Medicinal Parts of Mushrooms; Labeled Mushroom Anatomy Diagrams.. The label of the product should make it clear that it is made using only the mushroom. Ideally, the label will also indicate the percentage of beta-glucans. Real Mushrooms use only mushrooms in our powder extracts. Our product labels show exactly what ingredients we include. A mushroom spore is like a seed in that it contains all the genetic material required to grow new mushrooms. At the end of the mushroom growth cycle, mushrooms release their spores. Wind, water, animals or humans then disperse them. The spores need to land in a warm, moist, shaded area to germinate.
Paul Stamets Psilocybin Mushrooms Of The World All Mushroom Info
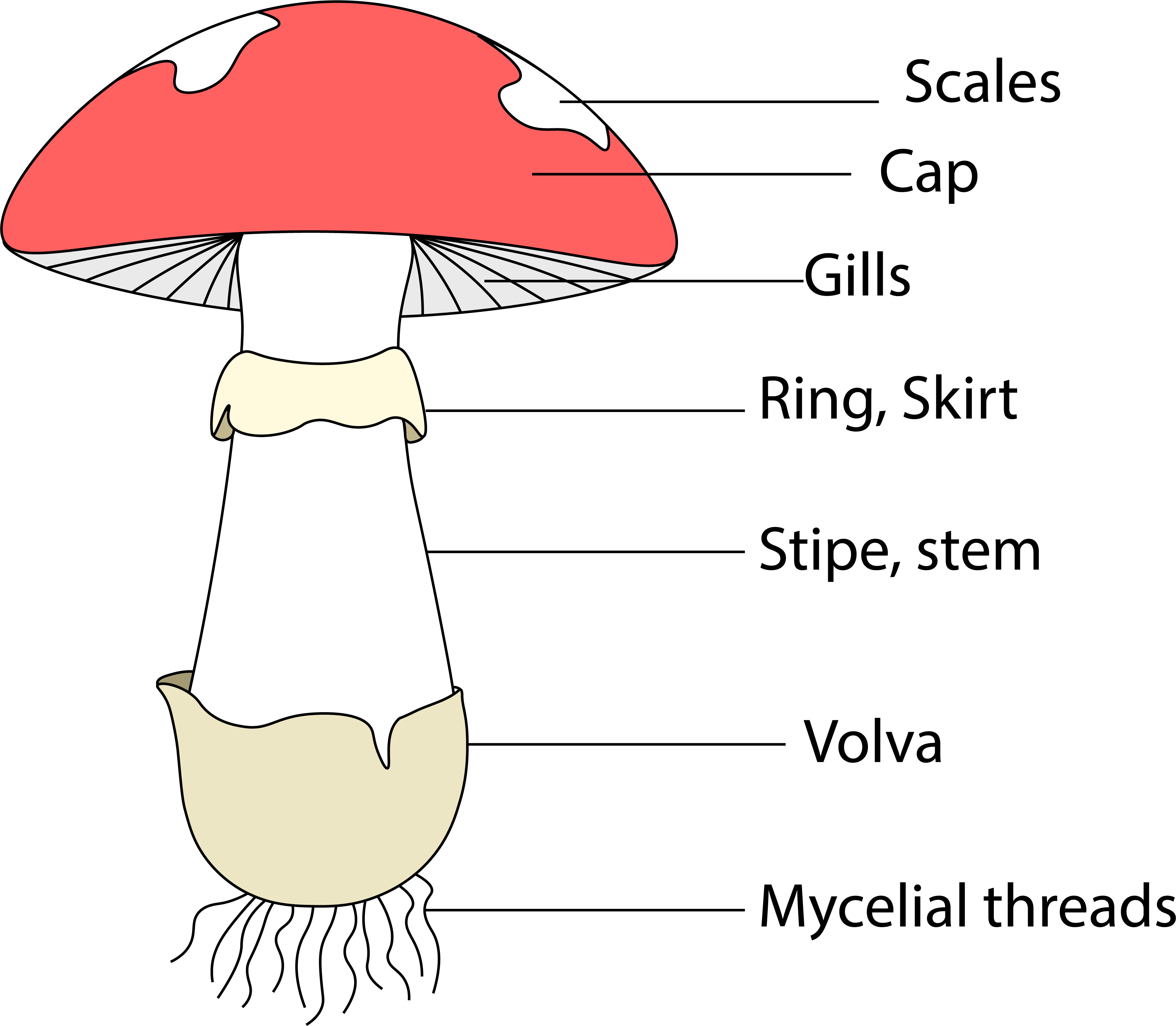
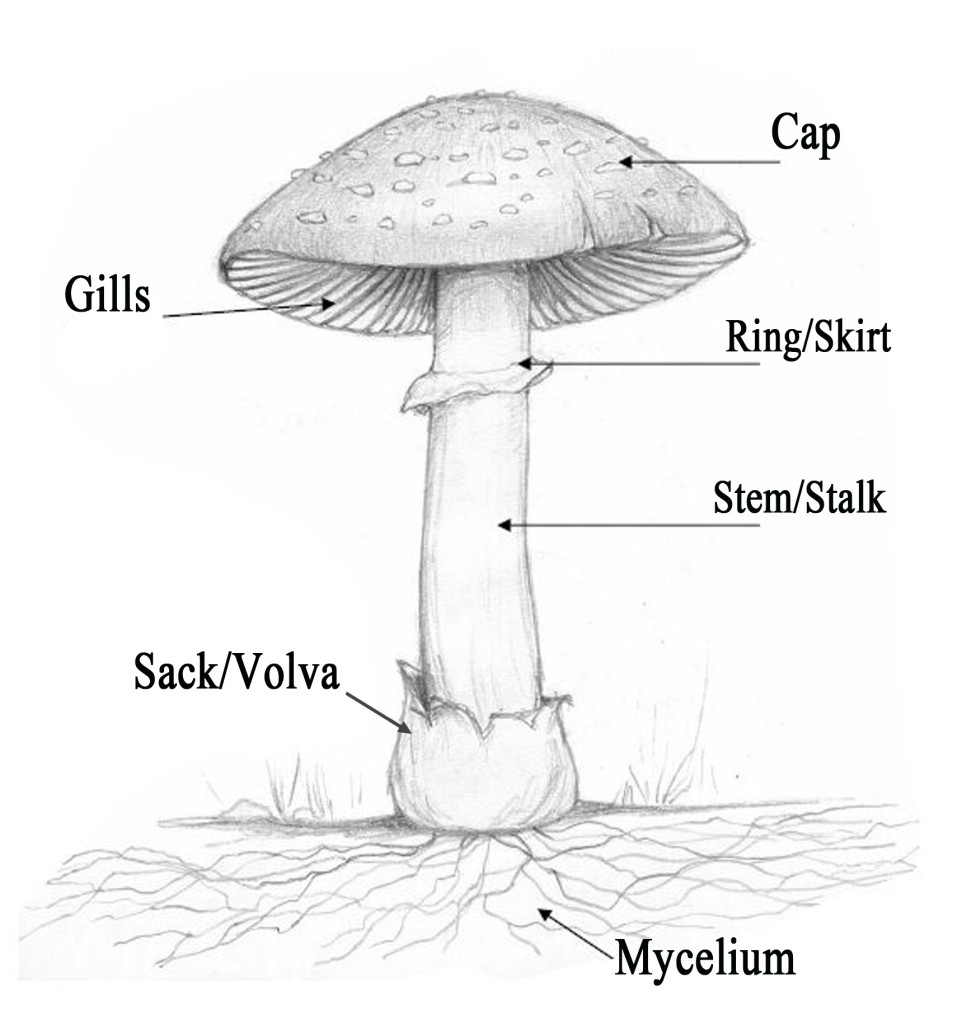
Typically, a mushroom has six different parts. These include: Cap: This is the part that gives the fungi its umbrella shape. The cap comes in a variety of colors, including white, brown, and yellow. In the same way that umbrellas protect us from the heat of the sun, rain, and other harsh weather conditions, the mushroom cap protects the pores. Veils and Remnants. The structures known as veils complicate identification in a number of species, since they change radically as the mushroom grows. Not all mushrooms have these structures, but many have one or both veils. The universal veil completely encases the mushroom when it first appears, rather like the shell of an egg. The basic mushroom anatomy. Anatomy of a Mushroom. A mushroom is made up of eight common parts. From the top to the bottom, they are the cap, gills or teeth, spores, a ring or skirt, the stem or stalk, the volva, the basal bulb, and mycelium. These organic matter parts are categorized into two parts of the mushroom: the fruiting body and mycelium. Answers. EnchantedLearning.com. Label the Mushroom Anatomy Diagram. Plants. Read the definitions below, then label the mushroom diagram. This is a thumbnail of the Label the Mushroom Anatomy Diagram. The full-size printout is available only to site members. To subscribe to Enchanted Learning, click here. If you are already a site member, click.

Parts of a mushroom — Science Learning Hub
The top portion of the fruiting body of a mushroom, which provides a protective covering. 2. Gills. The gills are located on the underside of the cap. The spores are released from the gills. 3. Stipe. The stipe is the main supportive stalk of the fruiting body of the mushroom. 4. Conclusion. Mushroom anatomy consists of the fruiting body—the mushroom spores, stem, cap, ring, and gills - and although they are mycelium and mushrooms are fungal, the mycelium is not part of the mushroom anatomy, it's only part of the life cycle of some mushrooms. Many mushrooms including adaptogenic mushrooms, are safe to eat and provide. Mushroom, the conspicuous umbrella-shaped fruiting body (sporophore) of certain fungi, typically of the order Agaricales in the phylum Basidiomycota but also of some other groups. Popularly, the term mushroom is used to identify the edible sporophores; the term toadstool is often reserved for inedible sporophores. The anatomy of a mushroom explained. Mushrooms have been consumed as a medicine and longevity foods since ancient times. From the Greek physician Hippocrates (the Father of Modern Medicine), who recorded mushrooms as potent anti-inflammatory foods, to the ancient Chinese texts dating back 5000-year-old that noted the use of mushrooms for longevity, wellbeing and spiritual growth.

What Makes a Fungus a Fungus? Jake's Nature Blog
See the below image for the Mushroom anatomy with labels diagram. Morphology refers to the form and structure of a fungal fruiting body. Understanding the various characteristics and anatomy of a mushroom will aid in accurate identification. The pileus exhibits numerous attributes that aid in identification. Here of some of the unique features to observe: Here are some guidelines for when you're creating a video for verification: The video should be less than 15 seconds long. The video should clearly show the faces of both the DIYer and their parent. Both the parent and DIYer must be heard saying "I am here to use DIY".
Fungi thrive in environments that are moist and slightly acidic; they can grow with or without light. Figure 24.1B. 1 24.1 B. 1: Division of hyphae into separate cells: Fungal hyphae may be (a) septated or (b) coenocytic (coeno- = "common"; -cytic = "cell") with many nuclei present in a single hypha. Mushroom Morphology. Mushroom morphology refers to the study of the form and structure of mushrooms. This intricate science offers a window into the anatomy and reproductive processes of fungi, showcasing the complex and diverse nature of these organisms. Understanding the morphology of a mushroom is pivotal for various reasons.
Mushroom Identification Basics Yellow Elanor
Suillus grevillei: The Ultimate Mushroom Guide. Royoporus badius: The Ultimate Mushroom Guide. Paxillus involutus: The Ultimate Mushroom Guide. Ganoderma applanatum: The Ultimate Mushroom Guide. Clavulina cinerea: The Ultimate Mushroom Guide. Massive Mushroom Library: Explore detailed descriptions and identification aided by real mushroom photos. Find Mushroom Diagram stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, 3D objects, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures added every day.. Mushroom anatomy labeled biology diagram vector illustration. Forest nature exploring and education. Spore bearing fruiting.




