Spacetime diagram. The world line (yellow path) of a photon, which is at location x = 0 at time ct = 0. A spacetime diagram is a graphical illustration of locations in space at various times, especially in the special theory of relativity. Spacetime diagrams can show the geometry underlying phenomena like time dilation and length contraction. A spacetime diagram is typically drawn with only a single space and a single time coordinate. Fig. 2-1 presents a spacetime diagram illustrating the world lines (i.e. paths in spacetime) of two photons, A and B, originating from the same event and going in opposite directions. In addition, C illustrates the world line of a slower-than-light.
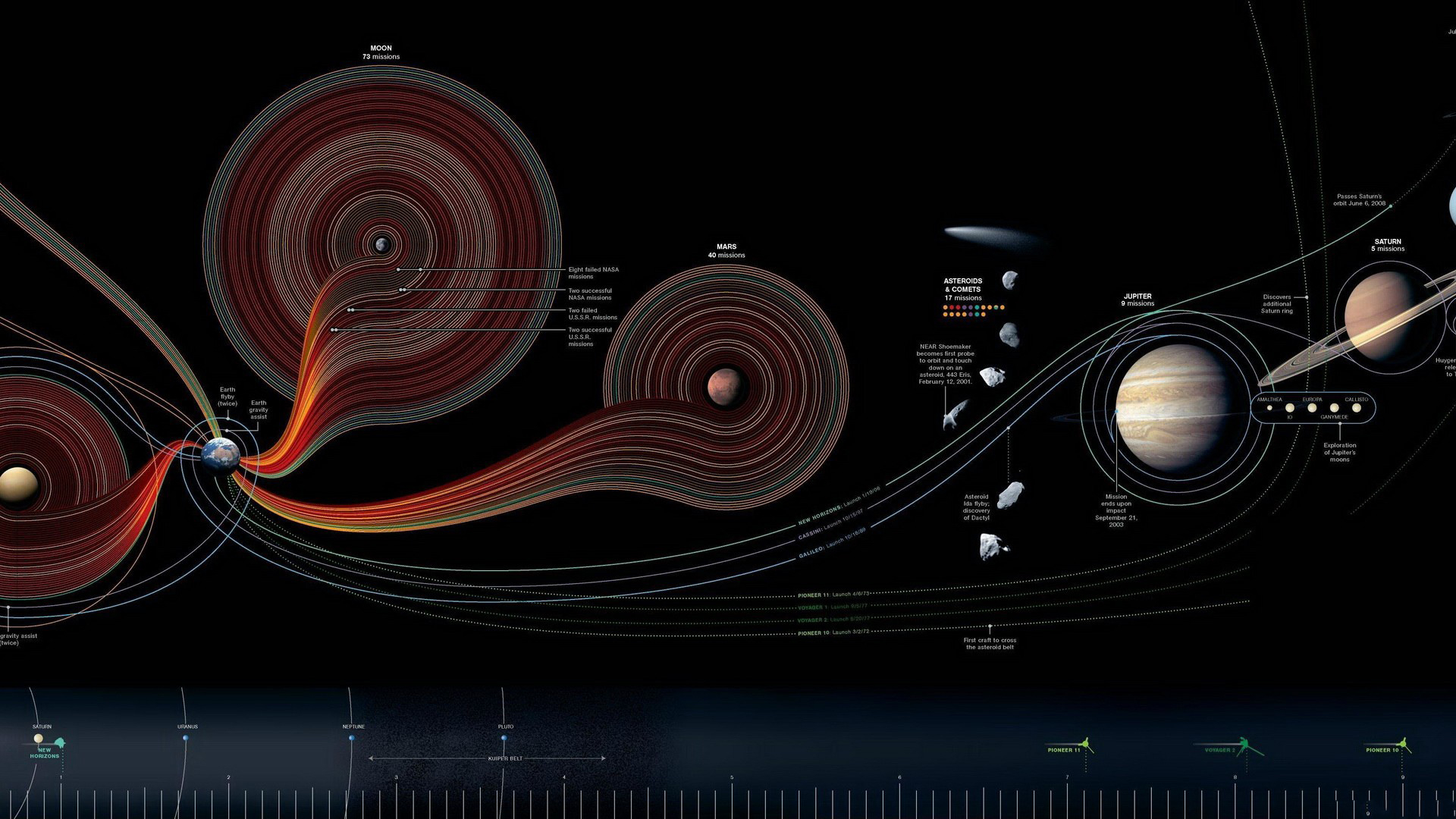
diagram Space Wallpaper (27962920) Fanpop
We will use a simple graphing technique called a Minkowski spacetime diagram, or simply a "spacetime diagram," to illustrate and understand complex scenarios in special relativity. This diagram was originally developed by Hermann Minkowski in 1908 and is useful for objects that move at a substantial fraction of the speed of light. Here we will repeat something we discussed at the end of Section 1.2, as it may make more sense now that we are armed with the visual aid of the spacetime diagram. We can rewrite Equation 2.1.6 by pulling c dt out of the radical: (2.1.7)Δs = ∫ path 1 − 1 c2 dx2 dt2− −−−−−−−−√ c dt = ∫1 − u(t)2 c2. The Milky Way Galaxy is part of the Universe. The Milky Way is one of at least 100 billion galaxies in the known Universe. Each galaxy is made of billions of stars and planetary systems. The Milky Way, a fairly typical galaxy, is surrounded by a number of dwarf galaxies that appear to orbit our galaxy. In the space-time diagram the angle of the light rays have no relation to the reflection angles in space. Light always moves at a 45 degree angle in a Minkowski spacetime diagrams. So when you show a reflection of light in a Minkowski spacetime diagram the light ray goes from 45 degrees one way to 45 degrees the other so it will always be at a.
Solar system diagram in the space Stock Photo Alamy
Spacetime Diagrams •Okay, now that we have our units for spatial distances and time, we want to introduce another tool - the spacetime diagram. •You will find this extremely useful, IF you understand how to set it up and use it… •We will begin with spacetime diagrams in general, and then consider spacetime diagrams Time and space together make spacetime, the stage on which physics is played out. Until 1905, physicists were trained to accept two mutually contradictory theories of spacetime.. and \(o\) vectors then appears on spacetime diagrams as a diagonal line at \(\pm 45\) degrees. In more than one spatial dimension, this boundary forms a cone. Let's do something similar with diagrams of spacetime. Figure 24.7, for example, shows the progress of a motorist driving east on a stretch of road in Kansas where the countryside is absolutely flat. Since our motorist is traveling only in the east-west direction and the terrain is flat, we can ignore the other two dimensions of space. in detail, and also define certain regions in space-time diagrams. So let's start again with Alice's space-time diagram here in which we plot or draw Bob's space-time diagram. The relative velocity difference is 0.5 times the speed of light, and that leads to a gamma effect of 1.2. We also plotted the world line of light in here in yellow.

US SPACE PROGRAM / SPACE SHUTTLE / DIAGRAMS WIKIARCHIVES.SPACE
what is the value of Bob's time axis and space axis for different values of Alice's spacetime diagram. So we start with drawing Alice's spacetime diagram. And then if you want to find the x-axis as seen by Bob, we have to set the time for Bob to equal 0 and then find the corresponding elements or tick marks on the axis. Solar System Overview Our solar system has one star, eight planets, five officially recognized dwarf planets, at least 290 moons, more than 1.3 million asteroids, and about 3,900 comets. It is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy called the Orion Arm, or Orion Spur. Our solar system orbits the center […]
1. Use the Spacetime Diagram Tool to create worldlines for a particle moving with a speed of 0.5c. To do this, adjust the "% speed of light" slider bar until it says 50%. The orange line will be the worldline for your particle. It should look like Figure A.9.3: Figure A.9.3: Worldline for a particle moving at 0.5c in the Spacetime Diagram. An example spacetime diagram is shown in Fig. 1.4.1. Figure 1.4.1 1.4. 1: A and B are events. The dashed lines are light cones at A and B. The solid line is an example of a wordline connecting A and B. The diagram shows two events, labeled A and B, that are connected by a wordline (solid line) that shows an object that starts at rest and.
Sample Space Diagrams (video)
The X axis represents time, going into the future and into the past and the Y axis represents scale, from the size of the electron to the distances between galaxies. It marks the relatively small "realm of direct human experience" and the much larger "realm of quantum physics" and "realm of special relativity." Dimensions in inches: 11 x 17. The solar system is part of the " observable universe ," the region of space that humans can actually or theoretically observe with the aid of technology. Unlike the observable universe, the universe is possibly infinite. The Sun, Moon, and brightest planets were visible to the naked eyes of ancient astronomers, and their observations and.




