Page 1: The questions Page 2: The answers practice problem 2 worksheet-transform.pdf The graph below shows velocity as a function of time for some unknown object. What can we say about the motion of this object? Plot the corresponding graph of acceleration as a function of time. Plot the corresponding graph of displacement as a function of time. Unit 1: Kinematics in 1D 1 - Vector and Scalar, Distance and Position There are two types of measurement: with ______________ or without. Scalars: Magnitude only Vectors: Magnitude and direction • Kinematics: The study of an object's _______________. Position, Distance and Displacement • Distance ( ): the separation between two points. Ex, the
kinematics graph
Motion Graphs & Kinematics Worksheet: 1. The graph below describes the motion of a fly that starts out going left. 15.0 V(m/s 10.0 5.0 5 10 15 20 time (s) -5.0 -10.0 -15.0 a. Identify section(s) where the fly moves with constant velocity. b. Identify section(s) where the fly moves right slowing down. 1. An object is in ______________________ when its distance from a(n) __________________ is changing. 2. Speed in a given direction is called _______________________________ 3. ___________________________ can be calculated if you know the distance that an object travels in one unit of time. 4. 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM On a racing circuit, John is cruising at a constant 121 km/h. Micheal starts from rest (maintaining constant acceleration) and catches John within 968 meters. Qualitatively draw the position vs. time graph for both cars from John's start to the point where he catches up. 1 Previous Topic Next Topic The velocity-time graph for the motion is: The distance traveled can be found by a calculation of the area between the line on the graph and the time axis. This area would be the area of the triangle plus the area of rectangle 1 plus the area of rectangle 2. Area = 0.5*b tri *h tri + b 1 *h 1 + b 2 *h 2.
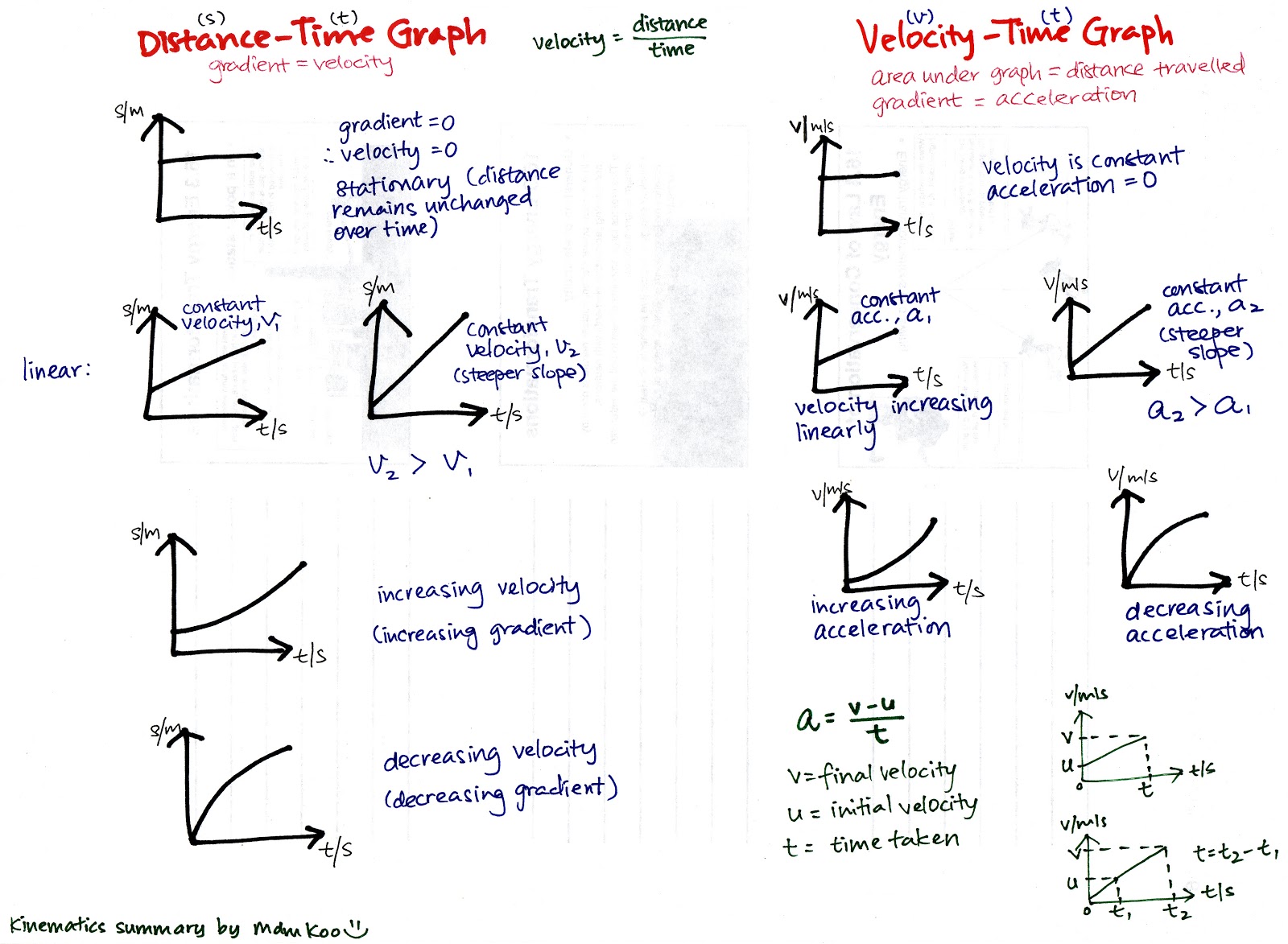
mdm koo ♥ science & mathematics Kinematics summary note
Six basic motion types are included. There are two constant velocity motions - one for moving to the right and one for moving to the left. There are two speeding up motions - one for moving to the right and one for moving to the left. And finally, there are two slowing down motions. Users tap a button to toggle between the six basic motions. There are 2 possibilities: a) (in red) object moves away from origin in positive direction, then back in negative direction b) (in blue) object moves away from origin in negative direction 3. a) Draw the velocity vs. time graph for an object whose motion produced the position vs time graph shown below at left. 1. A cart travels with a constant nonzero acceleration along a straight line. Which graph best represents the rela-tionship between the distance the cart travels and time of travel? Base your answers to questions 2 through 4 on the infor-mation below. A car on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 1.0 meter per second2 for 10 seconds. Using the Interactive. The Graph That Motion Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame. Dragging this hot-spot allows you to change the size of iFrame to whatever dimensions you prefer. Our Graph That Motion simulation is now equipped with Task Tracker functionality.
Graphing Motion Kinematics Worksheet Answers Promotiontablecovers
When studying the motion of electrons around the nucleus, velocity and acceleration can be discussed to show how the electron changes speed when it encounters another electron or proton. Motion, especially vibratory motion, also is encountered with the study of states of matter and how the rate of motion changes during phase changes. FIGURE EX2.9 shows the velocity graph of a particle. Draw the particle's acceleration graph for the interval . FIGURE EX2.12 shows the velocity-versus-time graph for a particle moving along the x-axis. Its initial position is at x0 = 2m at t0 = 0s (b) What are the particle's position, velocity, and acceleration at t = 3.0s.
Motion Graphs & Kinematics Worksheet: You must show all work for full credit. Please show all details of the calculations you perform for converting the motion graphs from one type to another. 1. The graph below describes the motion of a fly that starts out flying left. Its initial position is 5.0m right. • Line up the graphs vertically. • Draw vertical dashed lines at special points except intercepts. • Map the slopes of the position graph onto the velocity graph. • A red peak or valley means a blue time intercept. t x v t Graphing Tips The same rules apply in making an acceleration graph from a vel oci ty gr aph. Ju s! N : n

Reading Kinematics Graphs Mini Physics Learn Physics Online
Question 1 A ball is dropped vertically from a height h above the ground .It hits the ground and bounces up vertically to a height h/2.Neglecting subsequent motion and air resistance ,its velocity v varies with the height h as Solution Before hitting the ground ,the velocity v is given by v2 = 2gh v 2 = 2 g h Showing 8 worksheets for Graphing Motion. Worksheets are Ap physics b review, Work motion graphs name, Motion kinematics, Distance vs time graph work,.




