The Ring of Fire has been the setting for several of the largest earthquakes in recorded history, including the Chile earthquake of 1960, the Alaska earthquake of 1964, the Chile earthquake of 2010, and the Japan earthquake of 2011 as well as the earthquake that produced the devastating Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004. The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) [note 1] is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes, about 40,000 km (25,000 mi) long [1] and up to about 500 km (310 mi) wide, [2] which surrounds most of the Pacific Ocean.
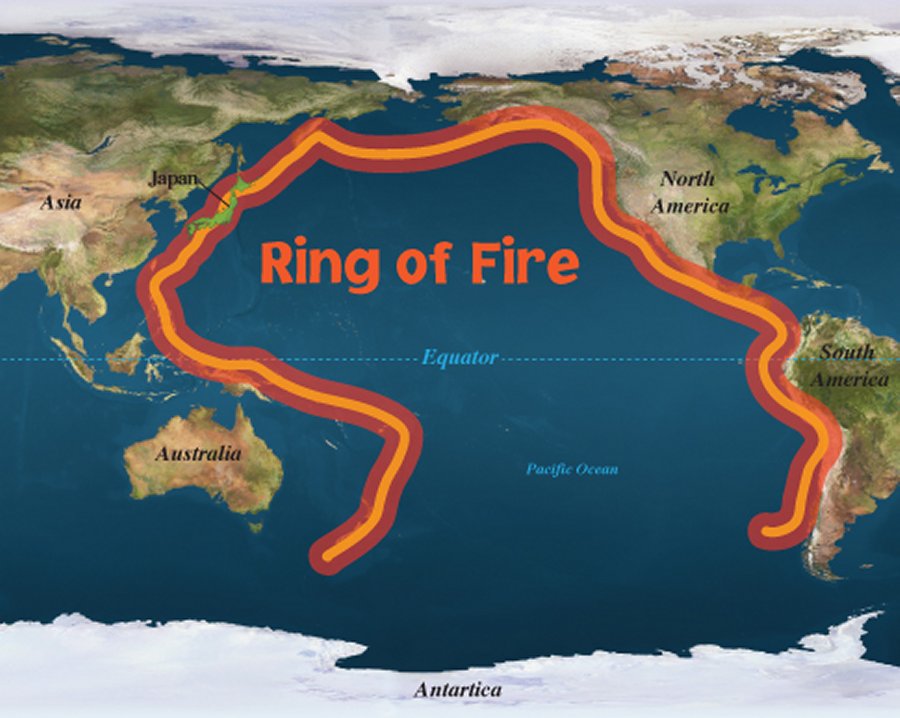
Ring Of Fire Gigantic Zone Of Frequent Earthquakes And Volcanic
This is a map that shows different volcanoes located along the Ring of Fire The map below shows the path of the eclipse, and the approximate local time when the ring of fire will be visible. 40% 30% 20% 10% 60% 50% 70% 80% Percentage of the sun obscured Edmonton. noun molten, or partially melted, rock beneath the Earth's surface. seismic adjective having to do with earthquakes. Maps National Geographic MapMaker: Plate Tectonics The Ring of Fire is a string of volcanoes and sites of seismic activity, or earthquakes, around the edges of the Pacific Ocean. Roughly 90 percent of all earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, and the ring is dotted with 75 percent of all active volcanoes on Earth.

Unfulfilled Expectations Feeling the Earth Move
Detailed Description Volcanic arcs and oceanic trenches partly encircling the Pacific Basin form the so-called Ring of Fire, a zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The trenches are shown in blue-green. The volcanic island arcs, although not labelled, are parallel to, and always landward of, the trenches. The Ring of Fire The Ring of Fire is home to 75% of the world's volcanoes and 90% of its earthquakes. 4:43 Volcanoes 101 About 1,500 active volcanoes can be found around the world. Learn about. Japan is frequently hit by earthquakes because of its location along the "Ring of Fire," an arc of volcanoes and fault lines in the Pacific Basin. Katada warned the situation remains. Japan is frequently hit by earthquakes because of its location along the "Ring of Fire," an arc of volcanoes and fault lines in the Pacific Basin. Katada warned the situation remains precarious.
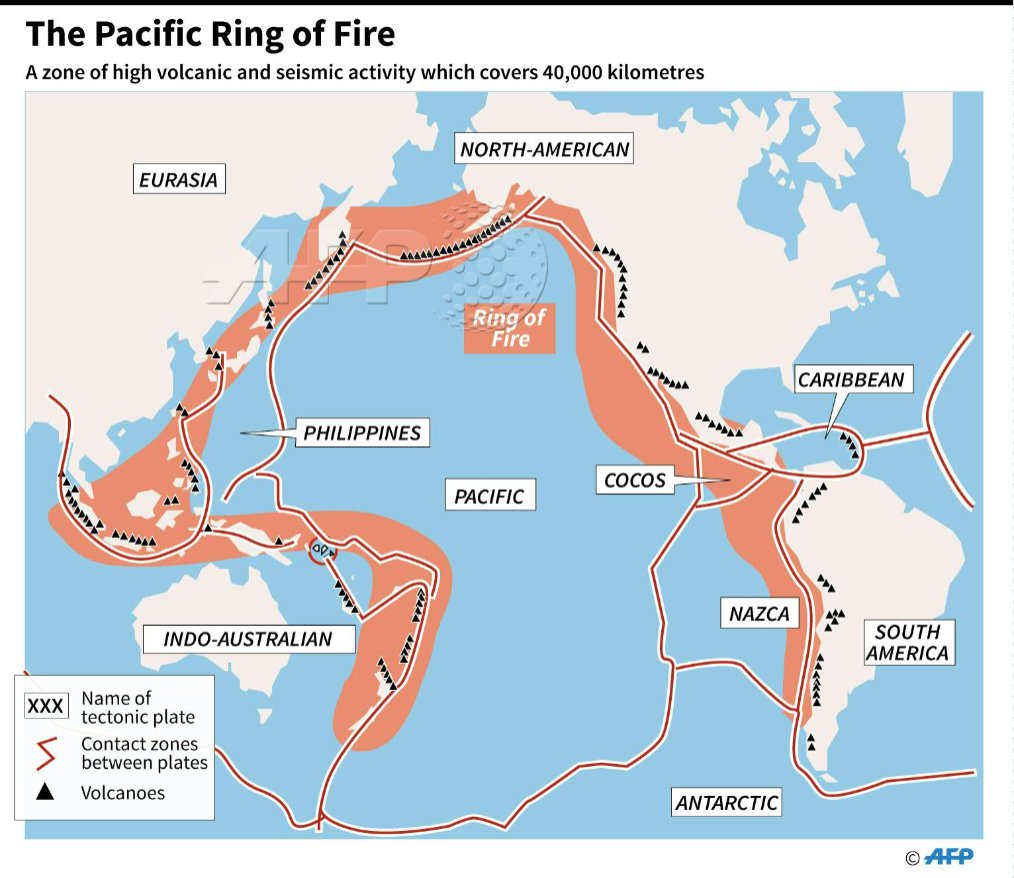
Map showing the the pacific ring of fire, a zone of strong seismic and
Pacific Ring of Fire; Fold Mountains; Population. What is population distribution? What is population density? What factors affect population density? How has world population changed? What causes population change? What is life expectancy? What is the Demographic Transition Model? What are population pyramids? Population change in LEDCs. Case. What is the "Ring of Fire"? Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions do not strike randomly but occur in specific areas, such as along plate boundaries. One such area is the circum-Pacific Ring of Fire, where the Pacific Plate meets many surrounding tectonic plates. The Ring of Fire is the most seismically and volcanically active zone in the world.
Situated on the "Ring of Fire" arc of volcanoes and oceanic trenches that partly encircles the Pacific Basin, Japan accounts for about 20% of the world's earthquakes of magnitude 6 or greater, and. The Pacific Ring of Fire is known variously as Ring of Fire, Circum-Pacific Belt, or Girdle of Fire. It is an underwater region on the edges of the Pacific Ocean where numerous earthquakes and volcanic eruptions take place. The majority of the world's earthquakes and volcanic activities take place around the Ring of Fire.
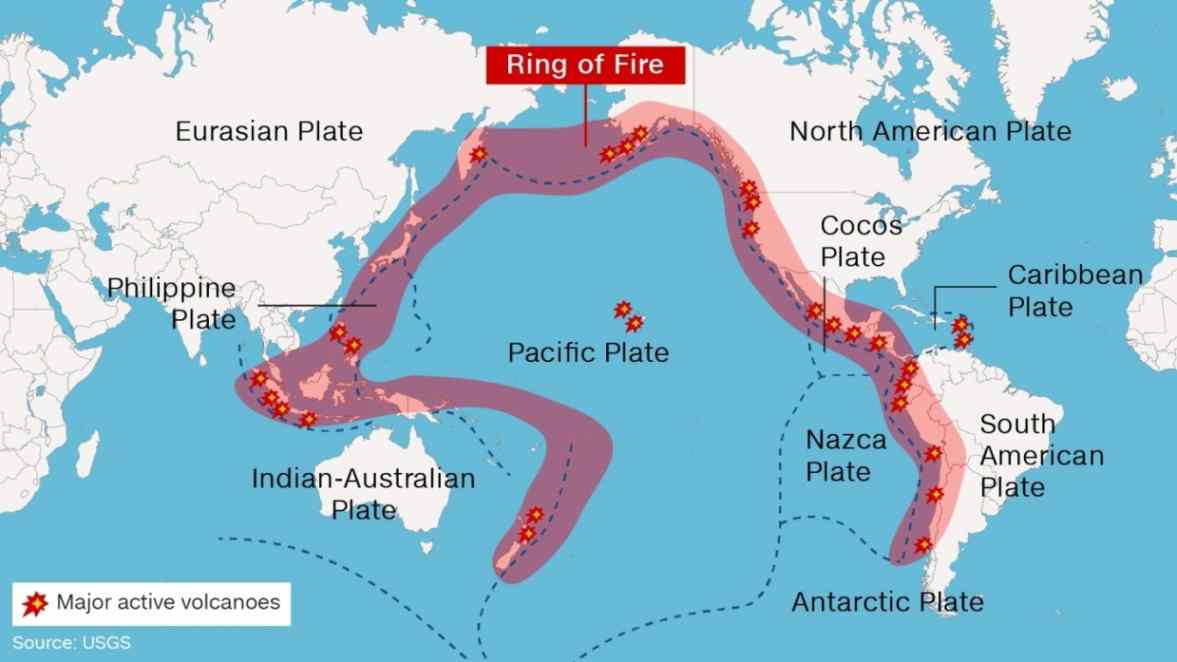
The Ring of Fire
Volcanic arcs and oceanic trenches partly encircling the Pacific Basin form the so-called Ring of Fire, a zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The trenches are shown in blue-green. The volcanic island arcs, although not labelled, are parallel to, and always landward of, the trenches. The Ring of Fire is a semi-circle of volcanoes, oceanic trenches, and mountains that edges the Pacific basin. In the United States, the Cascade Range is part of the Pacific Rim. the rock begins to melt and turns into magma. Many people associate the term "Ring of Fire" with the eponymous Johnny Cash song, recorded in 1963.




