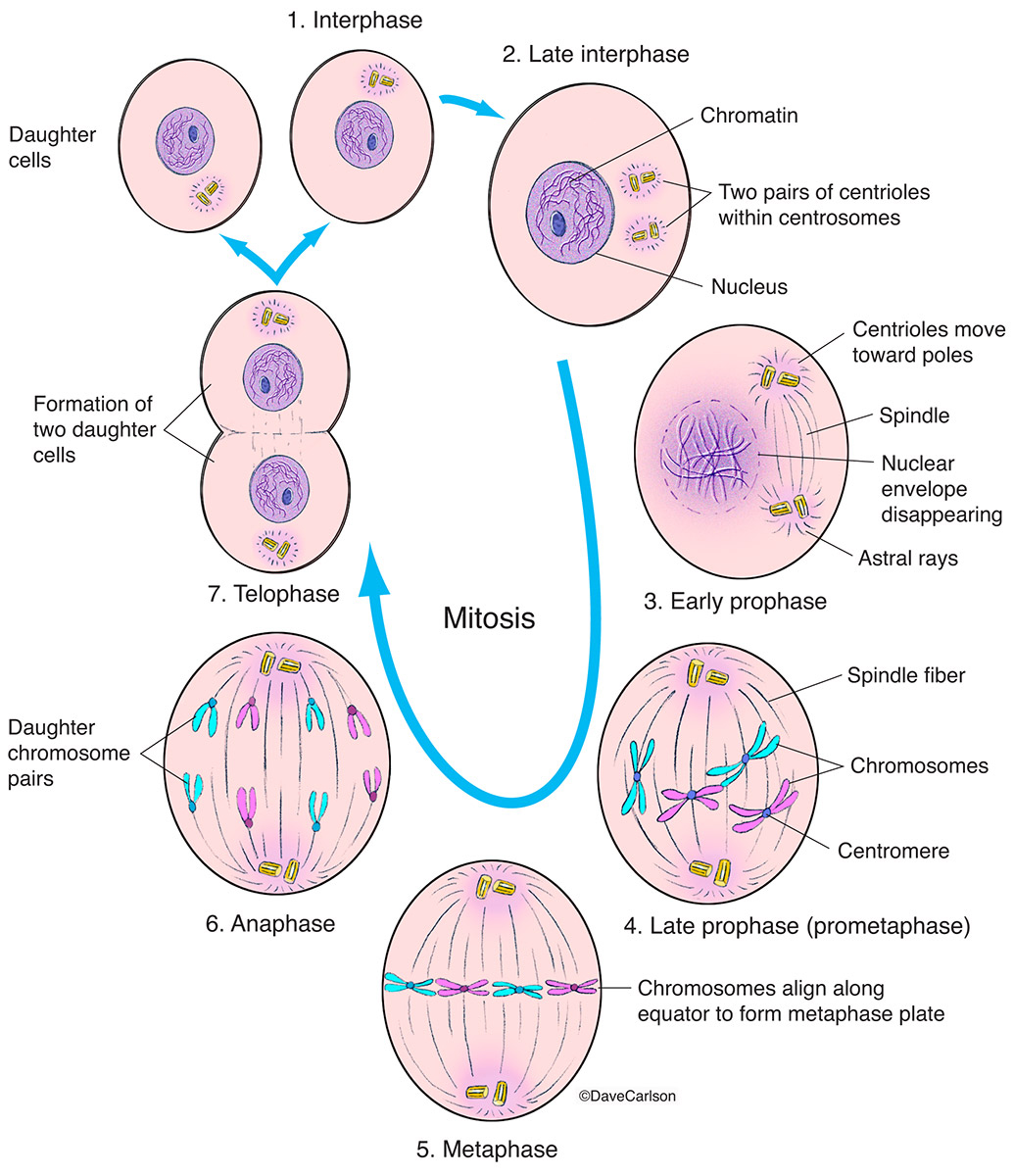
This cell is in interphase (late G 2 phase) and has already copied its DNA, so the chromosomes in the nucleus each consist of two connected copies, called sister chromatids. You can't see the chromosomes very clearly at this point, because they are still in their long, stringy, decondensed form. Key terms The cell cycle In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (M) phase). Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. This is when the cell grows and copies its DNA before moving into mitosis.
What Is Interphase? — Overview & Diagrams Expii
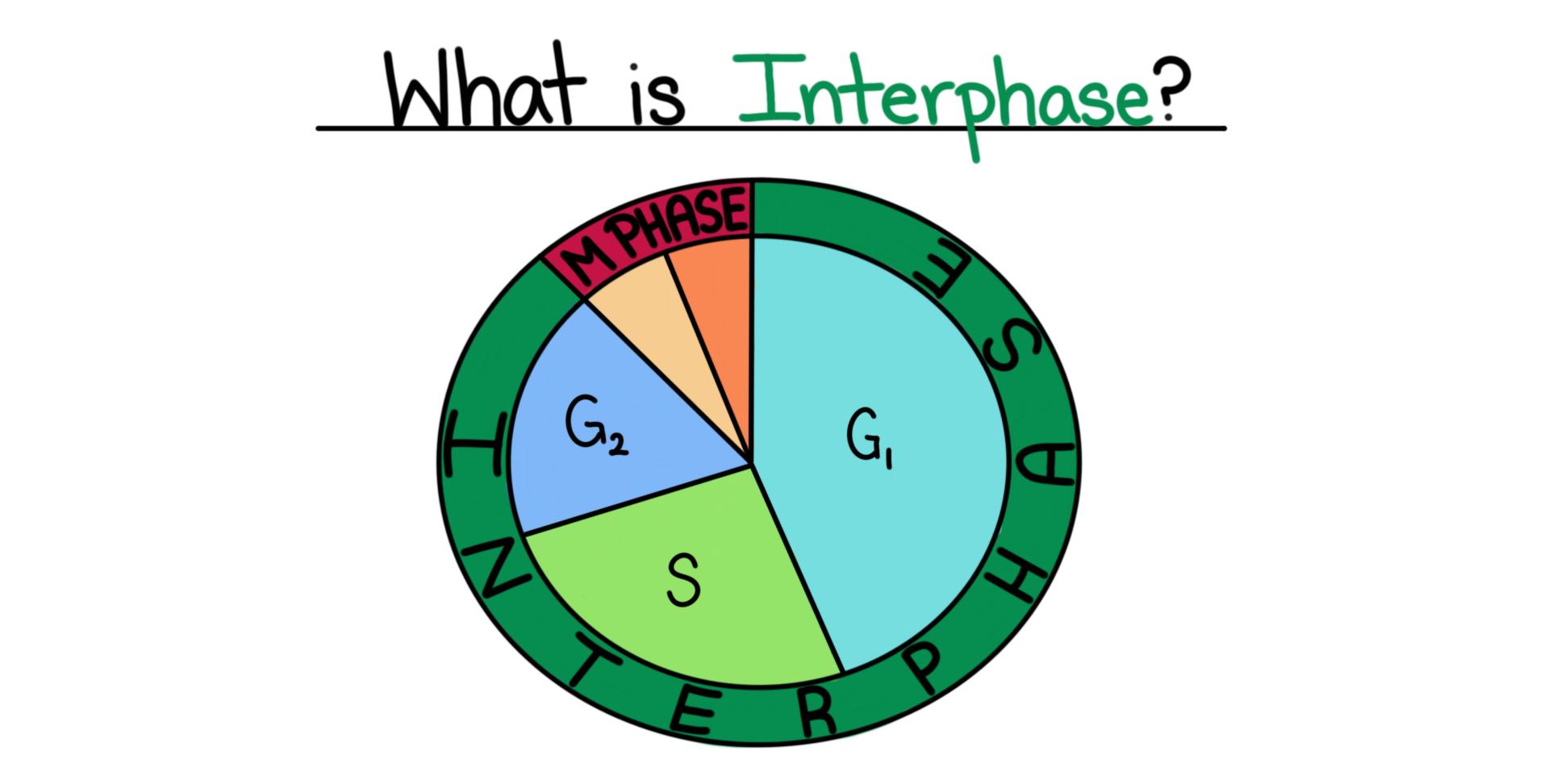
Gap 1 After cells have finished dividing their chromosomes, and cytokinesis has divided the cell membrane, the two new cells enter the first stage of interphase, Gap 1 or G 1. During this stage, the cell performs its normal functions, and grows in size. The cell replicates organelles as necessary. Interphase. A cell spends most of its life in interphase, which has three phases: G1, S, and G2. In the G1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. In the S phase, the cell's DNA is replicated. Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. The G2 phase is another growth phase, after which the. There are two ways cell division can happen in humans and most other animals, called mitosis and meiosis. When a cell divides by way of mitosis, it produces two clones of itself, each with the same number of chromosomes. When a cell divides by way of meiosis, it produces four cells, called gametes. Gametes are more commonly called sperm in. Figure 6.3 A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. During interphase, G 1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the S phase involves DNA replication and the replication of the centrosome, and G 2 involves further growth and protein synthesis. The mitotic phase follows interphase. Mitosis is nuclear division during which duplicated chromosomes are segregated and.
Interphase & Mitosis Carlson Stock Art
G 1 Phase (First Gap). The first stage of interphase is called the G 1 phase (first gap) because, from a microscopic aspect, little change is visible. However, during the G 1 stage, the cell is quite active at the biochemical level. The cell grows and accumulates the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins as well as sufficient energy reserves to complete the task of. Figure 10.3.1.1 10.3.1. 1: Cells in an onion root in interphase and prophase. Cell A has a large, dark nucleolus surrounded by greyish material (chromatin) that is enclosed within the nuclear membrane. A cell wall makes a box around each cell and the plasma membrane would be located just inside this box, though we cannot easily see it. Figure Detail. Today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and. Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images. Before a dividing cell enters mitosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. About 90 percent of a cell's time in the normal cell cycle may be spent in interphase. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA.In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division.

Protein Synthesis. Events During the Mitotic Stage Protein synthesis
Gap 1 (G1) Synthesis (S), and Gap 2 (G2). G1 and G2 phase represents the time of growth and preparation for mitosis. The synthesis (S) phase is the phase of cell copying or cell duplication of its DNA of its entire genome. Gap 1 (G1) This is the phase in which the cell undergoes normal growth and cell function synthesizing high amounts of proteins. Mitosis is the process of nuclear division. At the end of mitosis, a cell contains two identical nuclei. Mitosis is divided into four stages (PMAT) listed below. Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase. Cytokinesis, the process of cell division, occurs during the last stage of mitosis (telophase).
Figure 10.6 G2 of Interphase - The last stage of interphase is the second gap period, G2. During this stage, cells grow, replenish energy and synthesize needed macromolecules, such as proteins and lipids. Mitosis - When G2 is complete, the cell will enter mitosis. Although there are 5 phases in mitosis, with the exception of the metaphase to anaphase transition, these phases are not discrete. Before entering meiosis I, a cell must first go through interphase. As in mitosis, the cell grows during G 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during S phase, and prepares for division during G 2 phase. During prophase I, differences from mitosis begin to appear.

The Cell Cycle Interphase & Mitosis ALevel Biology Revision Notes
Cell Cycle Definition The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. It is sometimes referred to as the "cell division cycle" for that reason. New cells are born through the division of their "parent" cell, producing two "daughter" cells from one single "parent" cell. F. Interphase Mix and Match (Match the phases to the left with what happens at each phase/stage.) 1. ____ Includes, G1, S, and G2 phases. 2. ____ The Cell "double checks" the duplicated chromosomes for. Label the diagram: Use the following stages/phases and label the digram A. Interphase B. Cytokinesis C. Telophase




