The dog humerus bone anatomy comprises a long shaft and proximal and distal extremities. Here, the proximal extremity of the dog humerus consists of the head, neck, and tubercles. Again, the distal extremity contains condyles, crest, and fossa. Some important muscles of the dog thoracic limb originate or insert on the dog's humerus bone. Fracture of the Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) in Dogs Diseases Conditions Of Dogs Overview of Fractures Humerus in Dogs Fractures of the humerus (upper arm bone) are not frequently seen in veterinary medicine. These fractures are usually the result of major trauma, but can be caused by disease of the bone itself.

Dog Humerus OsteoID Bone Identification
Anatomically, the term leg means the part of the hind limb that extends from the stiffle joint to the hock joint (knee to ankle or tibia and fibula bones region). This short post will try to cover the dog leg anatomy in detail with labeled diagrams. The leg of a dog consists mainly of the two long bones - tibia and fibula. Article Search Humerus bone fracture: Causes and treatment. The humerus connects with other bones to form the elbow and the shoulder joints. The radial nerve is critical for normal function of the forelimb and wraps around the outer side of the humerus bone above the elbow joint. Causes. Osteochondritis of the dog humerus bone - development of a loose flap of cartilage may develop on the articular surface of the humerus bone, The most common injury to the dog is supraspinatus tendinopathy, medial shoulder instability, bicipital tenosynovitis, and shoulder luxation or dislocation. Here, I will not describe the details of all. Overview The long bones of dogs and cats are almost identical to the bones of the legs and arms of people. Dogs and cats can break these bones due to vehicular trauma, fights with other animals, and some sporting injuries, to name a few causes. Limb anatomy: A bone can break in many ways and we call these breaks "fractures."
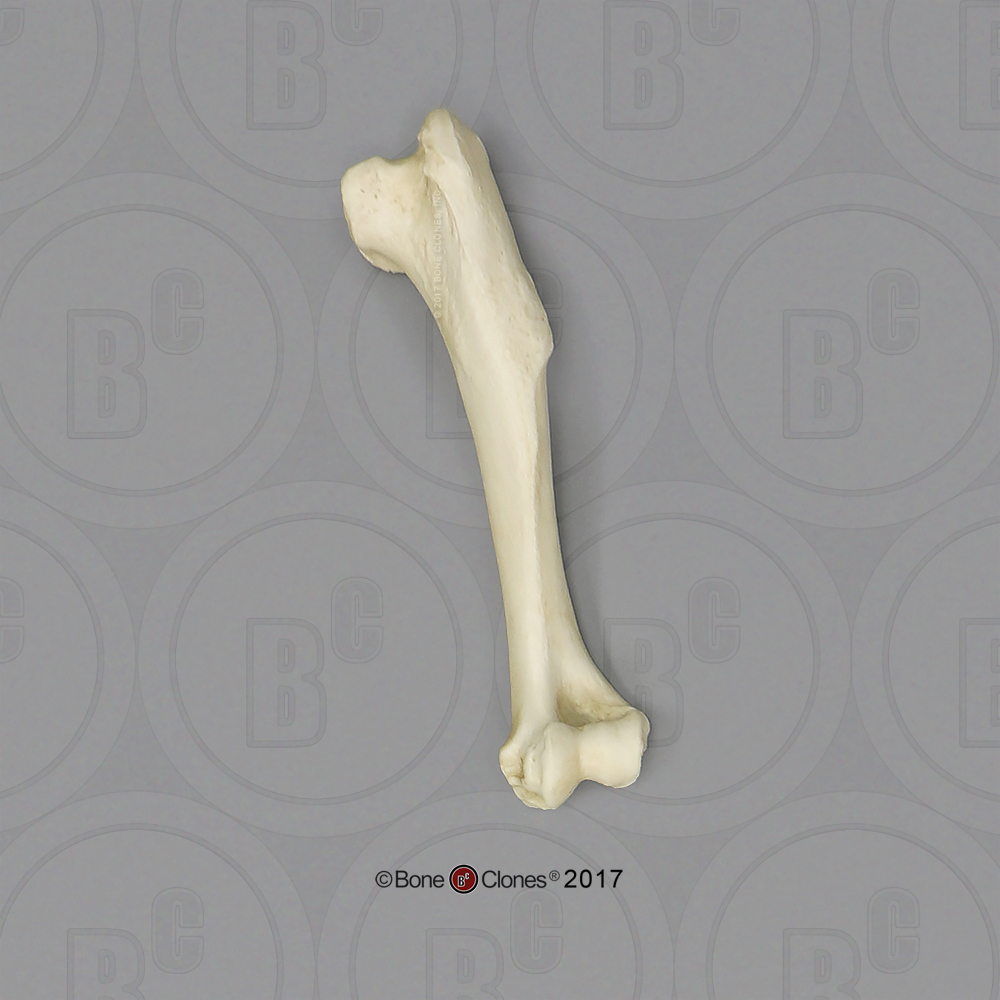
Large Dog Humerus Bone Clones, Inc. Osteological Reproductions
Dogs exhibit extreme variations in body weight, shape and size. Growth patterns vary based on breed with large dogs reaching adult weight around 15 months while small-medium dog attain their adult weight around 9-10 months. Even within the same size dog category, differences can be seen among various breeds.[1] Those differences emerge from the functions that each breed was originally. What are humeral condylar fractures? The humeral condyle is the name given to the end of the bone (called the humerus) at the top of the front leg (the forelimb). Together with the radius and ulna (the two bones of the antebrachium or forearm) the humeral condyle makes up the elbow joint. Veterinary Osteology Series Lectures by Dr Rajesh Banga. Detailed anatomy of humerus of Dog. The humerus is the only bone of the skeleton of the arm (thoracic stylopodium).It is composed by three basic segments: The proximal extremity, articulating with the scapula and bearing the head and the major and lesser tubercles The body (shaft) bearing the deltoid tuberosity The distal extremity bearing the humeral condyle and articulating with the radius and ulna
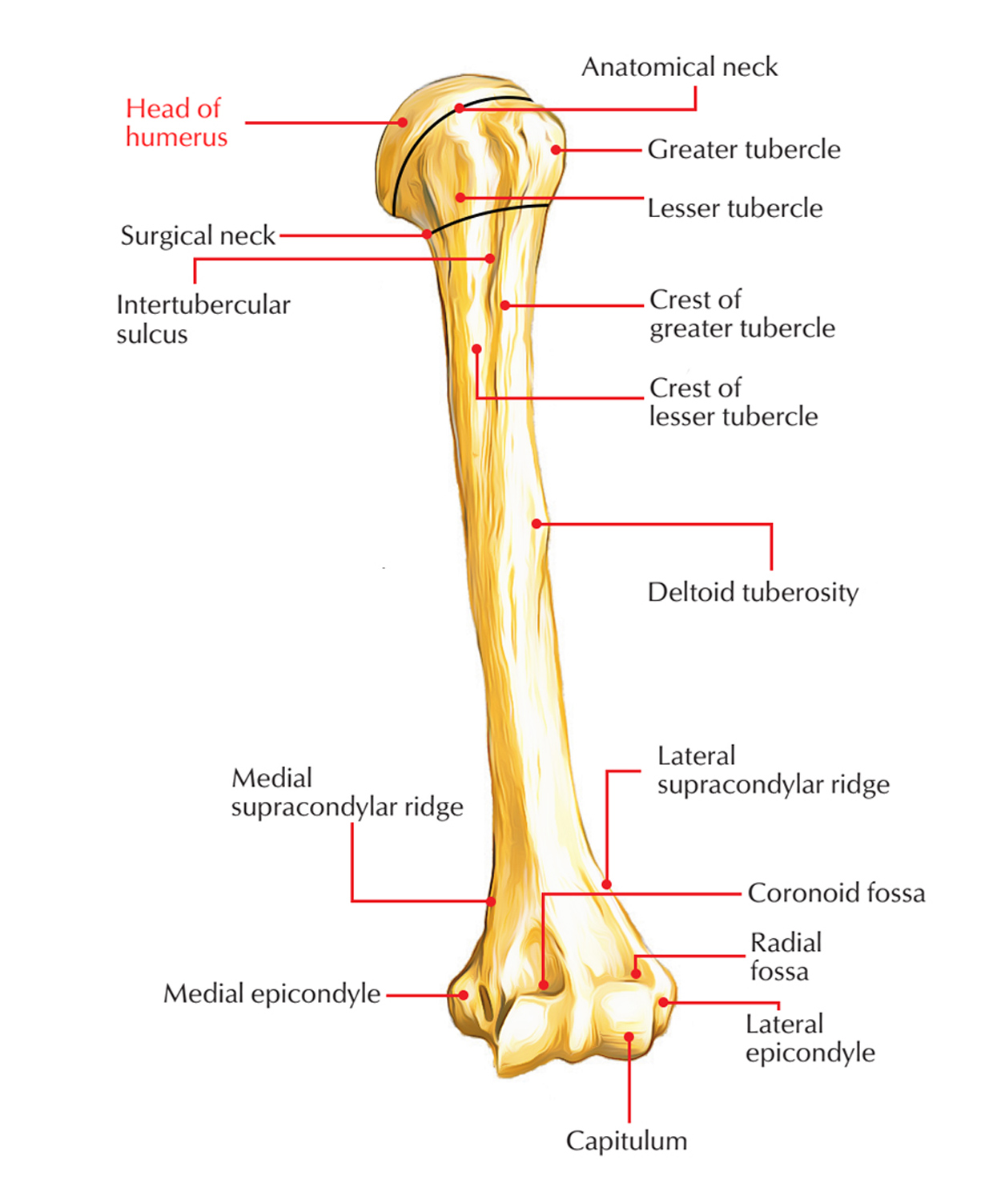
Head of the Humerus Earth's Lab
The Humerus is the long bone of the forearm, articulating with the scapula to form the shoulder and the radius and ulna to form the elbow. In situ, it lies obliquely along the ventral thorax and is more horizontal in larger species. The greater tubercle is not separated into two parts like in other species. The canine femur is the heaviest 4 and largest 5 canine bone. In most dogs, it is slightly shorter than the tibia and the ulna and approximately one-fifth longer than the humerus.. In dogs, caudal retraction of the humerus in relation to the scapula is shoulder flexion, whereas cranial motion of the humerus in relation to the scapula is.
The humerus is an important bone for transfer of weight and for propelling the body forward; by its position, it also provides a protective function for the thorax. The humeral head articulates proximally with the scapula, and the humeral condyle articulates distally with the radius and ulna. Speaking of skeletons, a dog has 320 bones in their body (depending on the length of their tail) and around 700 muscles. Muscles attach to bones via tendons. Depending on the breed of dog, they will have different types of muscle fibers.. The foreleg consists of a shoulder, elbow, ulna, humerus radius and wrist. Many large breeds can suffer.
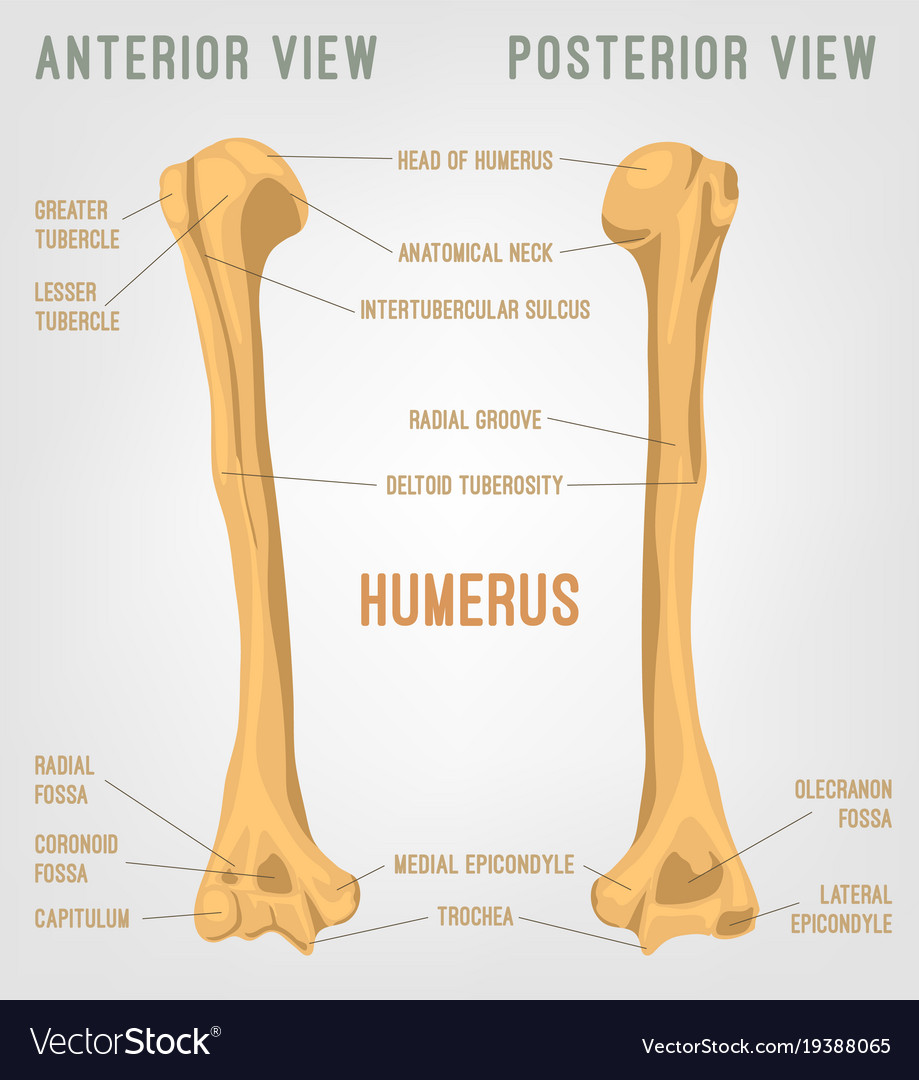
Human humerus bone Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
1. Introduction. Fractures of the humerus represent 8 to 12% of all fractures in dogs, with the humeral condyle the most commonly affected region [].The Y-T humeral fractures, also known as distal humeral bicondylar fractures [] may be simple (3-fragments) or comminuted in the supracondylar region [] and they represent a unique therapeutic challenge [4,5]. by Stephanie Hedgepath June 18, 2022 Form Follows Function - Closer Look at the Humerus (Upper Arm) of a Dog The forequarter of the dog is responsible for both the steering and braking ability of the animal. It lifts the center of gravity as the dog moves forward, acting somewhat similarly to the pole of the athlete participating in the pole vault.




