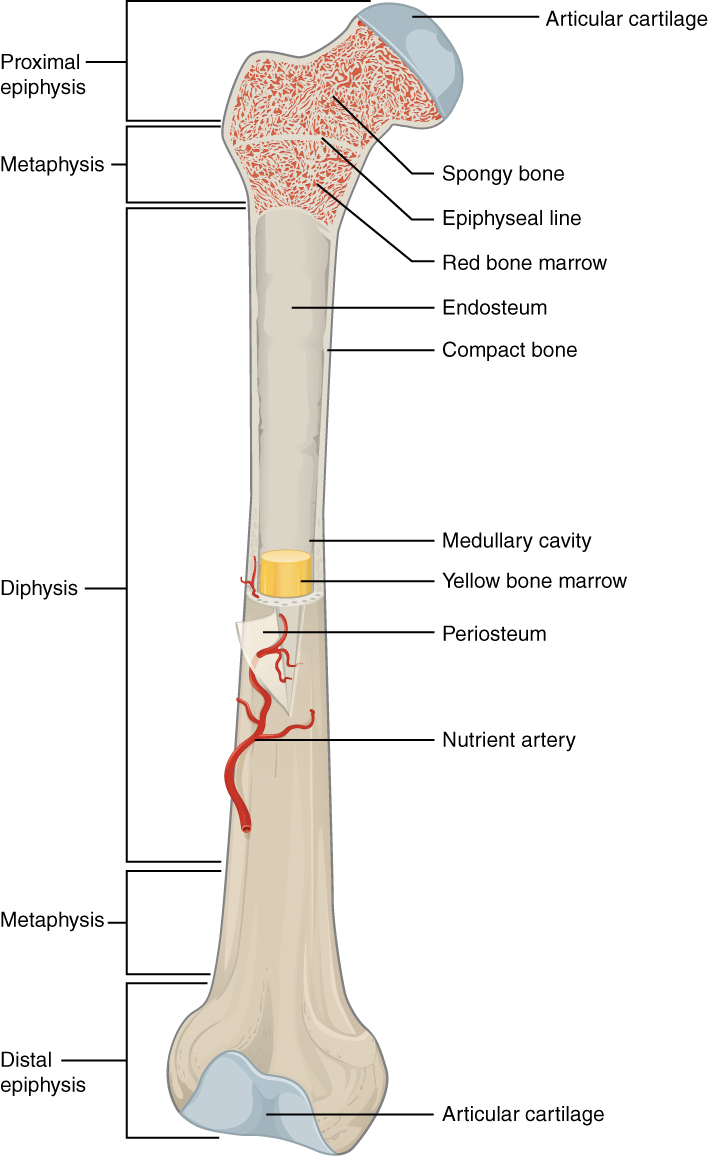
The diaphysis is the hollow, tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Inside the diaphysis is the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow bone marrow in an adult. The outer walls of the diaphysis (cortex, cortical bone) are composed of dense and hard compact bone, a form of osseous tissue. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( Figure 6.7 ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled.

Pin by Karen Davies on anatomy Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy
Anatomy of the Bone Bones and Joints What is bone? Bone is living tissue that makes up the body's skeleton. There are 3 types of bone tissue, including the following: Compact tissue. The harder, outer tissue of bones. Cancellous tissue. The sponge-like tissue inside bones. Subchondral tissue. These are (1) the axial, comprising the vertebral column —the spine—and much of the skull, and (2) the appendicular, to which the pelvic (hip) and pectoral (shoulder) girdles and the bones and cartilages of the limbs belong. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( [link] ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Figure 1. Anatomy of a Long Bone. A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone (Figure 1). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis.
File603 Anatomy of Long Bone.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Skeletal System: Labeled Diagram of Major Organs In addition to the bones, organs of the skeletal system include ligaments that attach bones to other bones and cartilage that provides padding between bones that form joints throughout your body. Bones are your body's main form of structural support. They're made of hard, strong tissue that gives your body its shape and helps you move. Your bones are like the frame under the walls of your home. If you've ever watched a home improvement show and seen the internal structure of a house, that's what your bones are — the supports. Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. The patellae (singular = patella) are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person. Table 6.1 reviews bone classifications with their associated features, functions, and examples. In addition, bones contain bone marrow and periosteum. You can see these tissues in Figure 4.4.2 4.4. 2. Bone marrow is a soft connective tissue that is found inside a cavity, called the marrow cavity. There are two types of marrow in adults, yellow bone marrow, which consists mostly of fat, and red bone marrow.

Long Bone Diagram Labled They are one of five types of bones
Key facts about the main bones, joints and muscles of the body. Axial skeleton: bones of the skull, ribs, vertebral column, sternum, sacrum, coccyx, hyoid bone and auditory ossicles. Appendicular skeleton: bones of the upper and lower limbs and the shoulder and pelvic girdles. Skull sutures, temporomandibular, shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee. The skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. Each bone is a complex living organ that is made up of many cells, protein fibers, and minerals. The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body. The skeletal system also provides attachment points for.
The human skeletal system consists of all of the bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments in the body. Altogether, the skeleton makes up about 20 percent of a person's body weight. An adult's. The structure of bones Tridsanu Thophet/EyeEm/Getty Images Bones are composed of two types of tissue. Compact (cortical) bone is a hard outer layer that is dense, strong, and durable. It.

Human Skull Diagrams 101 Diagrams
3. Label spongy bone structures shown in this micrograph (arrows): trabecula. bone marrow. 4. Identify the shape of the bones shown below as: long, short, flat, sesamoid or irregular. Write your answers on the spaces provided. 5. Name five bones of the axial skeleton and five bones of the appendicular skeleton. Differentiate between bones of the body based on the classification of the shape of the bone. 4. Identify the bones of the body using correct anatomical terminology. 5. Use correct anatomical terminology to correctly identify bone landmarks that serve as attachment points for skeletal muscles and ligaments. 6.




