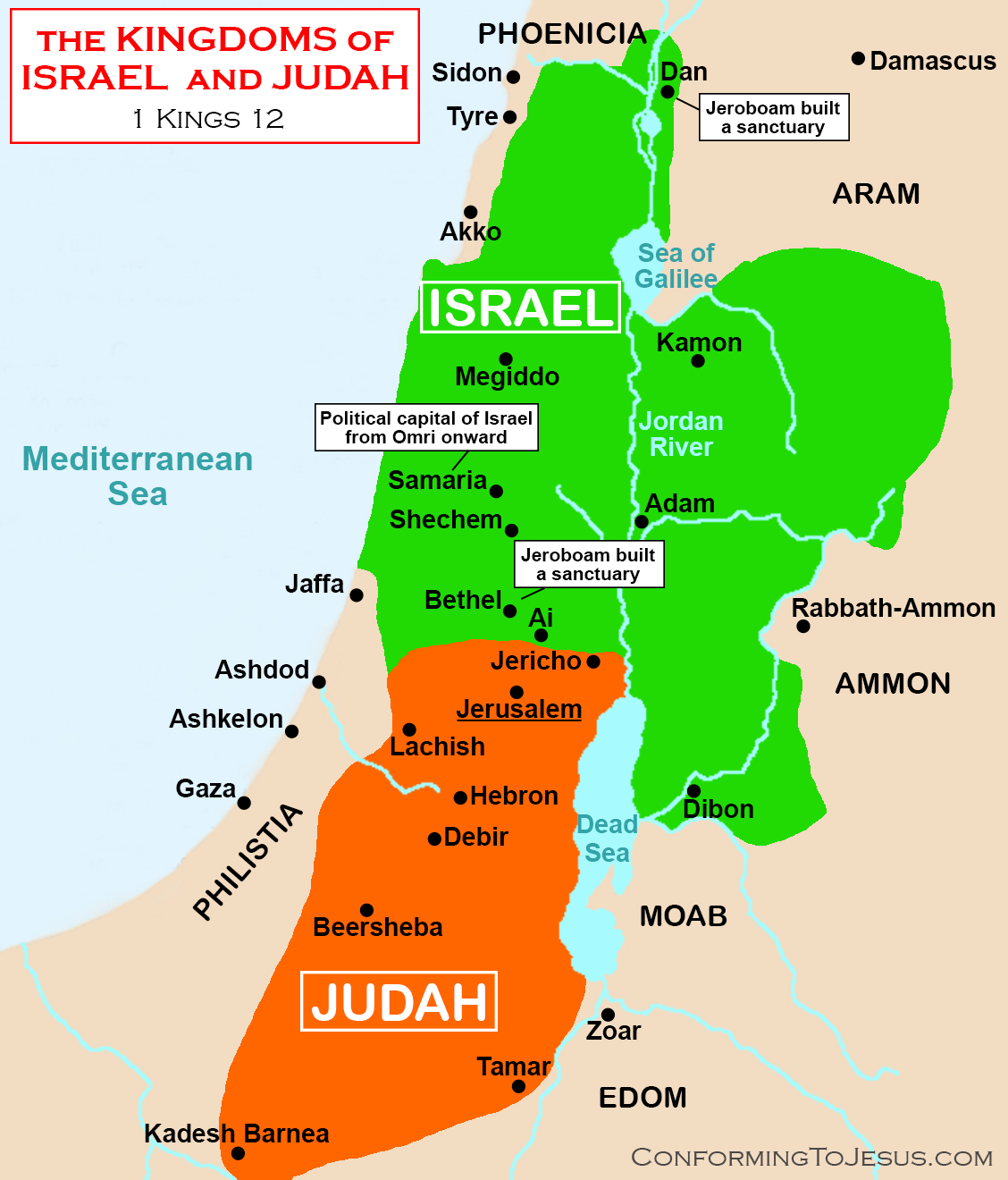
Maps of the Middle East, BCE: Israel and Judah (c. 733 BCE) Maps of the Middle East, BCE: Middle East, BCE Maps: Table of Contents Sources: World History Encyclopedia of Jewish and Israeli history, politics and culture, with biographies, statistics, articles and documents on topics from anti-Semitism to Zionism. History of ancient Israel and Judah Approximate map of the Northern Kingdom of Israel (blue) and the Kingdom of Judah (gold) with their neighbors (tan) during the Iron Age (9th century BCE) Part of a series on the History of Israel Early history Ancient Israel and Judah Second Temple period Late Antiquity and Middle Ages Modern history By topic

1720 Map of The Kingdom of Judah In Africa Black History In The Bible
Approximate map showinhjjjg the Kingdoms of Israel (blue) and Judah (orange), ancient Southern Levant borders and ancient cities. The map shows the region in the 9th century BCE. I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses: Israel was destroyed by the Assyrians in 722 B.C.E., whereas Judah, though severely damaged, narrowly escaped the dreadful onslaught of the Assyrian war machine. But Judah's escape from imperial domination would be brief. Jerusalem eventually fell to the Babylonian Empire and was destroyed in 586 B.C.E. According to the Bible, King David. The Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name "Judah" (written in Assyrian cuneiform as Ya'uda or KUR.ia-ú-da-a-a), [25] while an earlier reference to a Judahite envoy seems to appear in a wine list from Nimrud dated to the 780s BCE. [26] Jerusalem Stepped Stone Structure seen from the Large Stone Structure JUDAH, TERRITORY OF (yehudhah): I. GEOGRAPHICAL DATA 1. The Natural Boundaries 2. The Natural Divisions of Judah (1) The Maritime Plain (2) The Shephelah (3) The Hill Country of Judah II. THE TRIBE OF JUDAH AND ITS TERRITORY III. THE BOUNDARIES OF THE KINGDOM OF JUDAH LITERATURE I. Geographical Data.

Pin on for SBS
Judah, one of the 12 tribes of Israel, descended from Judah, who was the fourth son born to Jacob and his first wife, Leah. It is disputed whether the name Judah was originally that of the tribe or the territory it occupied and which was transposed from which. Old maps of the ancient kingdoms of Judah and Israel (14 F) Media in category "Maps of the Kingdom of Judah" The following 16 files are in this category, out of 16 total. Chorath.jpg 640 × 753; 166 KB Israel i Judà.jpg 350 × 678; 27 KB Izrael i Juda 900 pne.jpg 350 × 678; 160 KB Kingdoms of Israel and Judah map 830-el.svg 720 × 859; 510 KB English: This category is intended for old maps of the divided kingdoms of ancient Israel and Judah, that means in the times after the supposed "United Monarchy" under David and Salomon (for those, see Category:Old maps of the United Monarchy ). History of ancient Israel and Judah. The northern Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah to the south. Israel and Judah were Iron Age kingdoms of the old Near East. The area of time covered in this page is from the first mention of the name Israel in the archaeological record (1200 BCE) to the end of a independent Judean kingdom near the.
The Lost Tribes of Israel The Psalms 83 Conspiracy Black History In
Israel, either of two political units in the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament): the united kingdom of Israel under the kings Saul, David, and Solomon, which lasted from about 1020 to 922 bce; or the northern kingdom of Israel, including the territories of the 10 northern tribes (i.e., all except Judah and part of Benjamin), which was established in 922 bce as the result of a revolt led by Jeroboam I. Coordinates: 31°45′N 35°00′E The Judea and Samaria Area ( Hebrew: אֵזוֹר יְהוּדָה וְשׁוֹמְרוֹן, romanized : Ezor Yehuda VeShomron; [a] Arabic: يهودا والسامرة, romanized : Yahūda wa-s-Sāmara) is an administrative division of Israel.
Judaean desert See all media Category: Geography & Travel Also spelled: Judea, or Judah Hebrew: Yehudaḥ Major Events: Siege of Masada First Jewish Revolt Bar Kokhba Revolt Key People: St. John the Baptist Herod Pontius Pilate Herod Agrippa I Herod Agrippa II Judah Benjamin Related Places: Israel West Bank Caesarea See all related content → Biblical accounts tell that from Ziklag, David raided the towns of the northern Negev, suffered attacks from the Amalekites, and restored great wealth to the people of Judah (1 Samuel 27-30). Ziklag was also the place where David received the news of Saul and Jonathan's demise (2 Samuel 1:17).
Can someone enlighten me about SA's argument, please? Biblical
For hundreds of years, Israel was a unified nation under King Saul, Israel's first king. After his death, however, certain Israelites followed David while others preferred Saul's son, Ishbosheth. The people's divided ideologies split the country in two. Eventually, David became the king of Judah, also known as Judea. The earliest mention of the word "Israel" comes from a stele (an inscription carved on stone) found in Thebes (modern day Luxor) and erected by the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Merneptah, who reigned.




