The total potential energy of the system decreases for the exothermic reaction as the system releases energy to the surroundings. Figure 18.4.1 18.4. 1: A potential energy diagram shows the total potential energy of a reacting system as the reaction proceeds. (A) In an endothermic reaction, the energy of the products is greater than the energy. The mechanical energy of the object is conserved, E= K+ U, E = K + U, and the potential energy, with respect to zero at ground level, is U (y) = mgy, U ( y) = m g y, which is a straight line through the origin with slope mg m g. In the graph shown in Figure, the x -axis is the height above the ground y and the y -axis is the object's energy.
Potential Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
This is like a one-dimensional system, whose mechanical energy E is a constant and whose potential energy, with respect to zero energy at zero displacement from the spring's unstretched length, x = 0, is U (x) = 12 1 2 kx 2. Figure 8.5.2 8.5. 2: (a) A glider between springs on an air track is an example of a horizontal mass-spring system. 5.1K 419K views 7 years ago This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the forward and. Key points: Potential energy is energy that has the potential to become another form of energy. An object's potential energy depends on its physical properties and position in a system. Potential energy comes in many forms, such as: Gravitational potential energy due to an object's mass and position in a gravitational field. The total potential energy of the system decreases for the exothermic reaction as the system releases energy to the surroundings. Figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1: A potential energy diagram shows the total potential energy of a reacting system as the reaction proceeds. (A) In an endothermic reaction, the energy of the products is greater than the energy.

Lesson Video Elastic Potential Energy Nagwa
The Potential Energy Surface Captures the idea that each structure— that is, geometry—has associated with it a unique energy Since geometry changes are smooth, this idea creates a smooth energy "landscape" Chemistry becomes topology. Simplest Example is One-dimensional Standard Diatomic Bond Stretch rAB Dimensionality of the Generic PES Potential energy is energy stored in a system of forcefully interacting physical entities. he SI unit for measuring work and energy is the joule (J). The term potential energy was introduced by the 19th century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine. The potential energy surface for bond rotation is an example of a relaxed surface scan. The reaction coordinate is the dihedral angle between groups on the two atoms, which can be easily observed in a Newman projection. Potential energy surfaces for bond rotation are commonly used for conformational analysis of molecules like ethane and butane. Figure 5.5.1 5.5. 1: A potential energy diagram shows the total potential energy of a reacting system as the reaction proceeds. (A) In an endothermic reaction, the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants and ΔH Δ H is positive. (B) In an exothermic reaction, the energy of the products is lower than the energy of the.

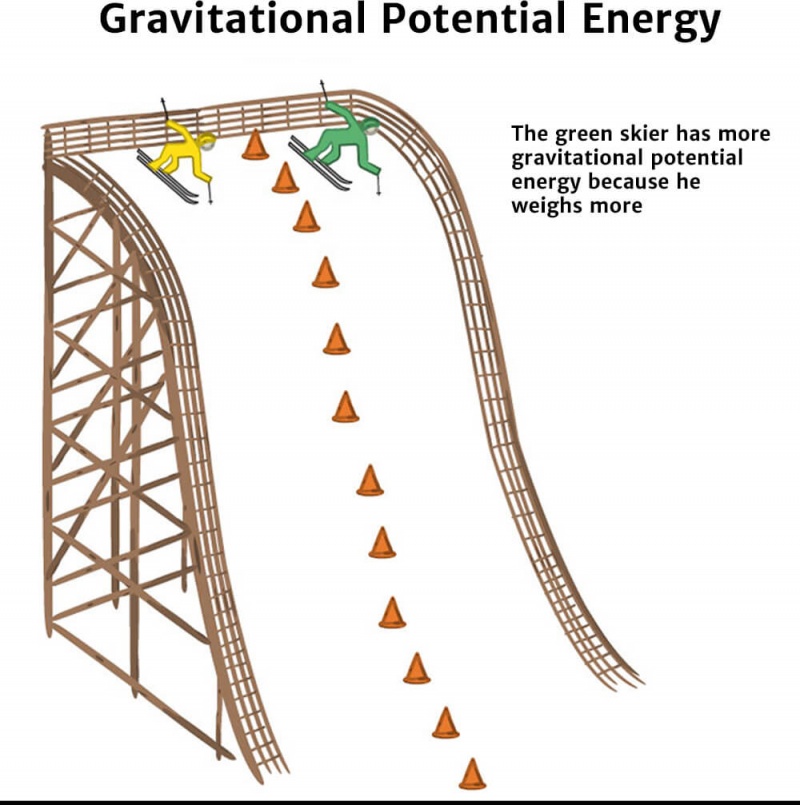
Gravitational Potential and Energy GCSE Physics Doodle
The Potential Energy Surface represents the concepts that each geometry (both external and internal) of the atoms of the molecules in a chemical reaction is associated with it a unique potential energy. This creates a smooth energy "landscape" and chemistry can be viewed from a topology perspective (of particles evolving over "valleys""and. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into endothermic and exothermic reactions as well as the corresponding potential energy diagrams..
e. In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors. [1] [2] The term potential energy was introduced by the 19th-century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine, [3] [4] [5] although it has links to the ancient. A potential energy diagram plots the change in potential energy that occurs during a chemical reaction. This first video takes you through all the basic parts of the PE diagram. Potential Energy Diagram Basics (PE Diagrams) Watch on
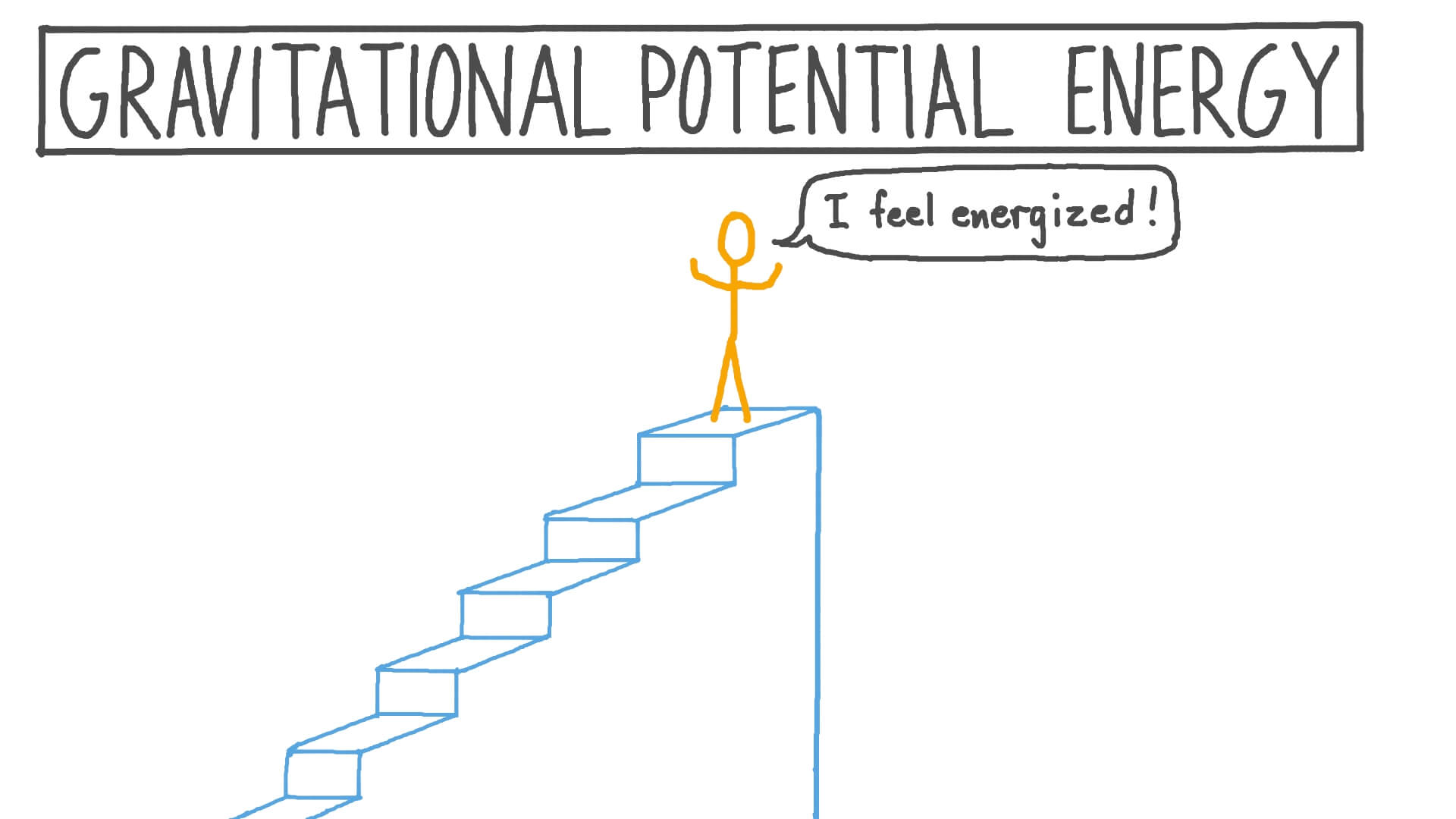
Find The Equation Of Potential Energy In A Gravitational Field
Draw a Potential Energy Curve for this Reaction (Given Mechanism) including activation energies of forward and reverse reactions, enthalpy change (delta H),. Elastic Force. We take precisely the same steps to draw the energy diagram for a mass on a spring, but there are some differences, such as two forbidden regions and a different slope for every position, and there is one additional feature for this potential that doesn't exist for the case of gravity: an equilibrium point.. Figure 3.7.3 - Energy Diagram for Object Influenced by Elastic Force




