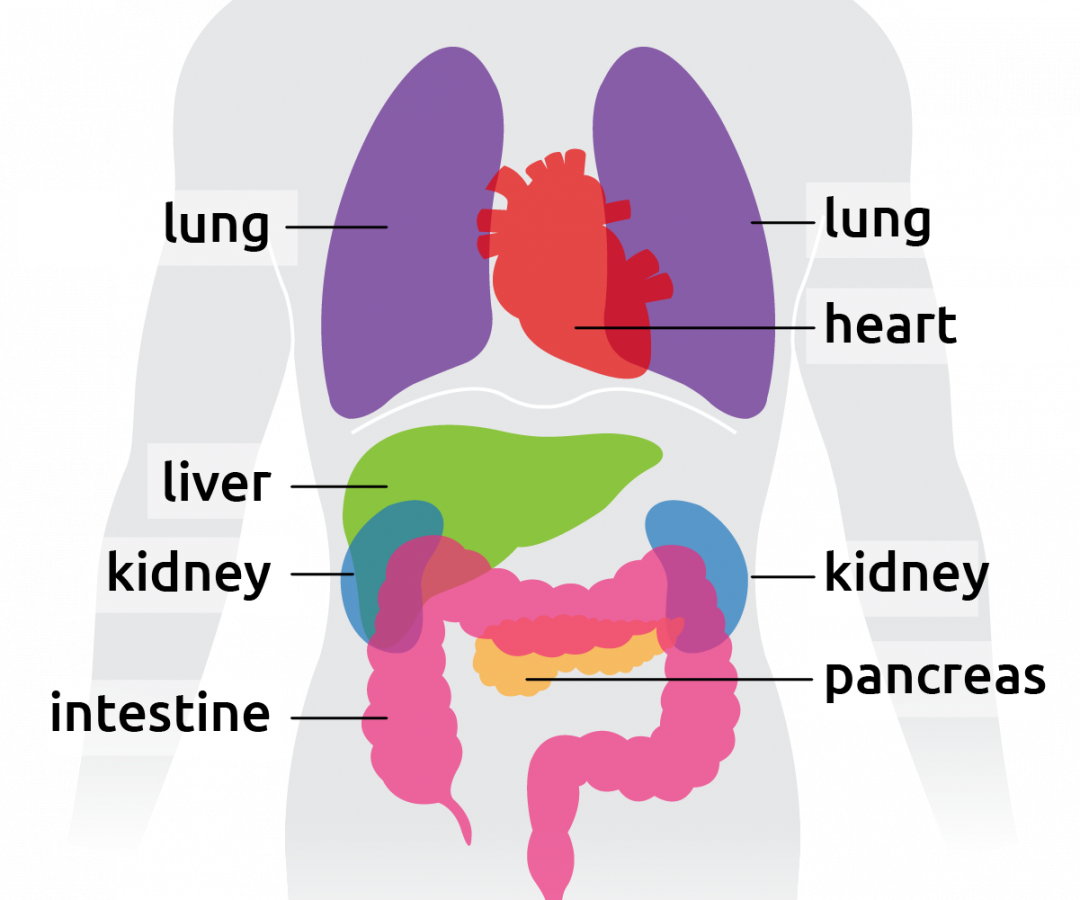
The five vital organs in the human body are the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver. Other organs include the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach. Organ systems, such as the nervous. BBC - Science & Nature - Human Body and Mind - Anatomy - Organs anatomy You are here: BBC Science > Human Body & Mind > The Body Human Anatomy - Organs Click on the labels below to find.
Transplant Living
human body, the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. Human body diagrams From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository Male shadow/silhouette template. The Wikimedia Human body diagrams is a collection of images whose main purpose is to provide a way of explaining medical conditions and other phenomena. Contents 1 Diagrams 2 Human body diagrams 2.1 How to derive an image Major organs Surface projections of major organs of the torso, using the vertebral column and rib cage as main reference sources. In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. The trunk (torso) is the central part of the body to which the head and the limbs are attached. Except for the brain, the trunk houses all the vital organs of the human body. The torso muscles attach to the skeletal core of the trunk, and depending on their location are divided into two large groups: anterolateral muscles of the trunk

6 Organs In Torso Diagram Organ (anatomy) Wikipedia Following are
Torso The human torso is also known as the 'trunk'. It is the central part of the body, and it is from here that the neck and the limbs extend. Some of the most critical human body organs are situated within the torso. Your complex body has over 30 trillion cells, and most of those cells aren't in direct contact with the external environment. 1 A cell deep inside your body—in one of your bones, say, or in your liver—can't get the nutrients or oxygen it needs directly from the environment. How, then, does the body nourish its cells and keep itself running? System of organs. A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body. Musculoskeletal system. Mechanical support, posture and locomotion. Cardiovascular system. Transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body and elimination of cellular metabolic waste. Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1 : These two people are both in anatomical position. (CC-BY, Open Stax ) When referencing a structure that is on one side of the body or the other, we use the terms "anatomical right" and "anatomical left.". Anatomical right means that the structure is on the side that a person in anatomical position would consider.

17 best Human Anatomy images on Pinterest Human anatomy, Human body
Information. The major cavities of the human body are the spaces left over when internal organs are removed. There are additional body cavities which we will only discuss in lecture. These are the cavities created by serous membranes-the pleural cavities, the pericardial cavity, and the peritoneal cavity-and the mediastinum. Human body Female (left) and male (right) adult human bodies photographed in ventral (above) and dorsal (below) perspectives. Naturally-occurring pubic, body, and facial hair has been deliberately removed to show anatomy. The human body is the entire structure of a human being.
Browse 11,712 human torso anatomy photos and images available, or search for human anatomy to find more great photos and pictures. Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Human Torso Anatomy stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Human Torso Anatomy stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and. Thoracic wall The first step in understanding thorax anatomy is to find out its boundaries. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature - all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage.
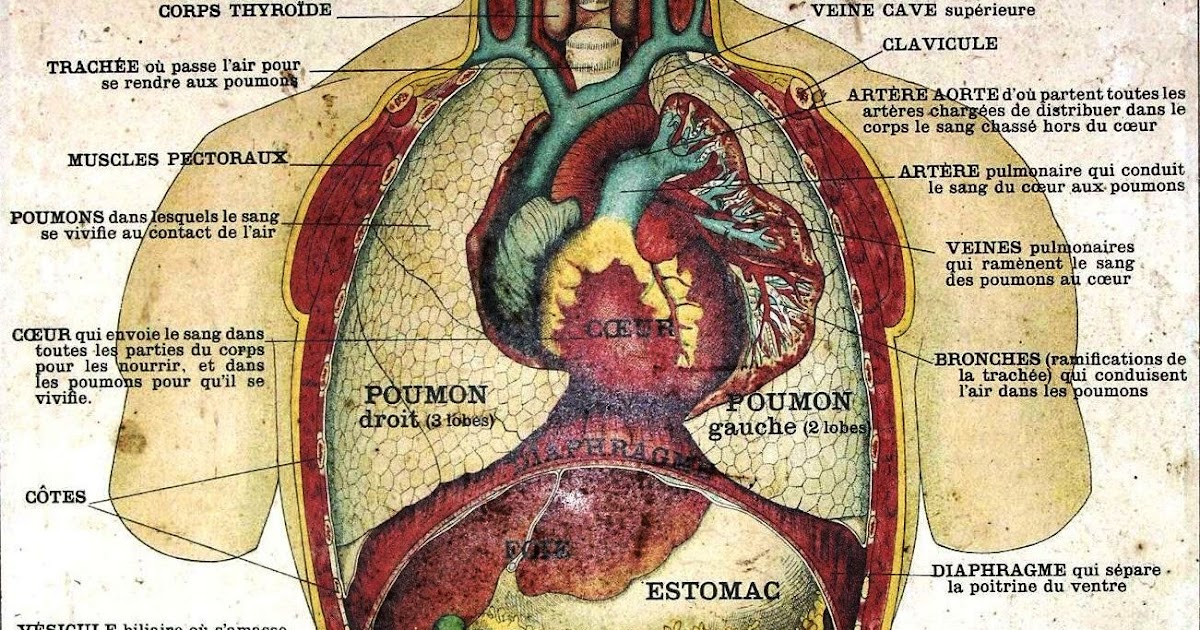
6 Organs In Torso Diagram Organ (anatomy) Wikipedia Following are
The transverse (or horizontal) plane divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions. Transverse planes produce images referred to as cross sections. Figure 1.4.3 - Planes of the Body: The three planes most commonly used in anatomical and medical imaging are the sagittal, frontal (or coronal), and transverse planes. Body. A diagram of the human skeleton showing bone and cartilage. Protection of the heart, lungs, and other organs and structures in the chest creates a problem somewhat different from that of the central nervous system. These organs, the function of which involves motion, expansion, and contraction, must have a flexible and elastic protective covering.



