470221-930 External Anatomy Incisions for Dissection Lay the worm dorsal side up. Pin the cranial and caudal ends. Incise beyond the clitellum, then extend the cut to both ends, from the middle out. Take great care to cut no more than 1/16 of an inch deep into the worm. With forceps, grasp the edges of the skin carefully. Earthworm Dissection: Internal Anatomy 1. Lay the worm on your dissecting tray with its dorsal side facing up. Use dissection pins to secure each end on the tray. Start your dissection about an inch posterior to the clitellum. Lift up the skin with a pair of and snip an opening with a pair of dissecting scissors.
Earthworm Anatomy and Dissection Guide BIOLOGY JUNCTION
In this earthworm dissection guide, you will learn to: • Describe the appearance of various organs found in the earthworm. • Name the organs that make up various systems of the earthworm. Materials: Earthworm Dissection Earthworms are ideal specimens to use for teaching basic anatomy and investigating simple organ systems. Although these annelids, or segmented worms, are one of the simpler preserved invertebrates, the digestive, circulatory, reproductive and nervous systems are well developed and easy to identify. 1. Find the anterior (front) end of the earthworm by locating the fleshy bump over its mouth, called the prostomium. The posterior (back) end has a small hole where sol-id waste is expelled, called the anus. The length of the worm is made up of many tiny segments, each separated by a thin wall called a septum. 2. 1. Work in groups of 4 students. Carefully collect and sign out the equipment from the front desk. Be cautious using the dissecting equipment. Be aware of the sharp edge on the scalpel and points on the scissors and needle probe. Only one person should be touching the earthworm at a time when tools are being used.
Earthworm dissection 001
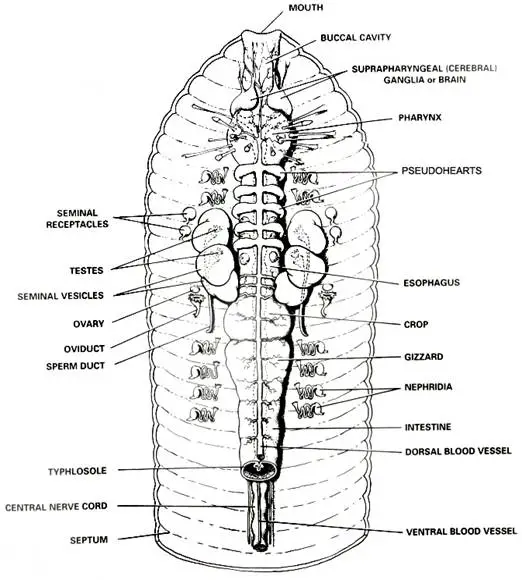
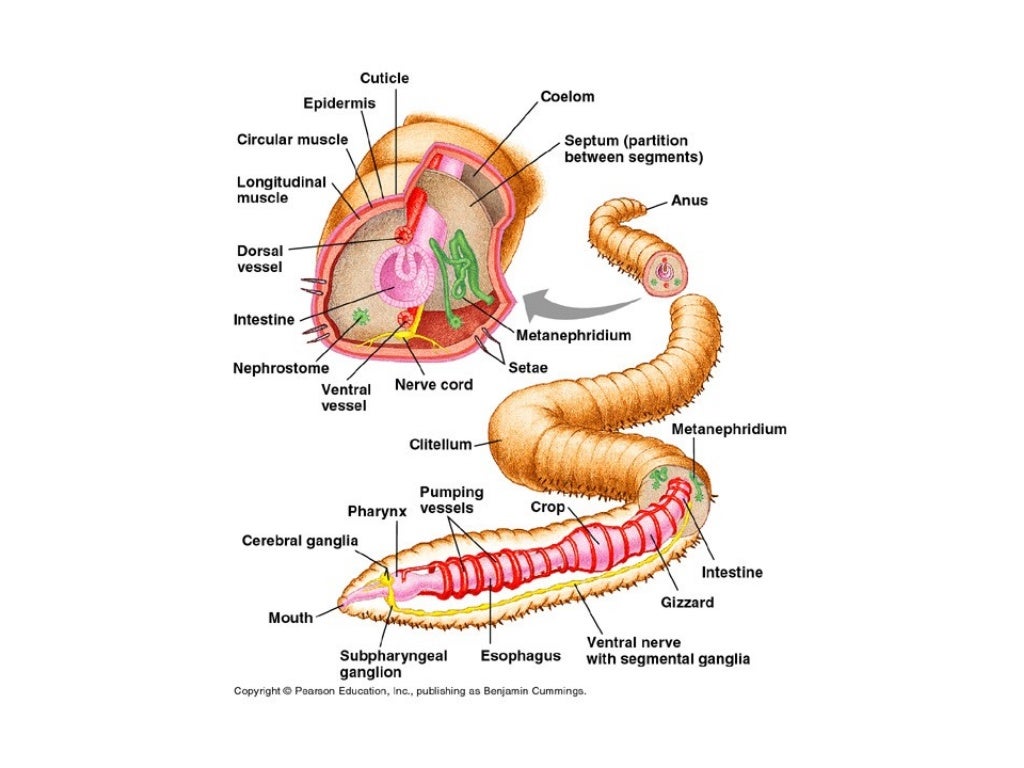
Draw and label the inside of the earthworm with the following structures Dorsal blood vessel Aortic arches Seminal receptacles Nerve cord Seminal vesicles Pharynx Esophagus Crop Gizzard Intestine Dissection 101: The Earthworm Lesson Plan: Earthworm Dissection Background: The earthworm is an invertebrate in the phylum Annelida; it is a segmented worm. The segments are distinguished on the exterior by noticeable band-like-rings; internally the segments are separated by septa. Posterior sections of the worm can be 1. Please fill in the following classification information on Earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris). (use http://www.itis.gov/index.html) a. Kingdom: b. Phylum: c. Class: d. Order: e. Family: f. Locate the mouth of the worm on the far anterior end of the worm.The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts. The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. Label them on the worm pictured below. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal side of the worm, this is the dorsal blood vessel.
Biol 11 Lesson 4 Mar 10 Ch. 27 Earthworm Dissection
Abstract Availability: Earthworms are found all over the earth. They prefer moist rich soil that is not too dry and sandy. Among earthworms there are many species which grow large enough to be used for dissection. There are a number of differences in the number and position of the internal organs which may affect the dissection. Earthworm Dissection Earthworm Dissection External Anatomy Examine your earthworm and determine the dorsal and ventral sides. Locate the clitellum which is on the anterior end of the worm. Locate the mouth of the worm on the far anterior end of the worm The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts
Learn about the anatomy and physiology of the earthworm, a common invertebrate animal, with this interactive online lab from McGraw Hill. You can explore the external and internal structures of the earthworm, compare it with other organisms, and test your knowledge with quizzes and activities. © 2023 Google LLC In this Biology lab, we will examine an earthworm. After studying its external anatomy, we will dissect the earthworm to explore its internal anatomy. We wil.

earthworm circulatory system
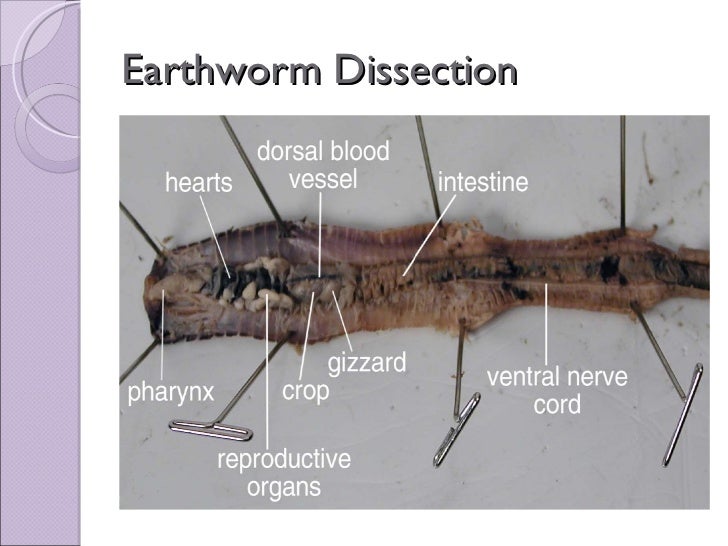
Starting with the mount on the anterior end of the worm, locate the organs. The first organ you see is the pharynx. The worm's esophagus protrudes from the pharynx. About halfway down your incision are the crop and gizzard. Skip the other organs for now and find those two. The crop is essentially a stomach. If your students are interested in animals and their anatomy at all, you can do dissections even without a curriculum! There are great guides and lessons available. Earthworm Dissection Tips. If you have decided to do an earthworm dissection, I want it to be a great experience for you and your student.




