Explore Our Excellent Selection Of Anatomical Spine Models. Shop & Save Today! Our Most Popular Spine Model For Patient & Student Education Is Also Our Most Affordable Looking for Spinal Model? We have almost everything on eBay. But did you check eBay? Check Out Spinal Model on eBay.
Spinal Cord Anatomy Worksheet Single FILLED Digital Download Human
The spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem. It extends from the foramen magnum at the base of the skull to the L1/L2 vertebra where it terminates as the conus medullaris (medullary cone). In these topics. Quick Facts: Injuries of the Spine and Spinal Cord Quick Facts: Overview of Spinal Cord Disorders Injuries of the Spinal Cord and Vertebrae Cervical Spinal Stenosis Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Neck Pain Sciatica Herniated Disk Low Back Pain Overview of Spinal Cord Disorders. Spinal Cord Models. Click on a photo for a larger view of the model. Click on Label for the labeled model. Back to Nervous System. Spinal Cord (transverse section) Spinal Cord (close up) Spinal Cord (longitudinal view) Below is a 3D model of the spinal cord, which is fully interactive. Explore the 3D model using your mouse pad or touchscreen to understand more about the spinal cord. Anatomy The.
BY 411 Advanced Human Anatomy Blog Neuroanatomy Post 3 Development
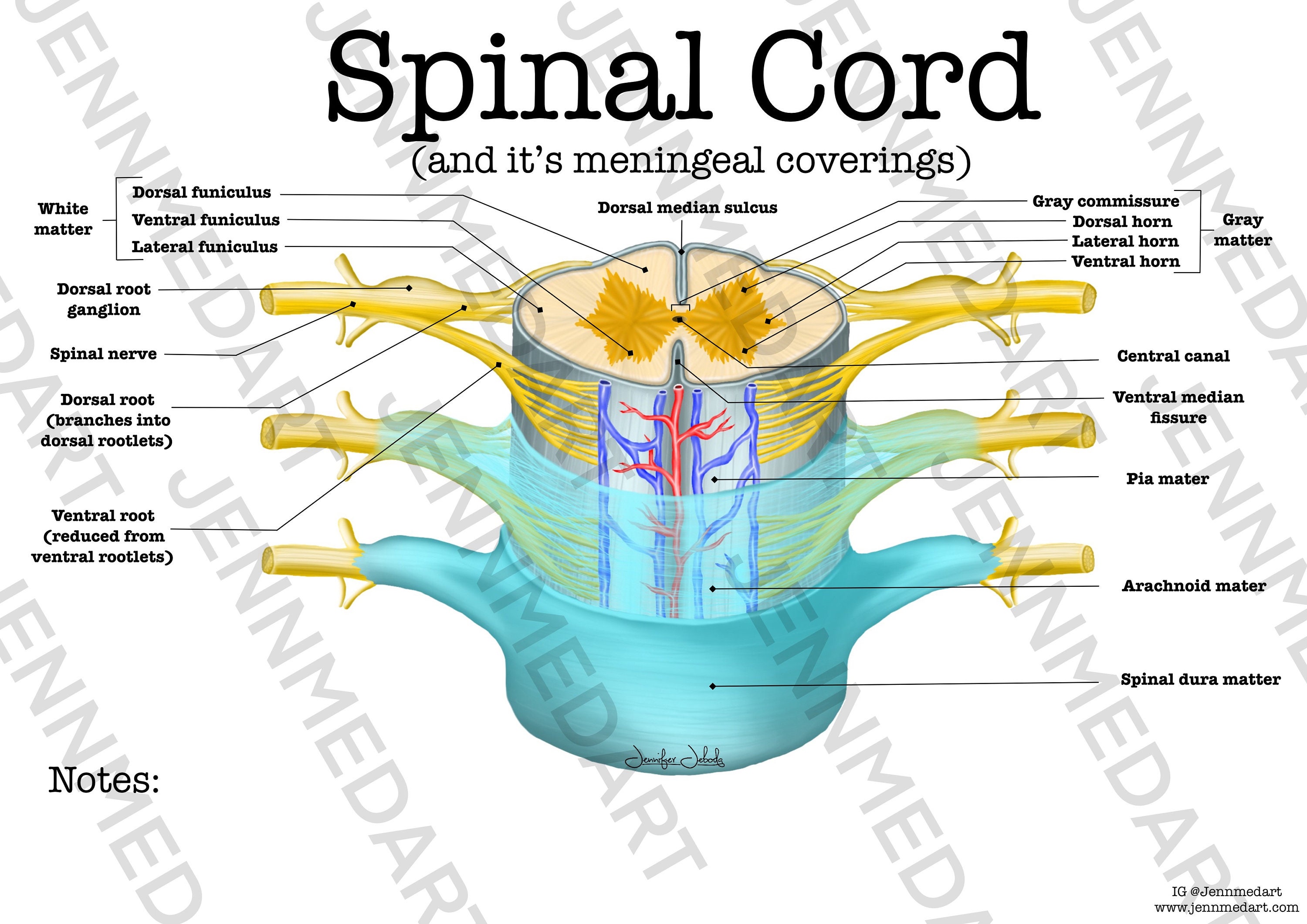
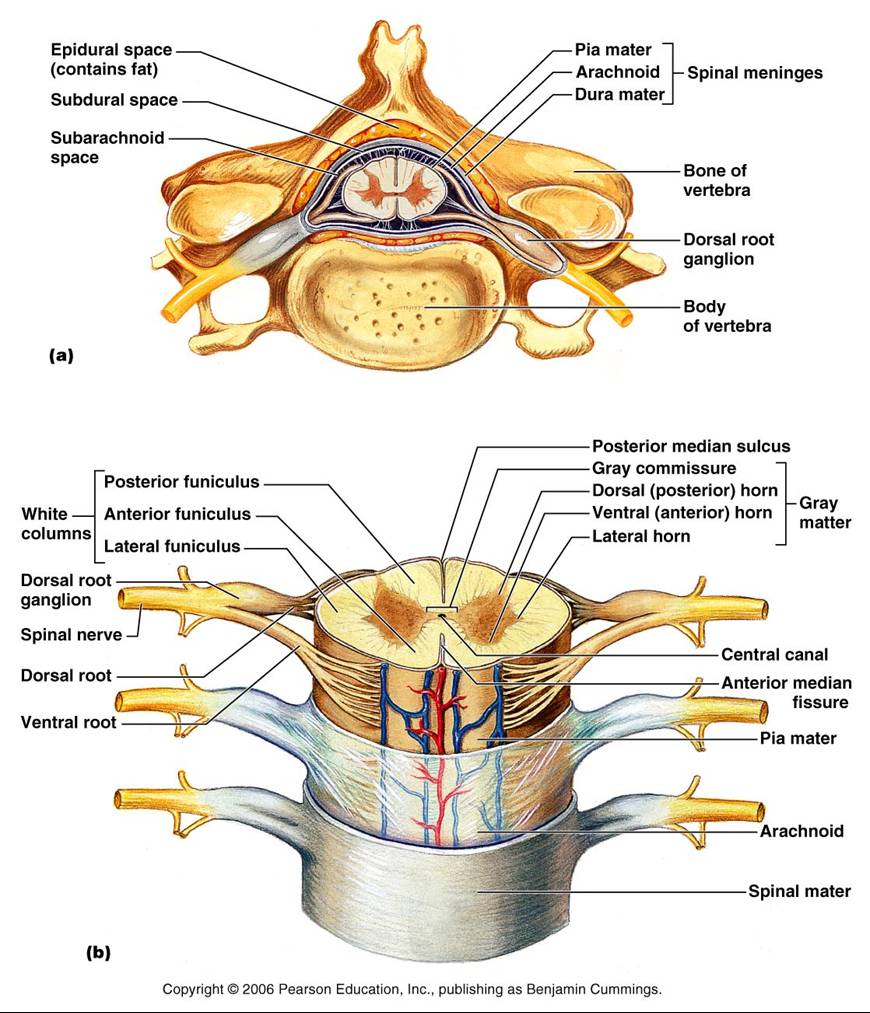
The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system (CNS) along with the brain. It is located within the vertebral canal of the spine. In the cranial direction, the spinal cord is continuous with the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. In the caudal direction, it terminates as the medullary cone (conus medullaris). The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. Overview of spinal cord anatomy The spinal cord is a cylindrical mass of neural tissue extending from the caudal aspect of the medulla oblongata of the brainstem to the level of the first lumbar vertebra (L1).While the length of the spinal cord varies from one individual to another, it is usually longer in males (approximately 45 cm) than it is in females (approximately 42 cm). The spinal cord, along with the brain, makes up the central nervous system (CNS). It is a long tubular structure comprised of nervous tissue, extending from the cervical to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. Just like other parts of the CNS, the spinal cord is comprised of white and gray matter. Spinal cord gray matter is the central.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1900/4wg7EtKVwtWY7wcLa4OtAA_anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_english.jpg)
Ascending tracts of the spinal cord Anatomy Kenhub
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS), which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS, i.e., the dura mater, arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. In most adult mammals it occupies only the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal as the growth of the bones composing the vertebral. The spinal cord is a mass of nervous tissue that extends inferiorly from the brain stem through the vertebral canal of the cervical and thoracic regions, ending around the T12 or L1 vertebra.mycontentbreak It is a long tube about 18 inches (45 cm) in length and around half an inch (1 cm) in diameter at its widest point.
This atlas of human anatomy describes the spinal cord through 18 anatomical diagrams with 270 anatomical structures labeled. It was designed particularly for physiotherapists, osteopaths, rheumatologists, neurosurgeons, orthopedic surgeons and general practitioners, especially for the study and understanding of medullary diseases. The spinal cord is a tubular bundle of nervous tissue and supporting cells that extends from the brainstem to the lumbar vertebrae.Together, the spinal cord and the brain form the central nervous system. In this article, we shall examine the macroscopic anatomy of the spinal cord - its structure, membranous coverings and blood supply.

Central Canal Of Spinal Cord terisl
A combination of a letter and a number is used to identify each section of the spinal cord; the letter corresponds to the vertebral section and the number refers to the number of bones down from the previous section (the smaller numbers are more anterior, larger numbers more posterior). Function What is the purpose of the spinal cord? Your spinal cord's main purpose is to carry nerve signals throughout your body. These nerve messages have three crucial functions. They: Control body movements and functions. Signals from your brain to other body parts control your movements.


:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1900/4wg7EtKVwtWY7wcLa4OtAA_anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_english.jpg)

