Map the Reformation by following the directions below exactly Step 1: Step 2: The first split in Christianity occurred before the Protestant Reformation when the Christians of the Byzantine Empire broke from the Catholic Church and formed the Orthodox Church because the leader of the Orthodox Church refused to recognize the authority of the Pope. The Protestant Reformation was a religious reform movement that swept through Europe in the 1500s. It resulted in the creation of a branch of Christianity called Protestantism, a name used collectively to refer to the many religious groups that separated from the Roman Catholic Church due to differences in doctrine.

The Protestant Reformation AP World History
Part of a series on the Reformation Ninety-five Theses, written by Martin Luther in 1517 Precursors Beginning Contributing factors Theologies of seminal figures Protestant Reformers By location Major political leaders Counter-Reformation Political and religious conflicts Art and literature Music Conclusion and commemorations Protestantism v t e The Protestant Reformation (1517-1648) refers to the widespread religious, cultural, and social upheaval of 16th-century Europe that broke the hold of the medieval Church, allowing for the development of personal interpretations of the Christian message and leading to the development of modern nation-states. Reformation, the religious revolution that took place in the Western church in the 16th century.Its greatest leaders undoubtedly were Martin Luther and John Calvin.Having far-reaching political, economic, and social effects, the Reformation became the basis for the founding of Protestantism, one of the three major branches of Christianity.. The world of the late medieval Roman Catholic Church. Luther sparked the Reformation in 1517 by posting, at least according to tradition, his "95 Theses" on the door of the Castle Church in Wittenberg, Germany - these theses were a list of statements that expressed Luther's concerns about certain Church practices - largely the sale of indulgences, but they were based on Luther's deeper concerns wit.

Which Best Describes Religious Practices in Western Europe
The Protestant Reformation was the 16th-century religious, political, intellectual and cultural upheaval that splintered Catholic Europe, setting in place the structures and beliefs that would. Historical Map of Western and Central Europe - The Progress of the Reformation of 1560. Illustrating. gray - Anglican. yellow - Calvinist. blue - Lutheran and kindred reformers. orange - Waldensians, Bohemian Brethren. pink - Socinians. green - Anabaptists. States which had adopted the Reformation are colored in full. Thirty-eight contributors offer cutting-edge research. This is the most comprehensive handbook of Protestant Reformations ever published to investigate the beliefs, practices, and institutions which followed medieval reform movements and Martin Luther's Reformation in Germany. The Protestant Reformation Today there are many types of Protestant Churches. For example, Baptist is currently the largest denomination in the United States but there are many dozens more. How did this happen? Where did they all begin?

Europe map, Reformation, Map
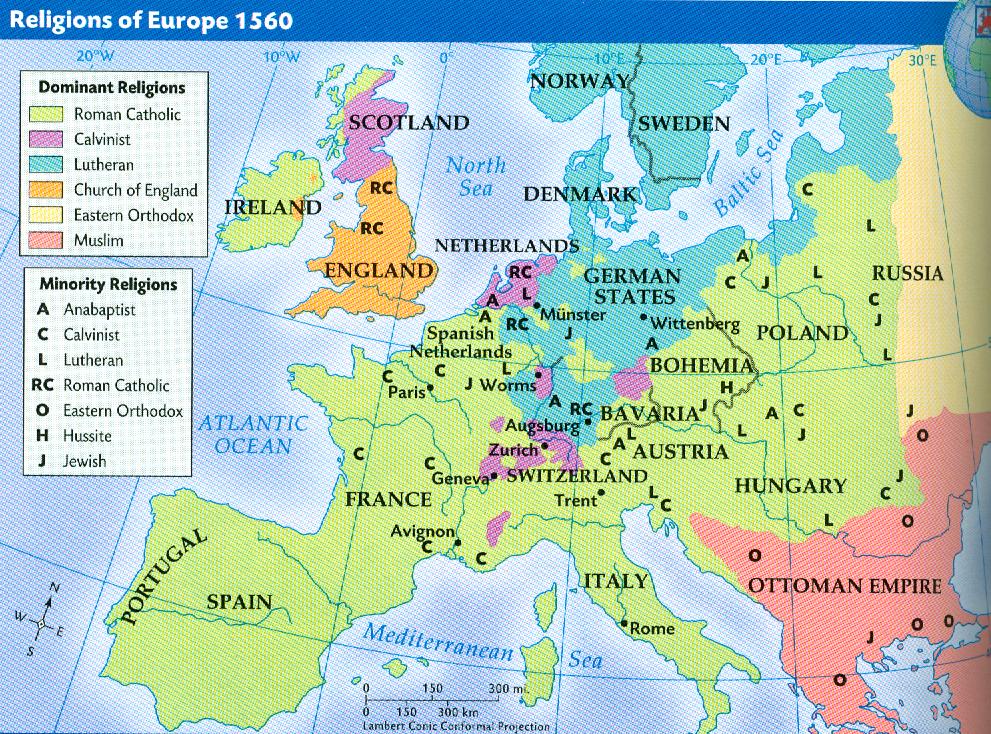
The Reformation thus spread to all aspects of life, and the Christian world found itself in the middle of the most profound upheaval since Roman Catholicism was founded around a.d. 600. The Protestant Reformation had a far-ranging impact on most of the major European countries—Switzerland, Denmark, Sweden, the Netherlands, France, and England. The religious revolution known as the Reformation swept through Europe in the 16th century. By the middle of that century, many people who had been Roman Catholic had converted to a Protestant faith, including Lutheranism, Calvinism, or Church of England. The map shows the predominant religions in Europe in the mid-16th century.
October 31 1517: one of the most influential dates in history. On this day, Martin Luther posted his 95 Theses on the door of a church in Wittenberg, Germany, forever altering history and marking what is considered to be the (official) start of the Protestant Reformation. Over the next century, many people would criticize the Roman Catholic Church, the Church would embark on a campaign to. This chapter analyzes the geography of Protestant Europe. It begins by considering the maps deployed in many studies of the Reformation to depict areas impacted by Protestant ideas. There are significant difficulties in providing any sort of clear visual impression of the dynamic and changing pattern of religious life as Protestants and Catholics contested and shared space in many parts of the.
World History (Romo) Protestantism Map, Science, & WIL 3.2 (12915)
The United States is home to approximately 20% of Protestants. [2] According to a 2019 study, Protestant share of U.S. population dropped to 43%, further ending its status as religion of the majority. Many history textbooks and studies of the Reformation include some sort of map that claims to depict Europe's religious divisions in the sixteenth century. Some of these maps show Catholic as opposed to Protestant states marked out in distinct colours. Other maps distinguish between varieties of Protestantism and show rival colours for.




