Mitosis is a process of cell division that helps you stay alive and healthy. In other words, in the world of cell biology, mitosis is kind of a big deal! But like with anything science-related, mitosis can be sort of confusing when you first try to understand it. Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase).
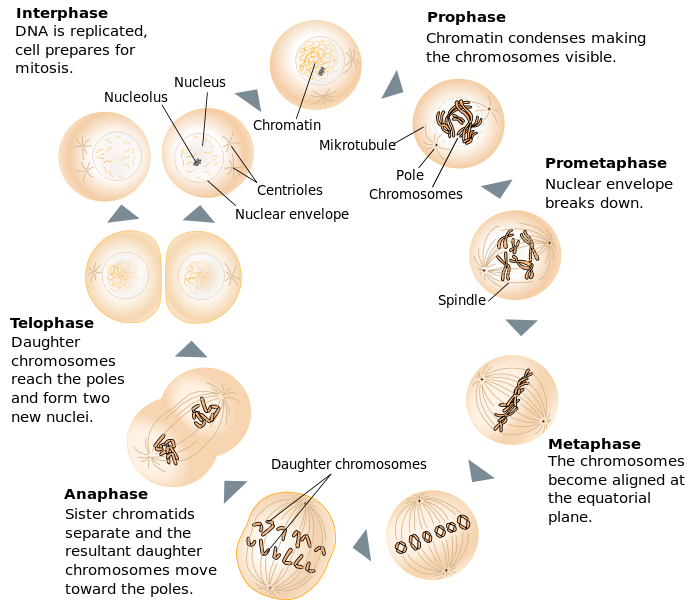
What are the Stages of Mitosis Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA. In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. The G1 phase is the first gap phase. S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized. The S stands for synthesis. What is mitosis? How are mitosis and meiosis different? Why is mitosis important to organisms? Divide into four phases the reproduction process of chromosomes in plant and animal cells Mitosis has four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. See all videos for this article During G 1 phase, also called the first gap phase, the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecular building blocks it will need in later steps. [Do cells always grow before they divide?] S phase. In S phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus. Figure Detail. Today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and.

Cell Cell division and growth Britannica
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division. At the end of mitosis, a cell contains two identical nuclei. Mitosis is divided into four stages (PMAT) listed below. Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase. Cytokinesis, the process of cell division, occurs during the last stage of mitosis (telophase). Mitosis occurs in four phases. The phases are called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. They are shown in Figure 7.3.3 7.3. 3 and described in detail below. Figure 7.3.3 7.3. 3: Mitosis is the phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle that occurs between DNA replication and the formation of two daughter cells. G 1 phase: first gap phase; the cell grows larger and organelles are copied S phase: synthesis phase; the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus G 2 phase: second gap phase; the cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, and begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell nucleus splits in two, followed by division of the parent cell into two daughter cells. The word "mitosis" means "threads," and it refers to the.
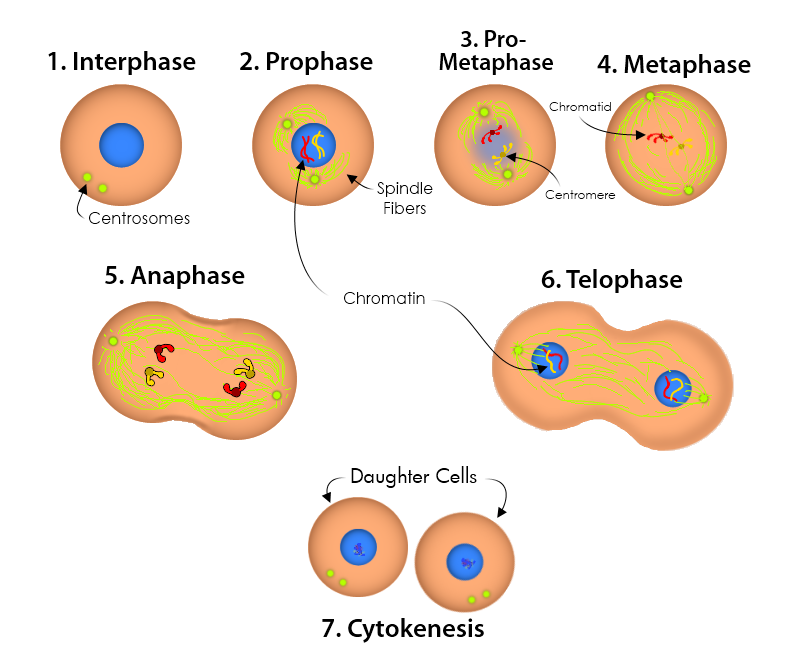
MITOSIS DIAGRAM Unmasa Dalha
The concept of mitosis The purpose of mitosis is to make more diploid cells. It works by copying each chromosome, and then separating the copies to different sides of the cell. The second stage of mitosis. In this stage the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell and become connected to the spindle fiber at their centromere. The third stage of mitosis. In this stage the sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are pulled apart. The fourth and last stage of mitosis.
Mitosis divides the chromosomes in a cell nucleus. Label-free live cell imaging of mesenchymal stem cells undergoing mitosis. Onion cells in different phases of the cell cycle enlarged 800 diameters. Mitosis ( / maɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. In Figure 6, identify the phase of mitosis and write the name of the phase below each diagram. The cells go in the appropriate temporal sequence through cell cycle and you are likely to use the same term multiple times.. Label Figure 7 with the stages of cell cycle (interphase, G1, S, G2, M). Licenses and Attributions : . : : . : Previous.

Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet
Microtubule Instability Increases Greatly at M Phase. The mitotic spindle begins to self-assemble in the cytoplasm during prophase. In animal cells, each of the replicated centrosomes nucleates its own array of microtubules, and the two sets of microtubules interact to form the mitotic spindle.. This can be seen by labeling the microtubules. Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei with an equal amount of genetic material in both the daughter nuclei. It succeeds the G2 phase and is succeeded by cytoplasmic division after the separation of the nucleus.




