human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). Understand the science of hearing and how humans and other mammals perceive sound How humans and other mammals perceive sound. 1/4 Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. The main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance.
How The Ear Works Step by Step Brief Explanation
Chapter 1 - Introduction Manual Format How to examine the ears Suggested Procedure Chapter 2 - Testing Audiogram Tympanogram Chapter 3 - Ear Anatomy Ear Anatomy - Outer Ear Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear Ear Anatomy Schematics Ear Anatomy Images Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear Fluid in the ear Discussion Fluid in the ear Outline Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes Here is a blank human ear diagram for you to label, so that you can memorize the different parts of this vitally necessary organ, for good. The ear is divided into three parts: Outer ear: The outer ear includes an ear canal that is is lined with hairs and glands that secrete wax. This part of the ear provides protection and. Your outer ear and middle ear are separated by your eardrum, and your inner ear houses the cochlea, vestibular nerve and semicircular canals (fluid-filled spaces involved in balance and hearing). What is the ear? Your ears are organs that detect and analyze sound. Located on each side of your head, they help with hearing and balance. Advertisement

Human ear anatomy. Ears inner structure, organ of hearing ve (1000410
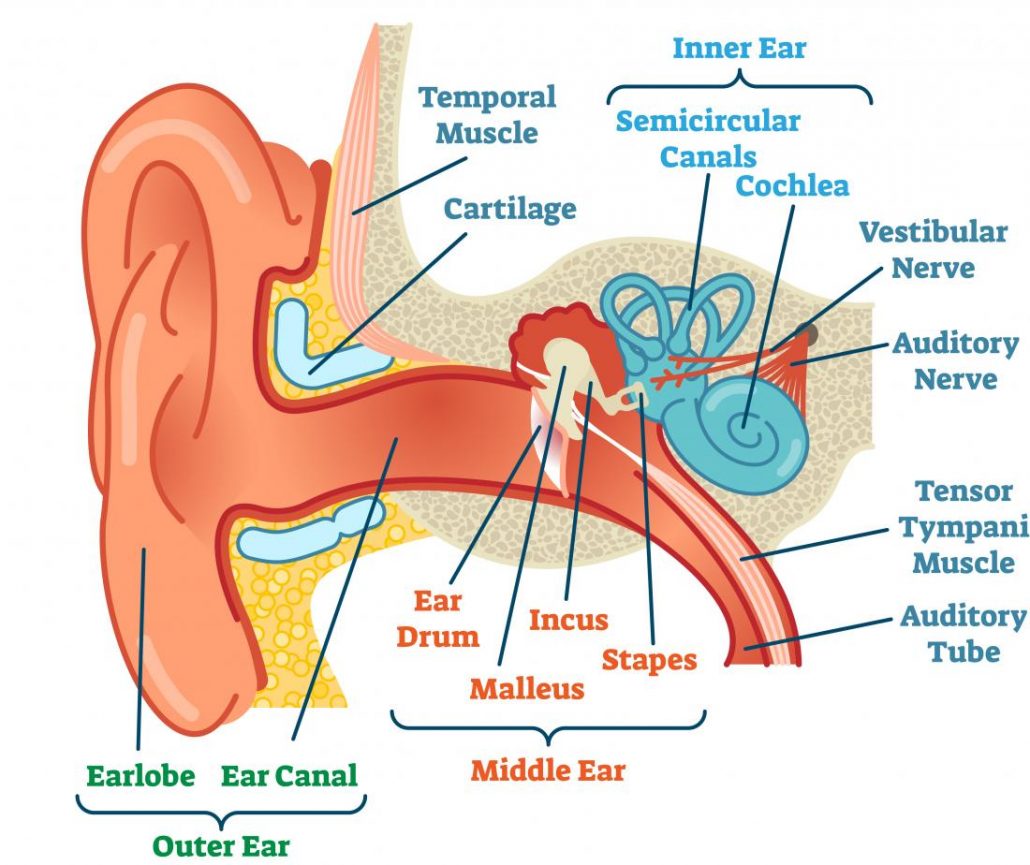
A brief description of the human ear along with a well-labelled diagram is given below for reference. Well-Labelled Diagram of Ear The External ear or the outer ear consists of Pinna/auricle is the outermost section of the ear. The external auditory canal links the exterior ear to the inner or the middle ear. Download this blank ear diagram below Contents Ear anatomy overview Ear diagrams (labeled and unlabeled) Accelerate your learning with interactive quizzes Sources + Show all Ear anatomy overview Although it's not obvious to look at, the ear is anatomically divided into three portions: External (outer) ear Middle ear Inner ear Protect your ears. If the noise is too loud, walk away, turn it down (Turn it to the Left), or use ear plugs. pinna ear canal ear drum hammer anvil stirrup Eustachian tube (connects to the nose) cochlea semicircular canals nerves (connect to the brain) Directions: Color in the diagram below using a different color for each part of the ear. Your inner ear is the last stop that sound waves make in a carefully orchestrated journey that starts from your outer ear. These waves travel from your outer ear through your middle ear to your inner ear. In the inner ear, the sound waves are converted into electrical energy, which your hearing nerve delivers to your brain as sound, making it.

How noise induced hearing damage and loss occurs
Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule. The helix begins the funneling of sound waves into the ear; Fossa, superior crus, inferior crus, and antihelix: These sections make up the middle ridges and depressions of the outer ear. The superior crus is the first ridge that emerges moving in from the helix. The purpose of the inner ear is to sense and process information about sound and balance, and send that information to the brain. Each part of the inner ear has a specific function. Cochlea: The cochlea is responsible for hearing. It is made up of several layers, with the Organ of Corti at the center.
The inner ear is the innermost part of the ear and consists of the cochlea, auditory nerve, vestibule and semicircular canals. The inner ear is a maze of tubes and passages, referred to as the labyrinth. The inner ear is mainly responsible for balance and detecting sound. The cochlea contains the cells responsible for hearing, the auditory. Photo name: Ear Diagram Picture category: Human Body Image size: 57 KB Dimensions: 670 x 510 Photo description: This excellent ear diagram labels all the important parts of the human ear system. The labeled parts include the pinna, auditory canal, eardrum, stapes, malleus, incus and cochlea.

De anatomie van de oorschelp Health Life Media
Anatomy by Shannan Muskopf activity, drag, drop, ear, label Use Google slides to label structures of the ear in this drag and drop activity. Diagram includes the tympanum, ossicles, cochlea, and other organs. Label a diagram of the structure of the human ear. Click "Start Assignment". Navigate to the "Science" tab and find the ear diagram. Label the main parts of the ear with Textables and arrows. Add extra information about the functions of the parts of the ear with text boxes.




