorly. The mouth, also called the oral cavity, is the opening in the human skull that allows food, liquids, and air to enter the body. The oral cavity begins at the lips and ends at the throat. What are.

23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy & Physiology
Your mouth — also known as the oral cavity — shapes the appearance of your face and helps you eat, speak and breathe. It takes many parts working together to handle so many important jobs. Get to know the functions of the different parts of your mouth, and you'll gain a greater appreciation for the importance of great oral health. Anatomy of a Mouth. The mouth (oral cavity) consists of several components, including the teeth, gingiva (gums), tongue, palate, cheeks, lips and floor of the mouth. With the exception of the teeth, the mouth is lined by mucous membranes. The Teeth. The teeth are held within the jaw bones and serve several important functions beyond allowing.



