Here are some common steps when creating a foundation plan for a house: Choose a location for the house. Determine the number of rooms you want. Plan for fixtures. Draw the floor plan. Add vertical circulation and structural elements like stairs or decks. Figure out where utilities like water and electricity go. Drawings must be prepared by a professional capable of designing in accordance with the National Building Code of Canada. WINDOW 48" X 24" 16'-4" OPENING IN CONCRETE 3'-4" X 2'-6" CONCRETE FLOOR 4" OPENING IN CONCRETE 10'-2" X 2'-6" PERIMETER DRAINAGE 4" PERFORATED PIPE 52'-0" FLOOR DRAIN SUMP PUMP DIA. 18" W.H. HRV

Foundation Plan PDF
Architectural foundation plans Foundation drawings created by architects will indicate the dimensions and layouts of foundation walls. The architect sets the floor elevations and often dictates where brick shelves or stem walls are needed. A foundation plan can serve as a key for the foundation details to be called out. 1. Decide What Type of Foundation You Need There are three main types of foundations: Slab-on-grade, Basement/Crawl Space, Full/B Wall. A slab-on-grade is built on top of the ground, usually reinforced with concrete. The dirt below should be compacted or crushed before construction begins. Foundation Plan Drawing: What is It and Why Do You Need It? You cannot successfully execute any construction project without a foundation plan drawing. But what is it and why is it important? 1 Document description: An example of a foundation plan you will include with your building and plumbing permit application. Download * yes An example of a foundation plan you will include with your building and plumbing permit application.
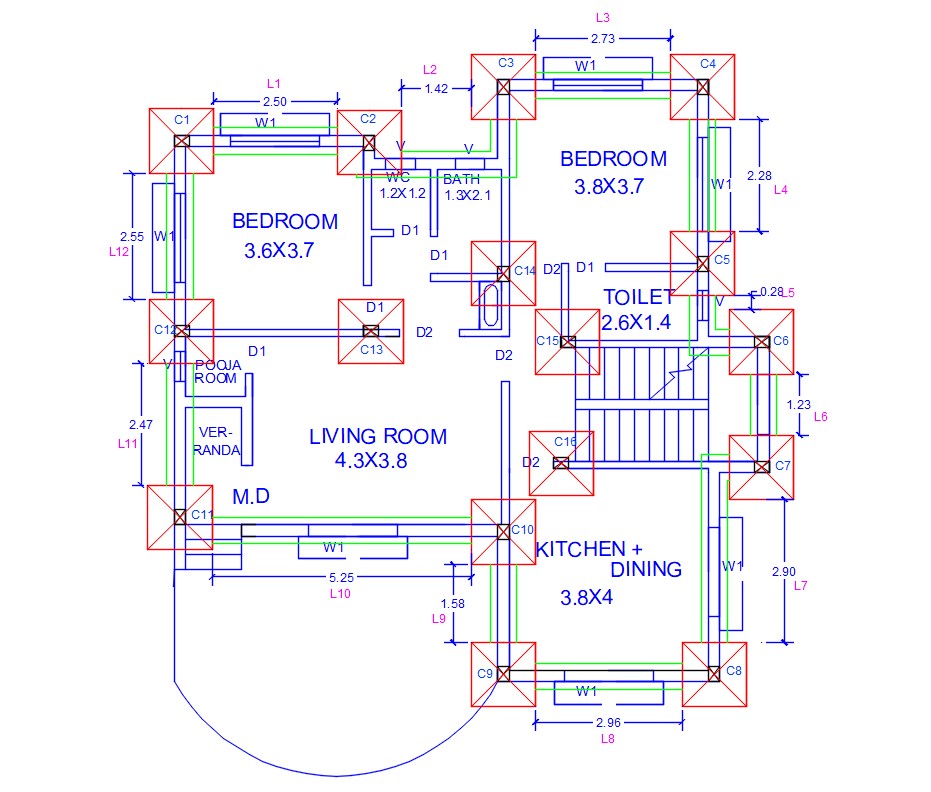
Foundation Plan Cadbull
What You Need To Know Learn about the different types of foundation plans. By Boyce Thompson Every house needs a strong foundation. But the ideal foundation plans for your home differs by soil type, lot slope, house style, and climate. In this video, a step by step guideline has been provided on how to draw a foundation plan.Shallow Foundations: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AwqS5LWRtKw&t. Components of Foundation Plan Drawings. 1. Foundation Layout: Foundation plans show the outline and dimensions of the building's foundation. This includes the location of all walls, columns, and other structural elements that support the load of the building. 2. Footings: The size, shape, and location of footings are specified on the. In the episode, I explained on how to draw a foundation plan or layout from an architectural plan and how to go about it on placing columns on the plan and s.

Foundation plan of new building. Download Scientific Diagram
Foundation Plan Design Steps. The location and scale of the foundation drawing can be customized. Draw the foundation walls, columns, and piers based on the floor plan. You can use the breaks in the walls to identify access holes, vents, windows, and doors. It is possible for you to plan your foundation walls, the foundations for the columns. conventional foundation requirements of the code or the design procedures of ACI 318. Masonry design procedures follow the allowable stress design (ASD) method of The Masonry Society's TMS 402 (TMS, 2011). Wood design procedures are used to design the connections between the foundation system and the structure above and
A foundation transfers the load of a structure to the earth and resists loads imposed by the earth. A foundation in residential construction may consist of a footing,. either 2,500 or 3,000 psi, although other values may be specified. For example, 3,500 psi concrete may be used for improved weathering resistance in particularly severe climates Example: Foundation plan See below for an example of a foundation plan. See also General arrangement drawings
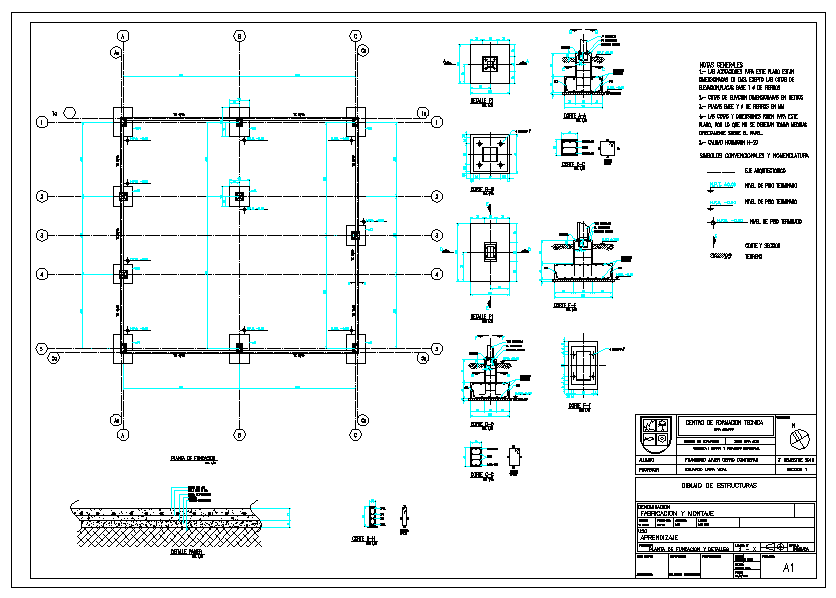
Foundation plan Cadbull
Figure 2 TYPICAL FOUNDATION PLAN EXAMPLE Solid blocking to carry 2nd floor beam. Solid blocking to carry 2nd floor beam. FOUNDATION PLANS Although the foundation system may entail only a small part of the total project, it must provide a firm, stable, fully de-signed base for the entire structure. It is responsible for the distribution of the total weight of the building and supports as well as all live loads imposed on it.



