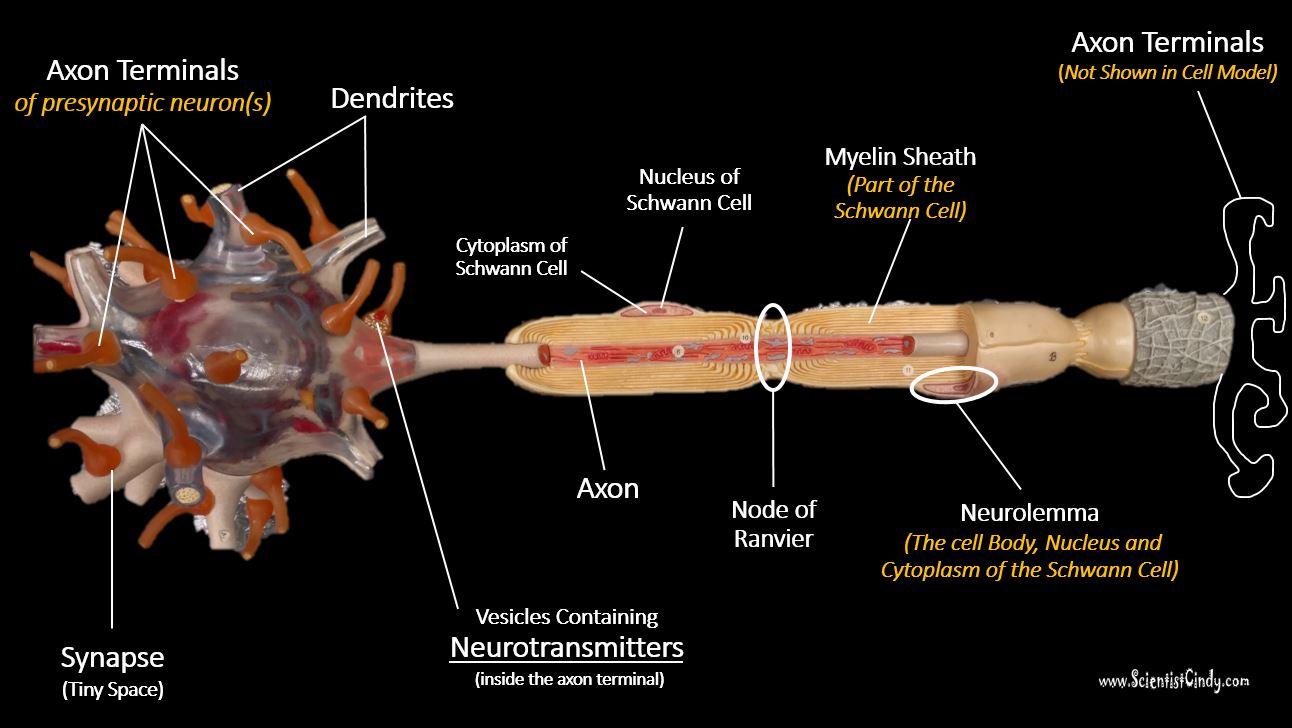
Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). Neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. Neuron Anatomy. Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. From there the message can move to the next neuron. Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.
Nervous Tissue SCIENTIST CINDY
For pictures of this model with answer keys to help you study, visit:http://www.humanbodyhelp.com/brain-and-spinal-cord/http://www.humanbodyhelp.com/neuron-m. Figure 12.8 Parts of a Neuron The major parts of the neuron are labeled on a multipolar neuron from the CNS. Where the axon emerges from the cell body,. Some cutting edge research suggests that certain neurons in the CNS do not conform to the standard model of "one, and only one" axon. Some sources describe a fourth type of neuron. Axon. Definition. long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. Location. Term. Cell Body aka Soma. Definition. is the spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus. The cell body connects to the dendrites, which bring information to the neuron, and. Neuron Models. Click on a photo for a larger view of the model. Click on Label for the labeled model. Back to Nervous System. Neuron. Cell Body & Dendrites. Axon.

Nervous and Spinal Cord Models
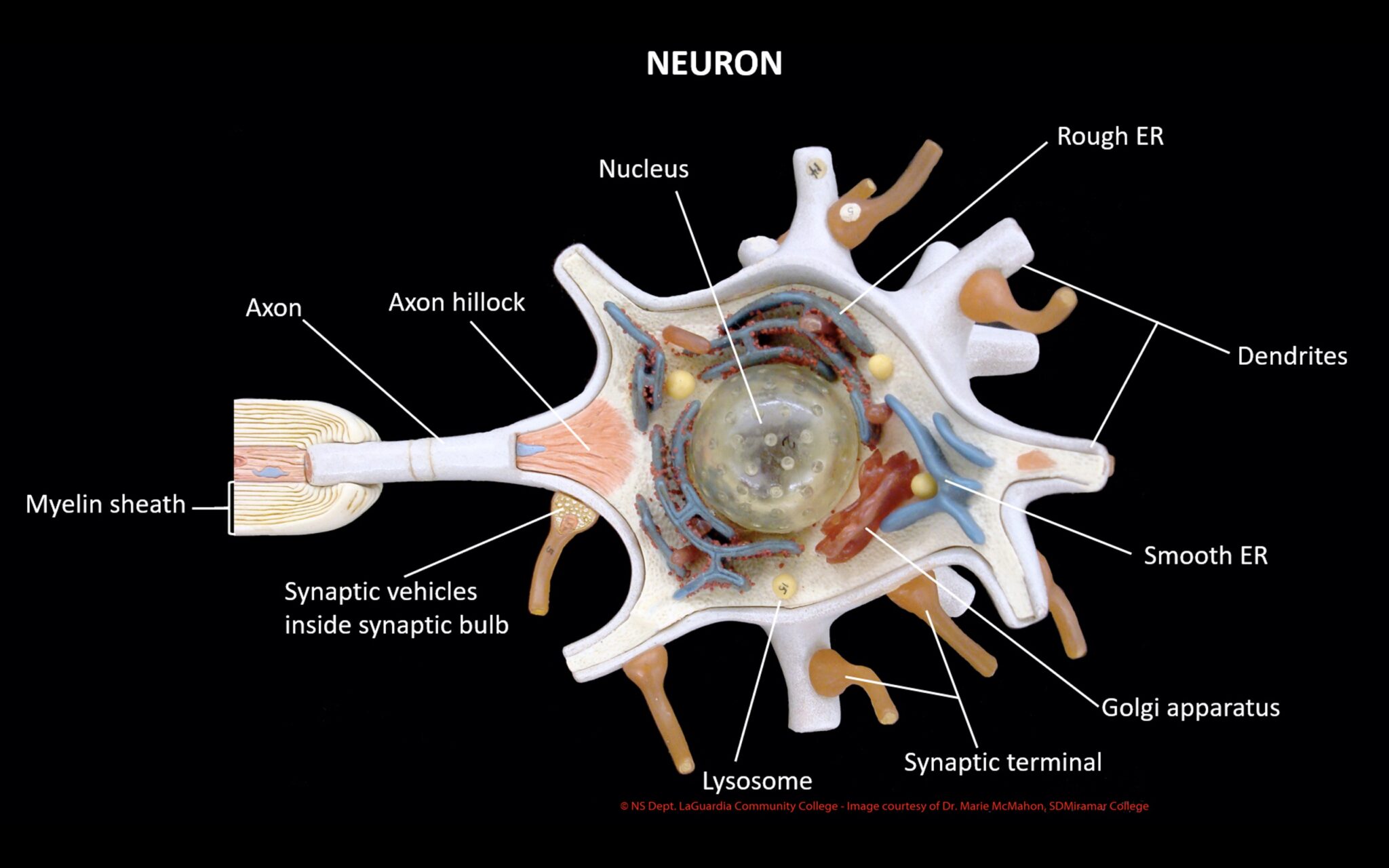
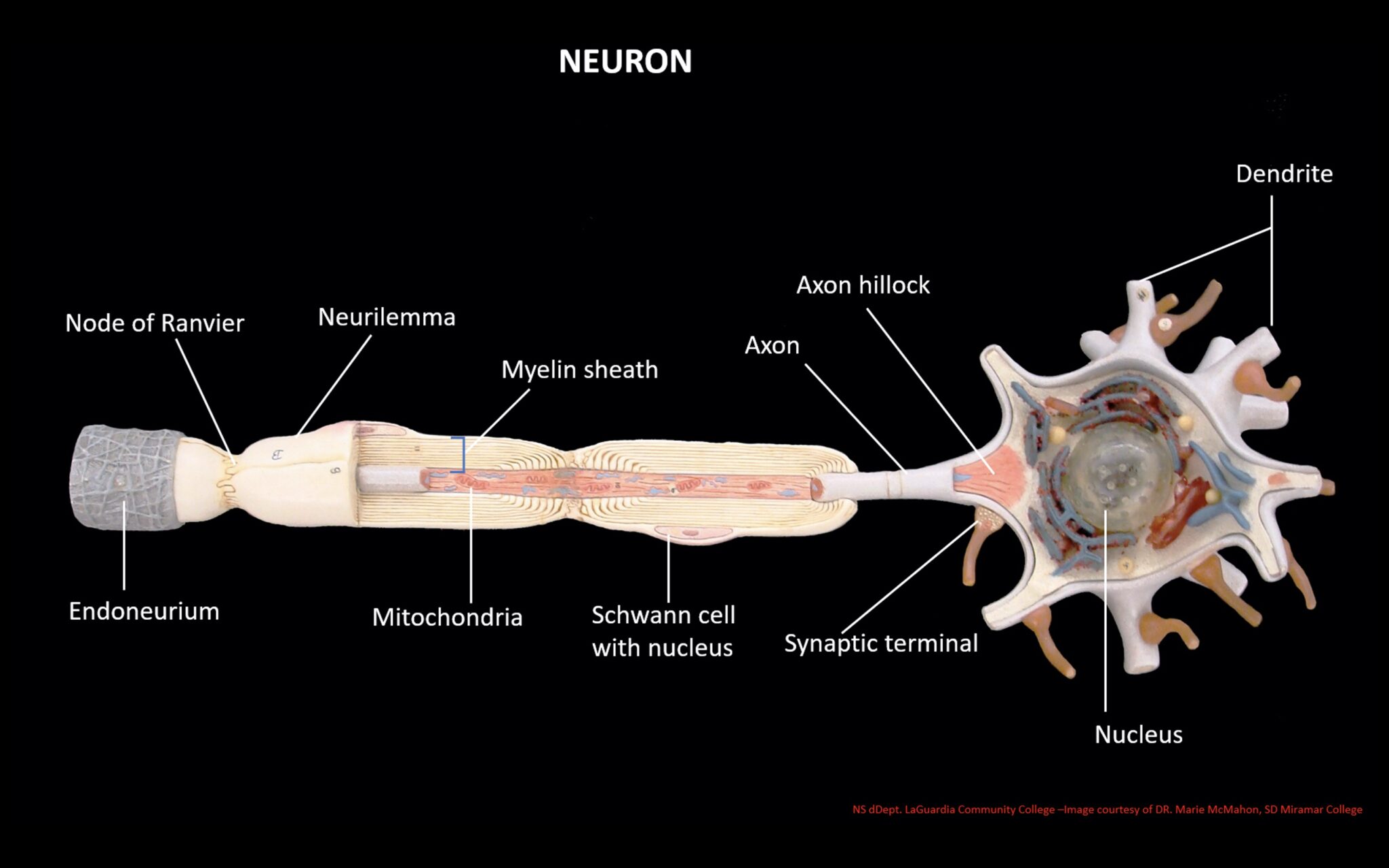
Figure 12.2.2 - Parts of a Multipolar Neuron: The major parts of the neuron are labeled on a multipolar neuron from the CNS. External Website. Visit this site (link not working as of 10/20/2021) to learn about how nervous tissue is composed of neurons and glial cells. Neurons are dynamic cells with the ability to make a vast number of. While they have the common features of a typical cell, they are structurally and functionally unique from other cells in many ways. All neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites , 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. Besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the neuron. 3. How to Draw a Neuron Diagram To learn about the structure of the neurons, the students can use a neuron labeled diagram. The students may follow these steps to make their neuron diagram, but the process is complex: 3.1 How to Draw a Neuron Diagram from Sketch Step 1: First, the students need to draw a circle. Based on it, they need to draw a. At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell. Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers. Other synapses are electrical; in these synapses, ions flow directly between cells. At a chemical synapse, an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters.
SCB209 Lab1 Natural Sciences Open Educational Resources
Diagram Of Neuron. A neuron is a specialized cell, primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. They are found in the brain, spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell. The structure of a neuron varies with their shape and size and it mainly depends upon their. Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. Every neuron consists of a body (soma) and a number of processes (neurites). The nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses ( action potentials) are generated. The processes stem from the body, they connect neurons with.
The cell body of a neuron, also known as the soma, is typically located at the center of the dendritic tree in multipolar neurons.It is spherical or polygonal in shape and relatively small, making up one-tenth of the total cell volume.. The functionality of the neuron is highly dependent on its cell body as it houses the nucleus, which contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell as well as. The labeling focuses on the neuron and supporting neuroglia (or glial) cells. These cells provide provide physical and metabolic support to neurons. Neuroglia cells are different from nerve cells in that they do not participate directly in synaptic interactions. Students can also label a nerve cell and color neuroglia cells using paper handouts.
SCB209 Lab1 Natural Sciences Open Educational Resources
The parts of the neuron have been labeled. Your challenge is to write the correct name for each part and explain what it does. If you need some help, visit the web article listed below. Neuron Anatomy Activity. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep. Choose the correct names for the parts of the neuron. (6) This neuron part receives messages from other neurons. (7) This neuron part sends on messages to other neurons. (8) This neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. (9) This neuron part processes incoming messages. (10) This neuron part contains instructions for making proteins that the.




