The Komodo dragon ( Varanus komodoensis ), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant species of lizard, growing to a maximum length of 3 m (9.8 ft), and weighing up to 70 kg (150 lb). April 16, 2008 Komodo Dragons' Skillful Skulls Komodo Dragons' powerful neck muscles generate huge forces when attacking prey. Their lightweight skulls can handle the forces thanks to a.
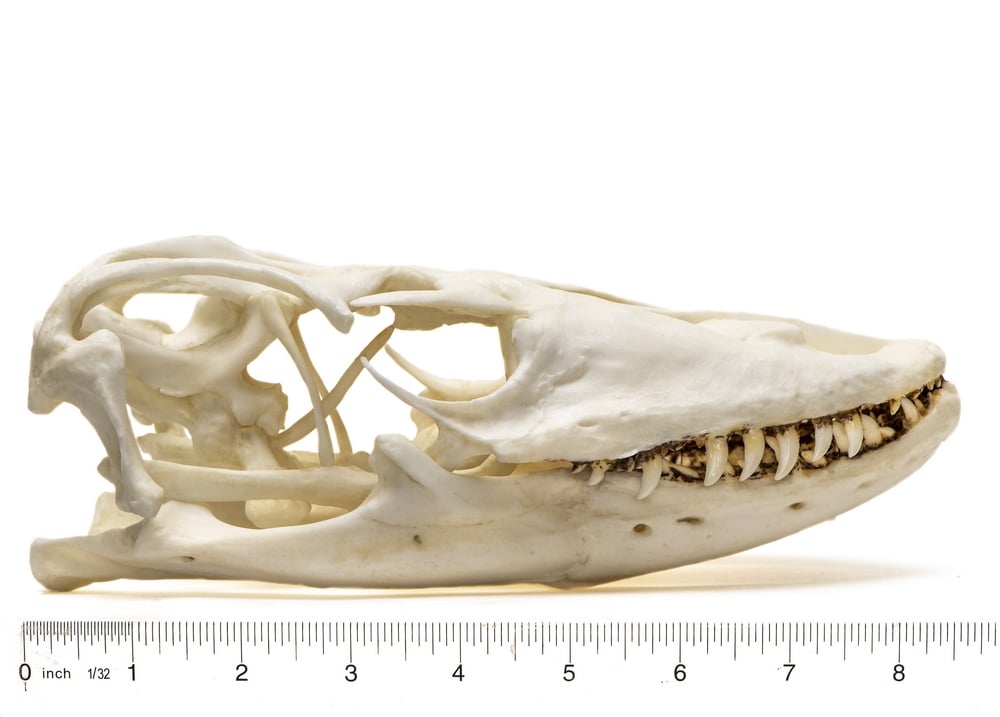

Komodo Dragon Skull Replica
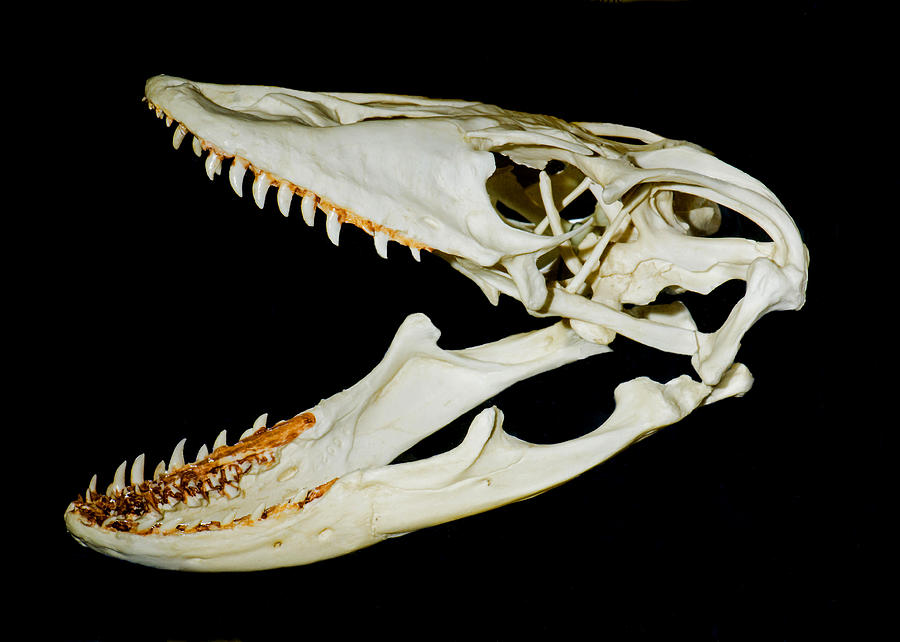
Just beneath their scales, Komodo dragons wear a suit of armor made of tiny bones. These bones cover the dragons from head to tail, creating a "chain mail" that protects the giant predators. However, the armor raises a question: What does the world's largest lizard - the dominant predator in its natural habitat - need protection from? File:KomodoDragon Skull.jpg. Size of this preview: 800 × 509 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 203 pixels | 640 × 407 pixels | 1,024 × 651 pixels | 1,280 × 814 pixels | 2,032 × 1,292 pixels. English: Skull of Komodo with serrated tooth. attribution - You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes. The Komodo dragon ( Varanus komodoensis) displays a unique hold and pull-feeding technique. Its delicate 'space-frame' skull morphology differs greatly from that apparent in most living large prey specialists and is suggestive of a high degree of optimization, wherein use of materials is minimized. Komodo Dragon Skull Anatomy 3D Model Blackburn Lab premium 8.6k 92 Triangles: 2.7M Vertices: 1.2M More model information Skull of a Komodo dragon, Varanus komodensis, with bones colored and labelled to demonstrate skull anatomy.

CompBiomechBlog Komodo dragon skull
What is the Komodo dragon? Reaching up to 10 feet in length and more than 300 pounds, Komodo dragons are the heaviest lizards on Earth. They have long, flat heads with rounded snouts, scaly. Given their ability to attack and butcher very large animal prey, one might assume the Komodo dragon would possess a steely, snapping jaw like an alligator's and a dense, sturdy skull. The. Far from being the special result of insular evolution, Komodo dragons are the last survivors of a group of huge lizards that ranged over much of Australasia Hanneke Meijer @DrHanneke Wed 17. Since the Komodo dragon has been included on The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, it is crucial to know in detail its biology as there is a limited availability of research material on these animals—mainly those who died in zoos or whose remains were found in the wild. Anatomy is essential for understanding physiology, identification of.
Timor Deer gets its throat ripped open by a Komodo Dragon r
[MUSIC] Inside the American Museum of Natural History's Hall of Vertebrate Origins, where fossils of a large sea turtle and long-necked swimming reptile hang from the ceiling. In the center, a mosasaur fossil behind glass, and the camera cuts into a close-up of its skull with many long sharp teeth. Lightweight skull (Fry et al. 2015) Weak bite force in proportion to body mass Strong pulling force allows them to de-flesh with high success (D'Amore et al. 2011). Decomposition releases volatile oils that Komodo dragons can detect; A pair of Jacobson's organs opens into the roof of the mouth
The Komodo dragon is the largest and heaviest of the lizards, well muscled, and covered with non-overlapping scales that give its surface a granular effect.. The flexible skull joints, along with loosely articulated jaws and powerful neck and throat muscles, allow chunks of flesh to be consumed quickly without chewing. The stomach expands. Physical Description Komodo dragons are large lizards with long tails, strong and agile necks, and sturdy limbs. Their tongues are yellow and forked. Adults are an almost-uniform stone color with distinct, large scales, while juveniles may display a more vibrant color and pattern.

Komodo Dragon Skull Replica
University of New South Wales. (2008, April 14). Ancient Komodo Dragon Has Space-age Skull. ScienceDaily. Retrieved December 17, 2023 from www.sciencedaily.com / releases / 2008 / 04. Habitat Adult Komodo dragons live mainly in tropical savannah forests. They prefer open lowland areas with tall grasses and bushes, but are also found in other habitats, such as beaches, ridge tops, and dry riverbeds. Young Komodo dragons are arboreal and live in forested regions until they are eight months old.




