The Levant (/ l ə ˈ v æ n t / lə-VANT) is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of West Asia.In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in western Asia: i.e. the historical region of Syria. Levant, historical term designating the region along the eastern Mediterranean, roughly corresponding to modern-day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, and adjacent areas. Common use of the term is associated with Venetian and other trading ventures and the establishment of commerce with cities such as Tyre and Sidon.
/Kingdoms_of_the_Levant_Map_830-5aa50e7aeb97de003690e595.png)
The Ancient Levant With Map
The Levant is an imprecisely defined region in the Middle East south of the Taurus Mountains, bounded by the Mediterranean Sea on the west,. View on OpenStreetMap; Latitude of center. 33.82° or 33° 49' 12" north. Longitude of center. 36.3° or 36° 18' east. Population. 44,600,000. Wikidata ID. Maps of the Levant. "Levant" or "The Levant" is a geographic term that refers to the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the nearby islands. Maps of the Levant don't show an absolute boundary, because at no time in the past was it a single political unit. Rough boundaries are generally west of the Zagros mountains, south of the Taurus. The Levant (/ləˈvænt/) is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, it is equivalent to the historical region of Syria, which included present-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine and most of Turkey south-east of the middle. MapMaster, . " Map of the Levant ." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 21 Feb 2021. Web. 05 Jan 2024. This map shows the place of the Levant (highlighted in red) within the eastern Mediterranean.
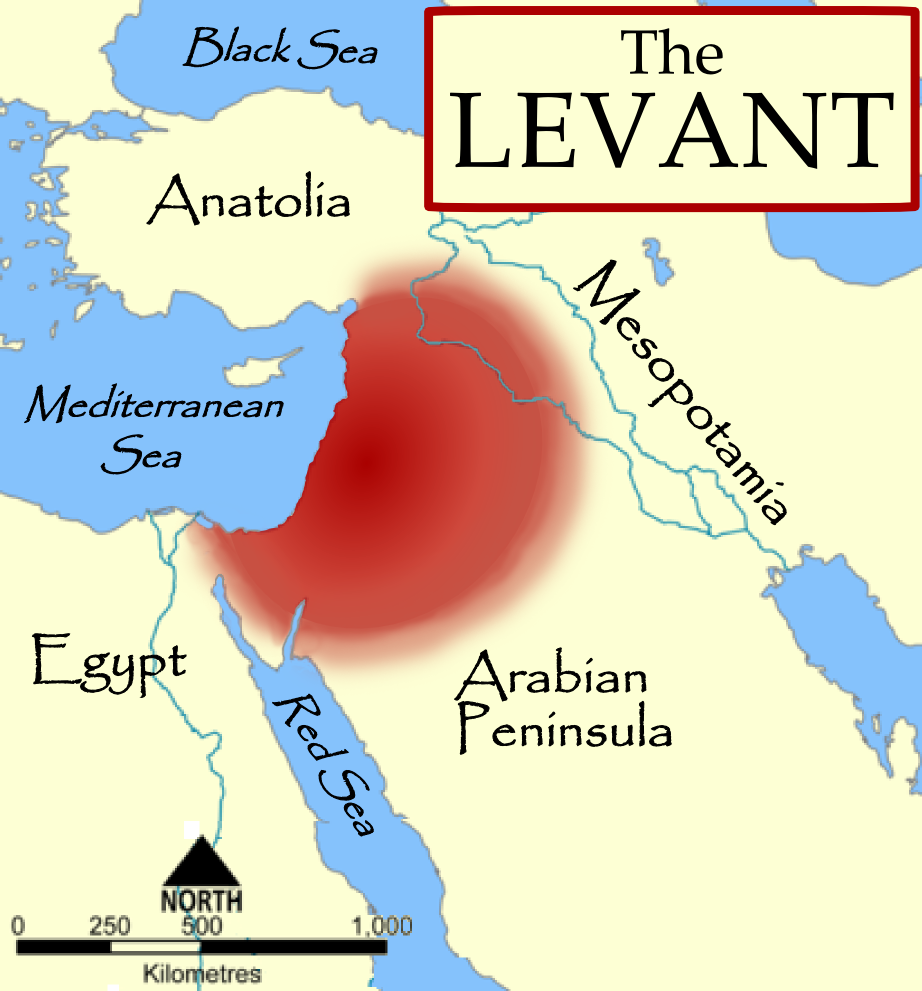
Map of the Levant (Illustration) World History Encyclopedia
Richardprins, . " Map of the Levant circa 830 BCE ." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 26 Apr 2012. Web. 03 Jan 2024. A map of Palestine circa 830 BC, showing the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, as well as the surrounding kingdoms and tribes. The Levant denotes a vast geographical region situated in the Eastern Mediterranean. The area termed as the Levant does not have fixed boundaries and it changes over time. The countries which comprise the Levant are characterized by similar linguistic, cultural, and religious traits. These countries and regions are Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Cyprus. The Levant is the area in Southwest Asia, south of the Taurus Mountains, bounded by the Mediterranean Sea in the west, the Arabian Desert in the south, and Mesopotamia in the east. It stretches roughly 400 mi (640 km) north to south, from the Taurus Mountains to the Sinai desert and Hejaz, and east to west between the Mediterranean Sea and the Khabur river. Levant is the name applied widely to the eastern Mediterranean coastal lands of Asia Minor and Phoenicia (modern-day Turkey, Syria, and Lebanon). In a wider sense, the term can be used to encompass the entire coastline from Greece to Egypt. The Levant is part of the Fertile Crescent and was home to some of the ancient Mediterranean trade.

Levant Map [IMAGE] EurekAlert! Science News Releases
Maps of the Levant region — in the northwest of Arabia. This is a main category requiring frequent diffusion and maybe maintenance. As many pictures and media files as possible should be moved into appropriate subcategories. Subcategories. This category has the following 13 subcategories, out of 13 total.. The Ancient Levant corresponds to the modern states of Syria (western part), Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan. Rooms 57-59 present the material culture of the region from the Neolithic farmers of the eighth millennium BC to the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in 539 BC, within the context.
This page is for a timeline of maps about the Levant, and the History of the Levant. Levant (English) Levant (Dutch) Levant (Dutch) Levant (Dutch) Levant (Dutch) Levant (Dutch) Contents. 1 8500-4000 BC; 2 2000 BC; 3 1350 BC;. Levant in the 1st century AD (English) Miscellaneous [edit] The Southern Levant refers to the lower half of the Levant but there is some variance of geographical definition, with the widest definition including Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, southern Syria and the Sinai Desert. In the field of archaeology, the southern Levant is "the region formerly identified as Syria-Palestine and including Canaan.". Many scholars studying the region's.

Map of the Levant 10971099 Map, Crusade, Ancient maps
The southern Levant refers to an area encompassed by modern Israel, Jordan, and Palestine. Canaan is the ancient name of this region, and a Canaanite culture was prominent until the Iron Age, when the kingdoms of Israel and Judah dominated. Owing to its proximity to the Mediterranean coast to the west, Egypt to the south, and Syria to the north. 34 The Northern Levant (Syria) During the Late Bronze Age: Small Kingdoms between the Supraregional Empires of the International Age
/Kingdoms_of_the_Levant_Map_830-5aa50e7aeb97de003690e595.png)


