The sperm cell diagram below shows multiflagellate fern cells. Sperm cells from the fern plant. Most motile spermatozoa have flagella to help them swim through fluids - the seminal fluid produced by males and the mucus membranes of the female reproductive tract. Flagellum movement requires a consistent energy source. Diagram of a human sperm cell Sperm ( pl.: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one).
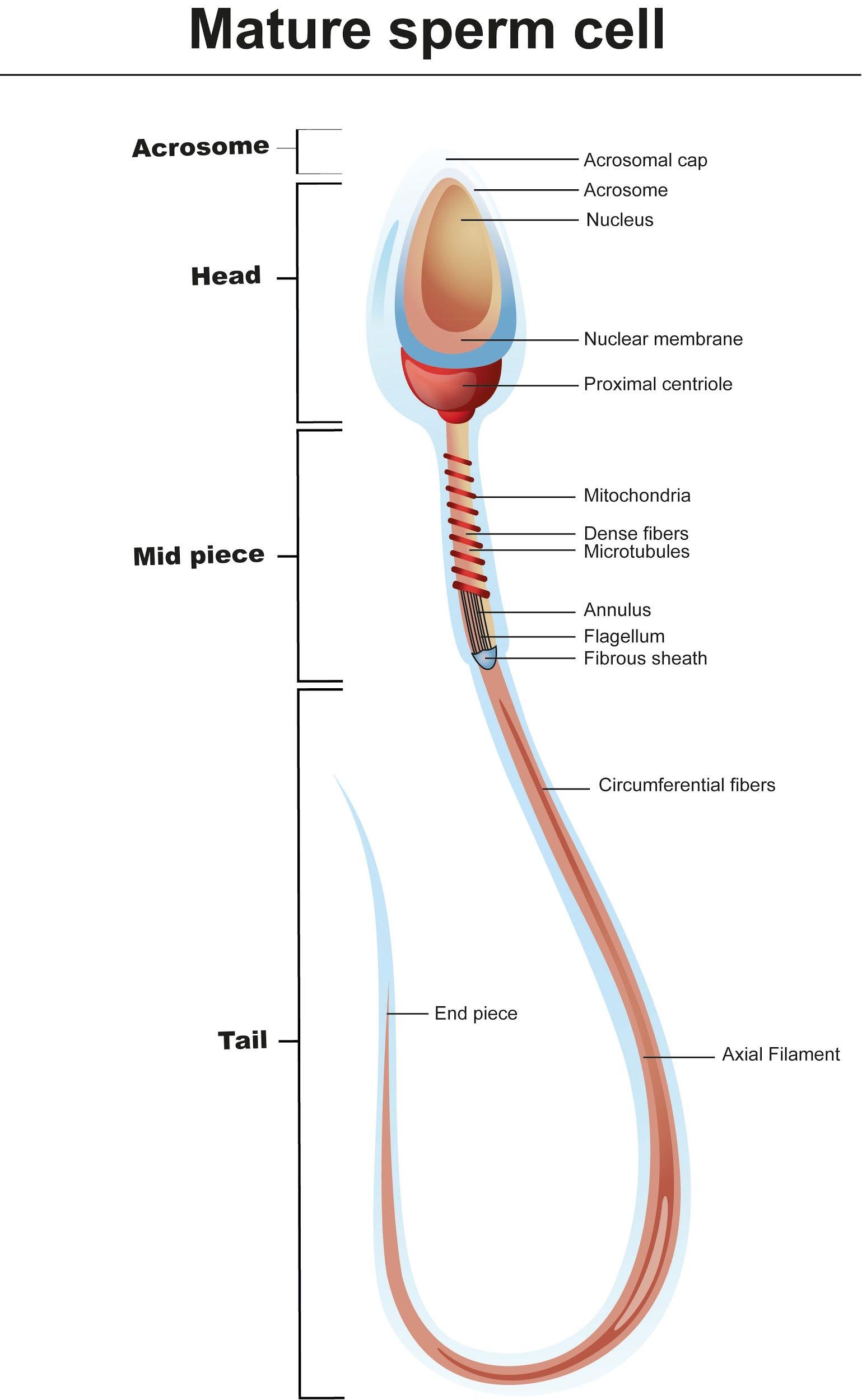
The middle piece of the sperm contains(a)Proteins(b)Centriole(c)Nucleus
22.3: Structure of Formed Sperm. Sperm are smaller than most cells in the body; in fact, the volume of a sperm cell is 85,000 times less than that of the female gamete. Approximately 100 to 300 million sperm are produced each day, whereas women typically ovulate only one oocyte per month. As is true for most cells in the body, the structure of. This labelled diagram shows the structure of a sperm cell in detail, which has the following parts: Head With its spheric shape, it consists of a large nucleus, which at the same time contains an acrosome. The nucleus contains the genetic information and 23 chromosomes. lysin See all related content → sperm, male reproductive cell, produced by most animals. With the exception of nematode worms, decapods (e.g., crayfish), diplopods (e.g., millipedes), and mites, sperm are flagellated; that is, they have a whiplike tail. In higher vertebrates, especially mammals, sperm are produced in the testes. Structure of Formed Sperm. Sperm are smaller than most cells in the body; in fact, the volume of a sperm cell is 85,000 times less than that of the female gamete. Approximately 100 to 300 million sperm are produced each day, whereas women typically ovulate only one oocyte per month as is true for most cells in the body, the structure of sperm.
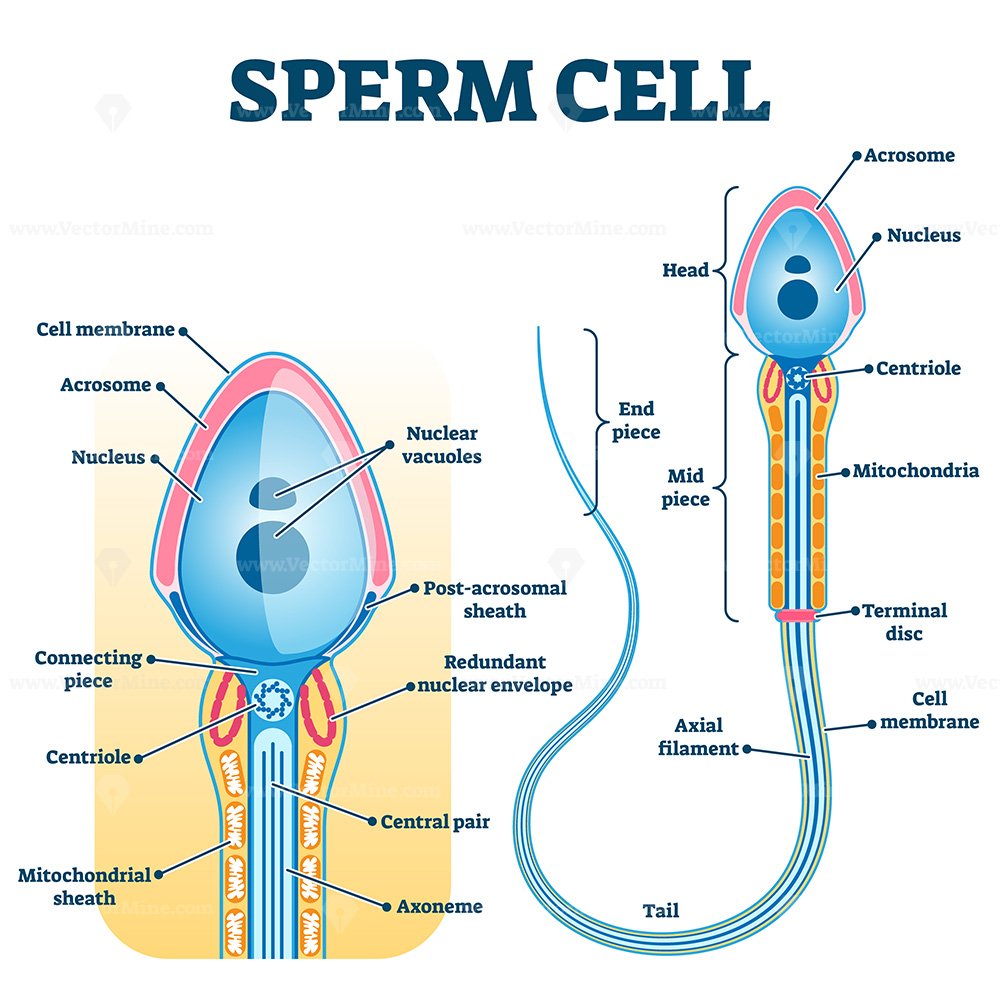
Sperm cell anatomy, education fertility diagram VectorMine
Sperm - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf , however, the progeny of a single spermatogonium develop as a large In most species, there are just two types of gamete, and they are radically different. The egg is among the largest cells in an organism, while the sperm (spermatozoon, plural spermatozoa) is often the smallest. A mature sperm cell has several structures that help it reach and penetrate an egg. These are labeled in the drawing of a sperm shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The head is the part of the sperm that contains the nucleus — and not much else. The nucleus, in turn, contains tightly coiled DNA that is the male parent's contribution to the. Key Terms. anisogamy: The form of sexual reproduction that involves the union or fusion of two gametes that differ in size and/or form.; spermatozoa: A motile sperm cell or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete.; acrosome: A caplike structure over the anterior half of the sperm's head.; ATP: An acronym for adenosine triphosphate, which transports chemical energy within. spermatozoonɜːr [1] also spelled spermatozoönspermatozoa; from Ancient Greek σπέρμα spérma 'seed', and ζῷον zôion 'animal') is a , or moving form of the haploid that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, that normally develops into an embryo .)
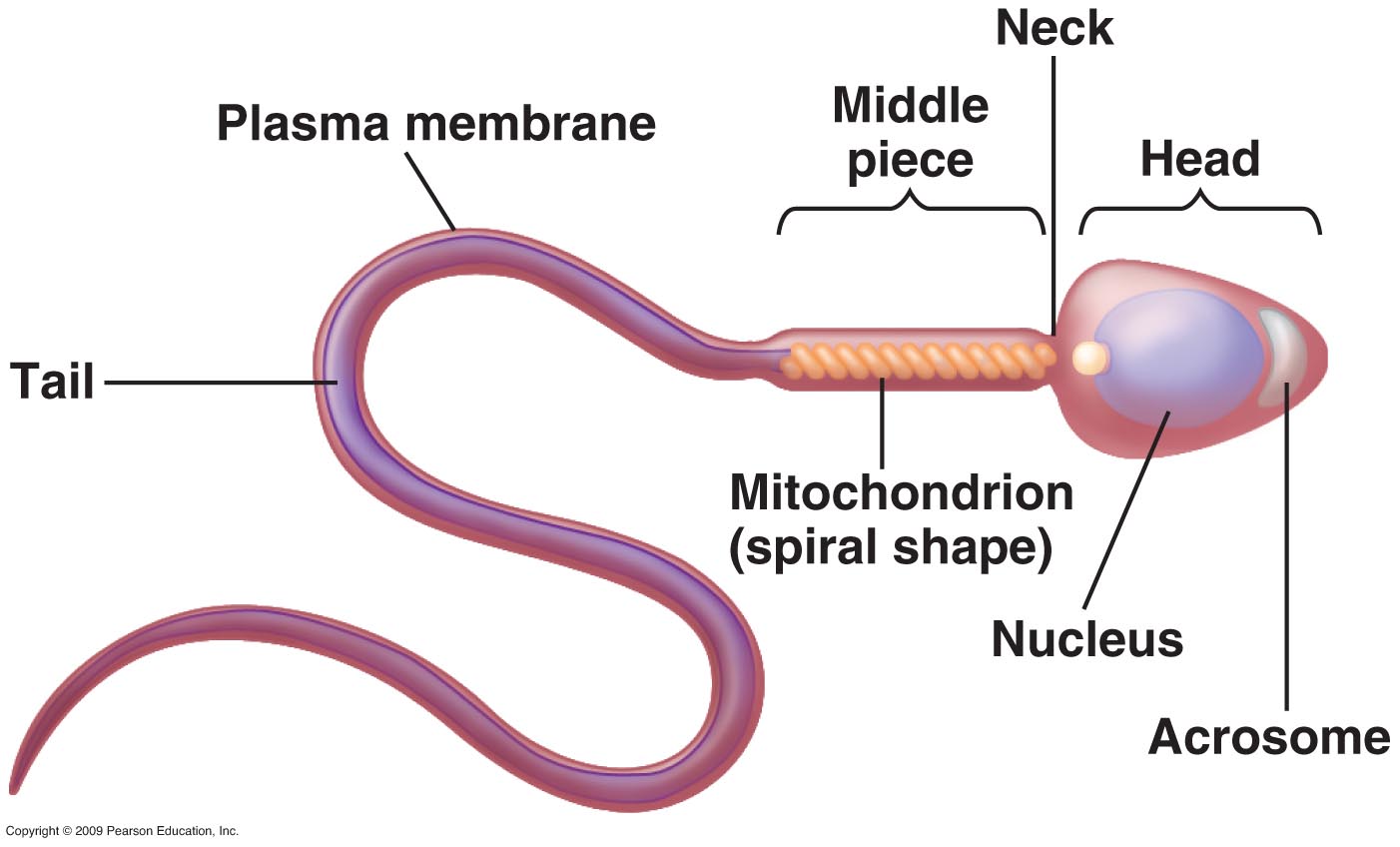
How is the body of a sperm suited for fertilization of an egg? Socratic
Definition: What are Sperm Cells? Sperm cells are gametes (sex cells) that are produced in the testicular organ (gonad) of male human beings and animals. Like the female gamete (oocyte), sperm cells carry a total of 23 chromosomes that are a result of a process known as meiosis. Diagram of a sperm cell showing many detailed components Summary [ edit] File history Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time. You cannot overwrite this file. File usage on Commons The following 26 pages use this file: User:LadyofHats/gallery1 User:Rocket000/SVGs/Biology File:Complete diagram of a human spermatozoa-ar.svg
A spermatozoon, in plural spermatozoa, or sperm cell is the male reproductive cell that is produced in the man´s testicles in a process called spermatogenesis. The sperm cell´s function is to enable sexual reproduction through its union with the female egg during fertilization. Structure of Formed Sperm. Sperm are smaller than most cells in the body; in fact, the volume of a sperm cell is 85,000 times less than that of the female gamete. Approximately 100 to 300 million sperm are produced each day, whereas women typically ovulate only one oocyte per month as is true for most cells in the body, the structure of sperm.

Illustration Of Sperm Cell Diagram Transparent PNG 640x575 Free
Sperm is the male reproductive cell or gamete. The term "gamete" implies that the cell is half of a whole. When a sperm combines with a female gamete, or egg, it results in a human embryo. Sperm are among the most specialized metazoan cell types, adapted for a single function—to find and fuse with the egg. The odyssey of the sperm cell is remarkable; in mammals, sperm must swim distances over ∼1,000-fold their own length while contending with fluid viscosity, shear flows, and physical barriers. 1.




