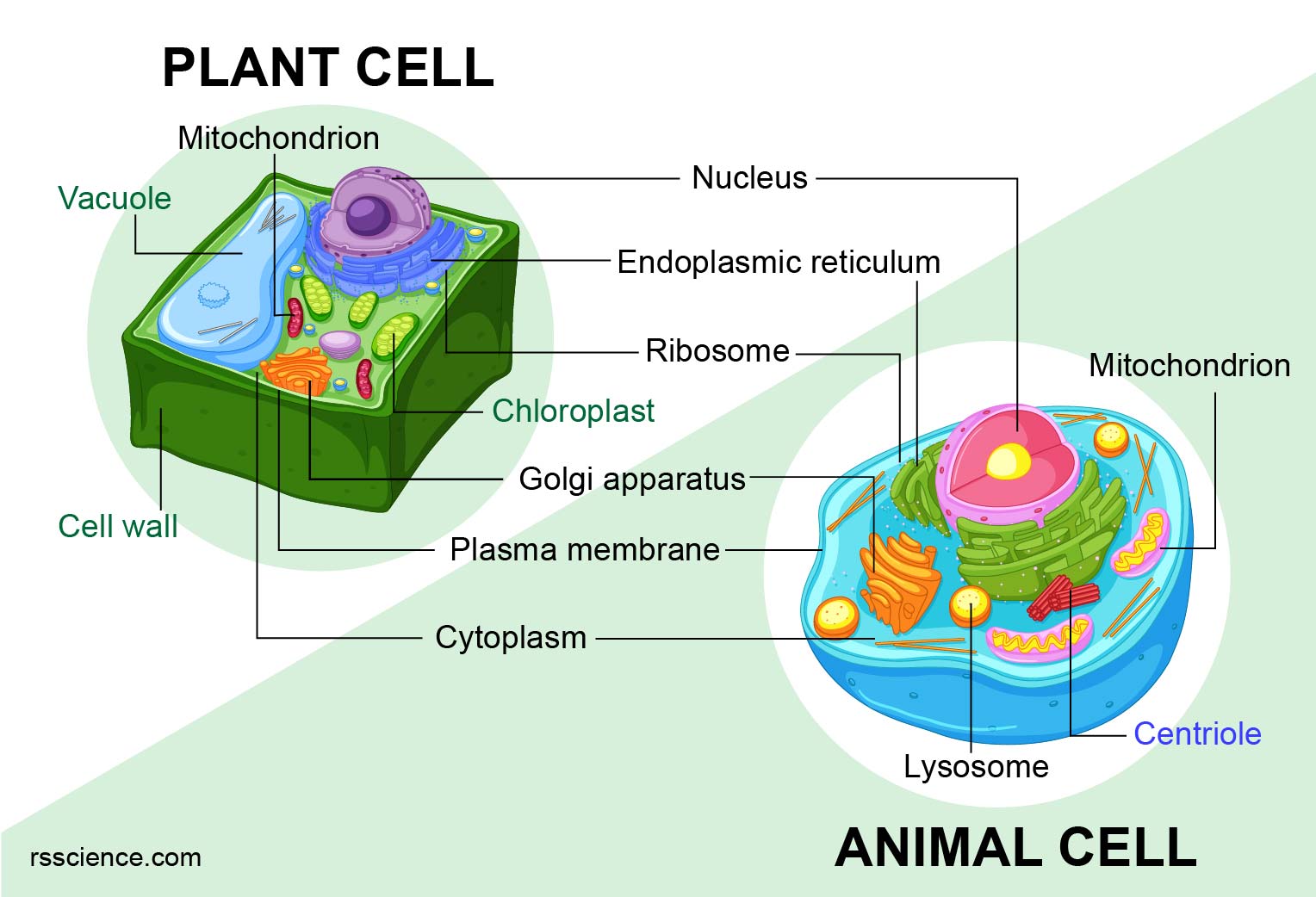
Diagram of a typical plant cell: Image modified from OpenStax Biology. Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don't get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar from sunlight. This process (photosynthesis) takes place in the chloroplast. In Figure 1b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell.. There are some differences in the ways that plant and animal cells do this. Plasmodesmata (singular.
Animal vs. Plant cells Similarities, Differences, Chart, and Examples
Animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. However, they differ in certain aspects. For example, plant cells have a cell wall and a central vacuole, while animal cells contain centrosomes.. The lipid bilayer is a more general term that refers to the structure of the membrane itself. The most important structures of plant and animal cells are shown in the diagrams below, which provide a clear illustration of how much these cells have in common. The significant differences between plant and animal cells are also shown, and the diagrams are followed by more in-depth information. Diagram of a plant cell Doc Sonic Animal Cells versus Plant Cells. Each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, a nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and in some, vacuoles; however, there are some striking differences between animal and plant cells. While both animal and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), animal cells also have. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell. Animal Cell Structure: Organelles and Their Functions. Animal cells contain many organelles, which are subunits within the cell that perform specialized functions. The organelles may be membrane-bound (enclosed within a.

Pin on my computer
Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria are four cell components that are found in both animal and plant cells. Game - onion cells Play an Atomic Labs activity to look at onion. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. While animal and plant cells have many common characteristics, they are also different. Differences Between Animal Cells and Plant Cells plant cell, the basic unit of all plants.Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. GCSE; AQA Trilogy; Cell structure - AQA Plant and animal cells. Organisms are made up of cells. Most organisms are multicellular and have cells that are specialised to do a particular job.
South Pontotoc Biology Plant and Animal Cell Diagrams
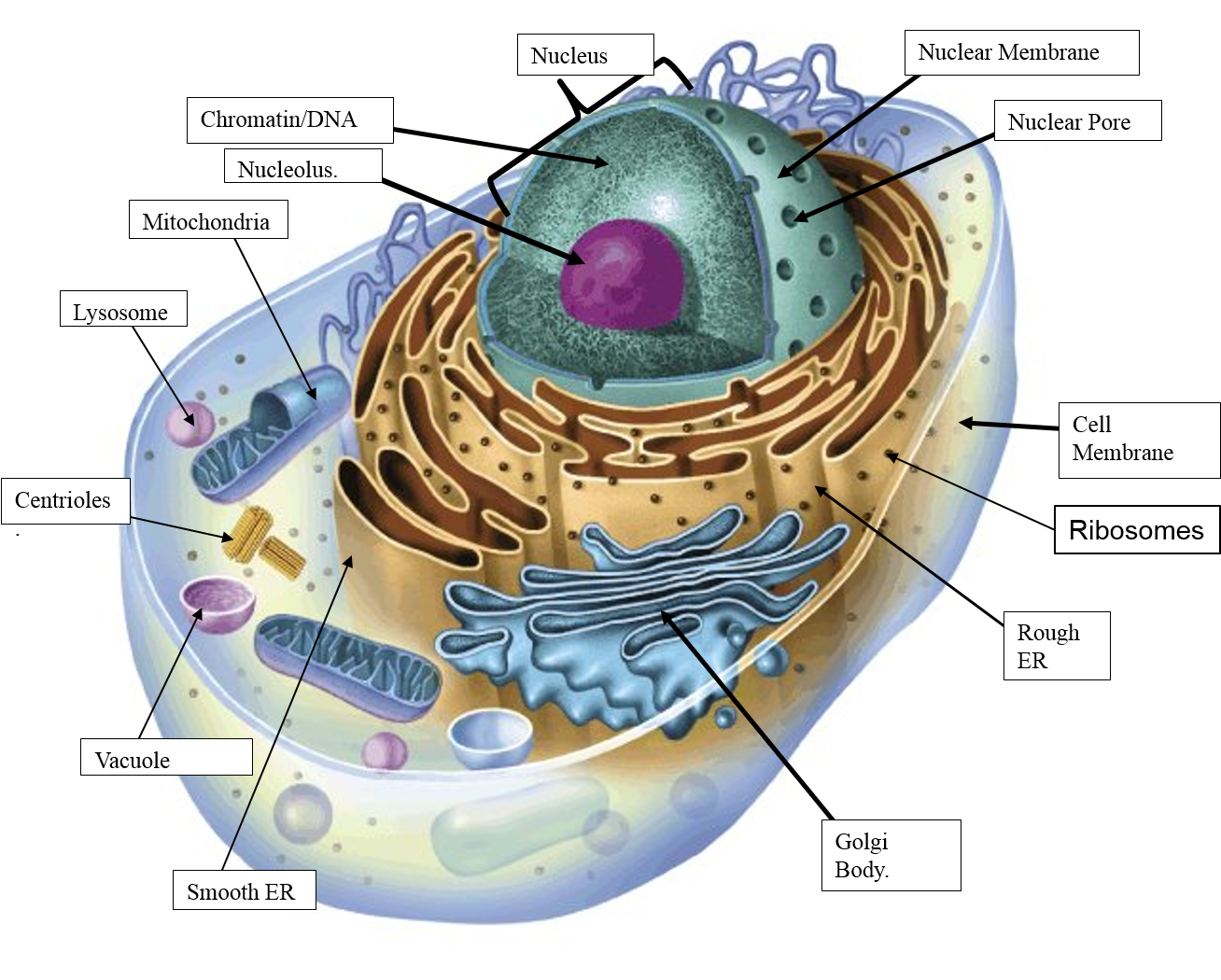
Updated July 31, 2019 By Rebecca E. Plant and animal cells have many similarities, but they differ in several ways, too. Although there are a number of ways in which they diverge, three key features differentiate cells from the plant and animal kingdoms. Download scientific diagram | Structure of animal and plant cell from publication: LECTURE NOTES: CELL BIOLOGY (BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE STUDENTS) | This book was prepared as lecture.
A plant cell consists of one large vacuole that maintains the shape of the cell and stores nutrients. Animal cells, on the other hand, have multiple smaller vacuoles. Both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane, but only the former has a cell wall. The absence of a wall makes it possible for animals to develop different types of cells and. Plant Cell Diagram Plant Cell Structure Plant Cell Types Plant Cell Functions What is a Plant Cell? Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that vary in several fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Both plant and animal cells contain a nucleus along with similar organelles.
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell (25 Major Differences)
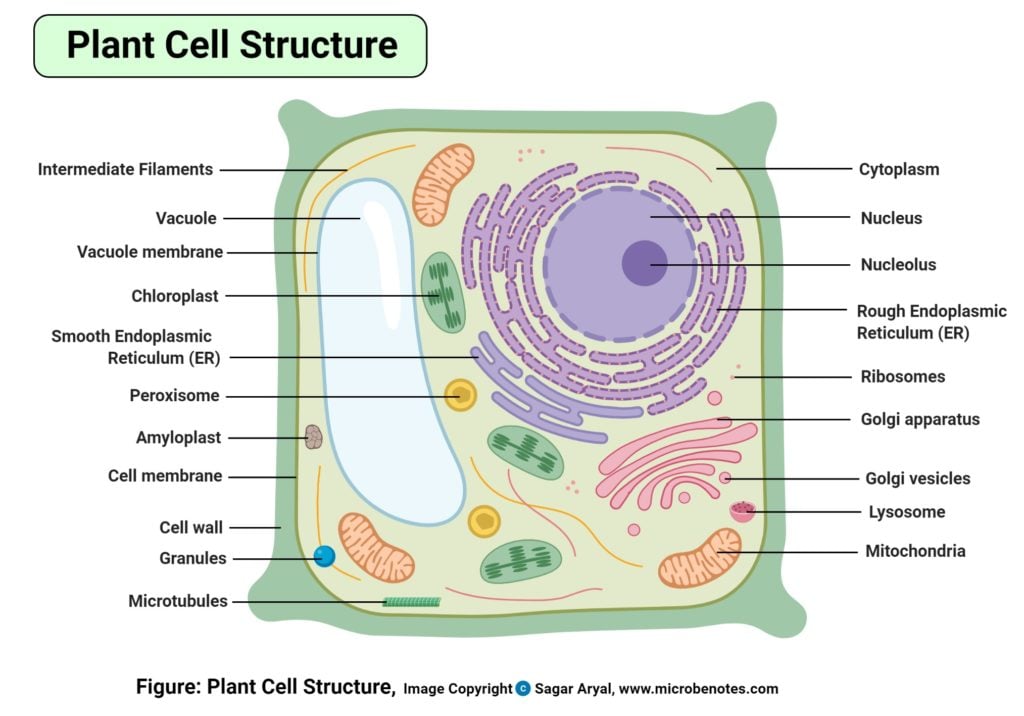
Plant Cells. shape - most plant cells are squarish or rectangular in shape. amyloplast (starch storage organelle)- an organelle in some plant cells that stores starch. Amyloplasts are found in starchy plants like tubers and fruits. cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell, but is inside the cell wall. A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Plant Cell Characteristics. Plant cells are eukaryotic.




