The radius and ulna are long bones that make up the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. In the anatomical position, the radius is found in the lateral forearm, while the ulna is found in the medial forearm. The radius and ulna are the two long (and only) bones of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. In the classical anatomical position, the radius is found laterally, while the ulna is the medial of the two bones. These two bones are of great significance for upper extremity function, as they support a whopping 20 muscles in this region.
[DIAGRAM] Elbow Ulna Diagram
Last updated: November 7, 2020 Revisions: 22 format_list_bulleted Contents add The radioulnar joints are two locations in which the radius and ulna articulate in the forearm: Proximal radioulnar joint - located near the elbow. It is articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna. The radius is a long bone in the forearm. It lies laterally and parallel to ulna, the second of the forearm bones. The radius pivots around the ulna to produce movement at the proximal and distal radio-ulnar joints. The radius articulates in four places: The radius and the ulna are long, slightly curved bones that lie parallel from the elbow, where they articulate with the humerus, to the wrist, where they articulate with the carpals. The radius is located laterally, near the thumb, and the ulna medially, near the little finger. The radius and the ulna have a styloid process at the distal end. Revisions: 33 format_list_bulleted Contents add Fig 1.0 - Overview of the anatomical position of the ulna in the upper limb. The ulna is a long bone in the forearm. It lies medially and parallel to the radius, the second of the forearm bones. The ulna acts as the stabilising bone, with the radius pivoting to produce movement.

Lateral Bone Of The Forearm Cheap Offers, Save 44 jlcatj.gob.mx
1 2 Radius The proximal end of radius features a head, a neck, and a prominent tuberosity known as the radial tuberosity. The head of the radius presents two articular facets: The articular circumference on the sides of the head, which serves to articulate with the ulna. The radius is the thicker and shorter of the two long bones in the forearm. It is located on the lateral side of the forearm parallel to the ulna (in anatomical position with arms hanging at the sides of the body, palms facing forward) between the thumb and the elbow. The radius and ulna pivot around one another to allow rotation of the wrist. The ulna is one of the two forearm long bones that, in conjunction with the radius, make up the antebrachium. The bone spans from the elbow to the wrist on the medial side of the forearm when in anatomical position. In comparison to the radius, the ulna is described to be larger and longer. It serves as the origin and/or insertion site for more than a dozen muscles and is involved in motions. Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.orgNinja Nerds!In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will present on the radius and ulna through the use of a.

Ulna Labeled Radius And Ulna, Science Diagrams, Human Organ, Laboratory
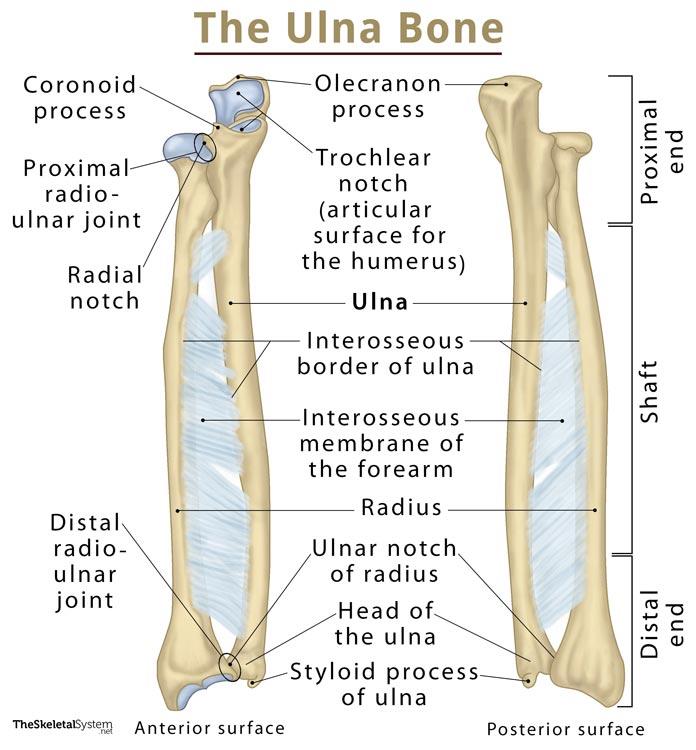
What is the ulna? The ulna is the longer of the two bones in your forearm. It helps you move your arm, wrist and hand. Your ulna also supports lots of important muscles, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels. The ulna is one of two bones that make up the forearm, the other being the radius. It forms the elbow joint with the humerus and also articulates with the radius both proximally and distally. It is located in the medial forearm when the arm is in the anatomical position. It is the larger of the two forearm bones. [1]
Radius and Ulna Anatomy: Forearm Bones In this anatomy lesson, I'm going to cover the anatomy of the two forearm bones, the radius and ulna. These bones are classified as long bones, and they make up part of the appendicular skeleton. ulna, inner of two bones of the forearm when viewed with the palm facing forward. (The other, shorter bone of the forearm is the radius.)The upper end of the ulna presents a large C-shaped notch—the semilunar, or trochlear, notch—which articulates with the trochlea of the humerus (upper arm bone) to form the elbow joint.The projection that forms the upper border of this notch is called the.

Anatomy Of Radius And Ulna Anatomical Charts & Posters
Definition: What is the Ulna. Ulna (plural: ulnae; pronunciation: úl-nu) is one of the two primary bones forming the forearms in humans, the other one being the radius. There is one ulna bone in each arm. It is a long bone [1] and is vital in forming both the wrist and elbow joints [2]. Anatomy Where is the radius located? Your radius is one of two bones in your forearm. The other is your ulna. The radius is opposite your ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of your forearm. Your radius rotates over your ulna when you stretch your arm straight out in front of you with your palms facing down.




