What is a Plant Cell? Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that vary in several fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Both plant and animal cells contain a nucleus along with similar organelles. One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane. Read more: Cells Plant Cell Diagram plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell.
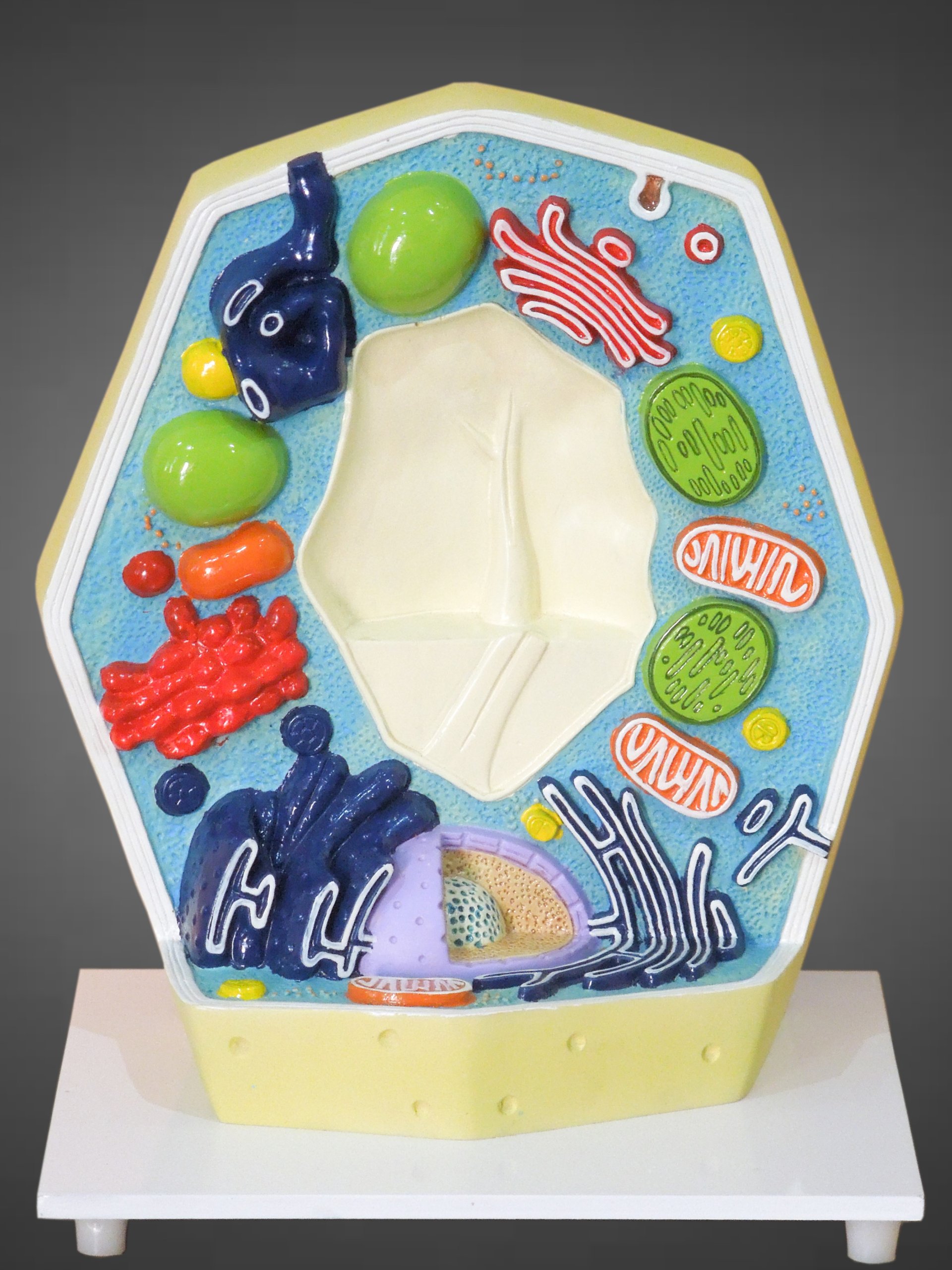

Plant Cell Model Medilab Exports Consortium 3D Model
However, plant cells also have features that animal cells do not have: a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts.. Chloroplasts look like flat discs and are usually 2 to 10 micrometers in diameter and 1 micrometer thick. A model of a chloroplast is shown in Figure below. The chloroplast is enclosed by an inner. Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are eukaryotic cells, which have a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Plant cells have special organelles called chloroplasts, which create sugars via photosynthesis. In this Focus Issue, we go back to the "roots" of the journal, that gave it its name, and turn our attention to the many fascinating facets of plant cell biology. The 11 review papers and 11 original research articles in this issue exemplify the breadth of the field and highlight both established concepts and recent achievements. The researchers capitalized on advances in the field of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (ssNMR) technology to infer refined details about the structural configuration of the cell wall, the intermolecular interactions, and the relative positions of the biopolymers within the wood. The paper is " Atomistic, Macromolecular Model of the.

Plant cell. Biology homework. Plant cell, Plant cell model, Plant
Plant cells assemble a strong yet extensible primary cell wall consisting largely of polysaccharides. Emerging models of wall growth integrate physical properties such as mechanical strength and. The paper is " Atomistic, Macromolecular Model of the Populus Secondary Cell Quantitatively Informed by Solid-State NMR .". The co-authors, all from NREL, are Lintao Bu, Vivek Bharadwaj. Introduction. Model species are essential in plant biology. For example, Barbara McClintock carefully tracked corn (Zea mays) kernel variation to characterize transposable elements and chromosome segregation (McClintock 1941, 1950).The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana (The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative 2000) and foundational mutant and germplasm collections like the Arabidopsis T-DNA Insertional. Phosphorus (P) is an essential element for all living cells. The available chemical form of P sources absorbed by plant roots and assimilated into metabolites is inorganic orthophosphate (Pi) 1.Pi.
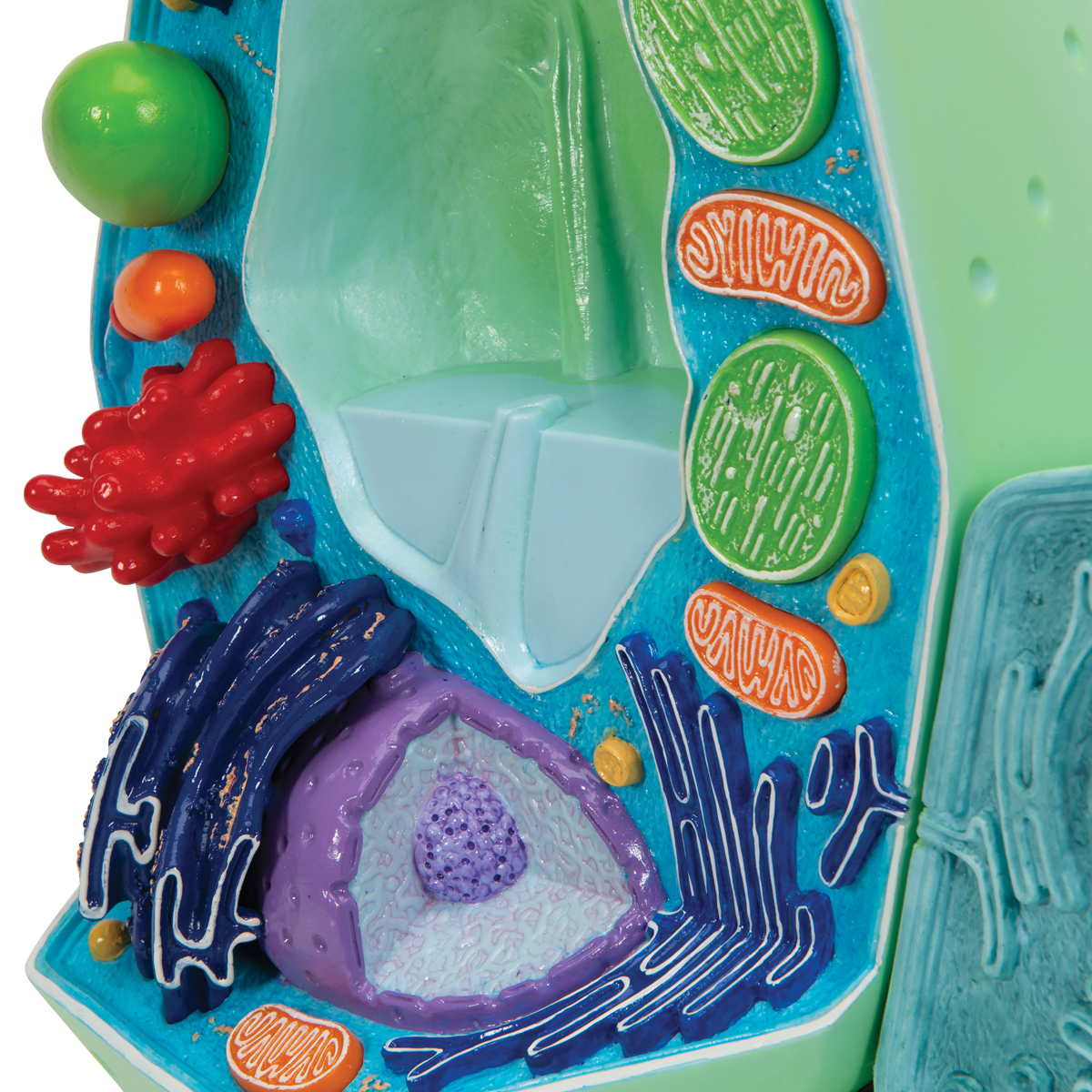
Plant Cell Model Plant Cell Teaching Model Plastic Plant Cell Model
The perfect home for your research . The Plant Cell is a journal of the American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB), a prestigious non-profit founded in 1924 to promote the growth and development of plant biology. With members on six continents, it serves plant biologists around the world through its publications, its conferences, its outreach, and its advocacy. Figure 10.1.5 10.1. 5: A micrograph of a cell nucleus. The nucleolus (A) is a condensed region within the nucleus (B) where ribosomes are synthesized. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (C). Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (D) is composed of many layers of folded membrane.
Features of a plant cell Cell wall - a rigid coating made of cellulose, this gives support to the cell. Vacuole - this is a large space filled with cell sap. Cell sap is a solution of sugar and salts. Chloroplasts - these contain chlorophyll which is needed for photosynthesis. Plant Nutrition Did you know plants make their own food? List of 14 Plant Cell Organelles Plant Cell Wall Structure of plant cell wall The function of the plant cell wall Plant cytoskeleton Structure of the plant cytoskeleton Functions of the plant cytoskeleton Microfilaments Intermediate Filaments Microtubules Other functions of the cytoskeleton in plants include: Plant Cell (Plasma) membrane
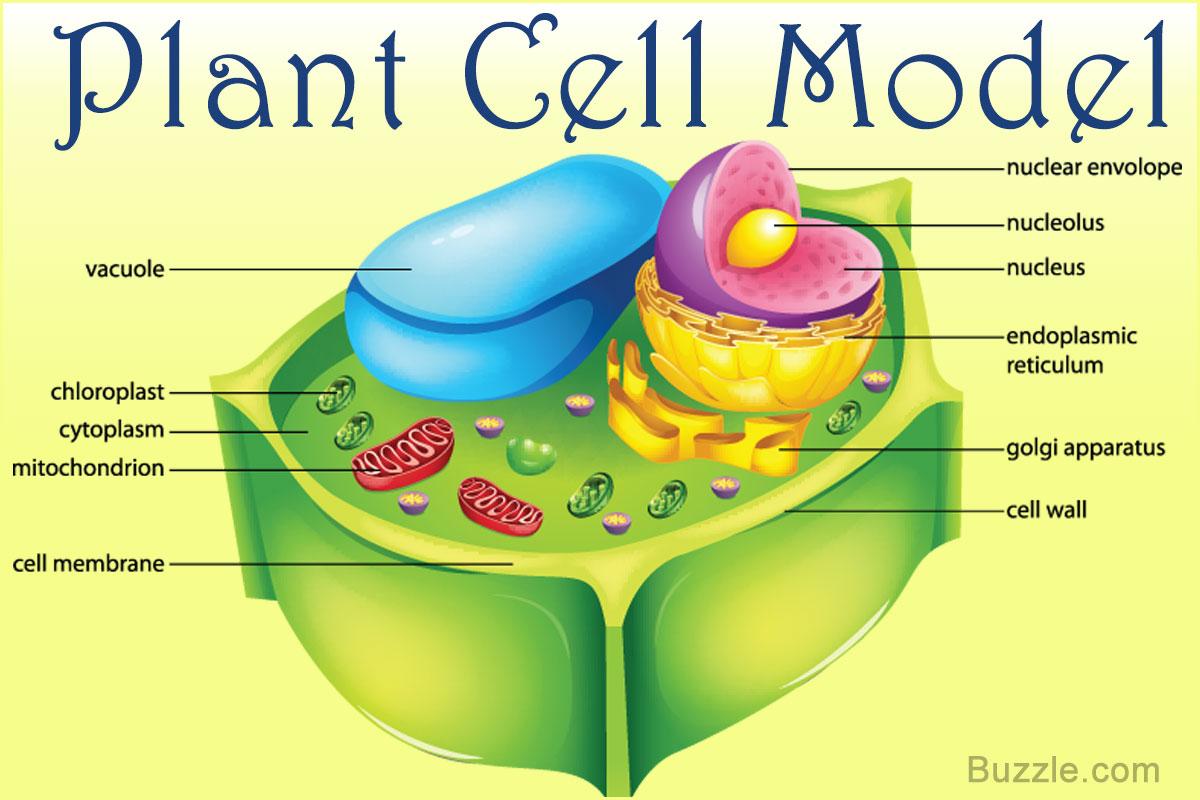
Incredibly Creative Tips on How to Make a Plant Cell Model Biology Wise
A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Plant Cell Characteristics Plant cells are eukaryotic. A model of a typical plant cell is found to be rectangular in shape, ranging in size from 10 to 100 µm. Under the microscope, it shows many different parts.. Cell Wall. It is the outermost, protective layer of a plant cell having a thickness of 20-80 nm. Cell walls are made up of carbohydrates such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.




