This translation of aerodynamic force to rotation of a generator creates electricity. Types of Wind Turbines The majority of wind turbines fall into two basic types: Horizontal-Axis Turbines Vertical-Axis Turbines Wind turbines can be built on land or offshore in large bodies of water like oceans and lakes. How a Wind Turbine Works. A wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades, which work like an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade. When wind flows across the blade, the air pressure on one side of the blade decreases. The difference in air pressure across the two sides of the blade creates.

Wind Energy Diagram Sustainable Energy
Total annual U.S. electricity generation from wind energy increased from about 6 billion kilowatthours (kWh) in 2000 to about 380 billion kWh in 2021. In 2022, wind turbines were the source of about 10.2% of total U.S. utility-scale electricity generation. Step-by-step look at each piece of a wind turbine from diagram above: (1) Notice from the figure that the wind direction is blowing to the right and the nose of the wind turbine faces the wind. (2) The nose of the wind turbine is constructed with an aerodynamic design and faces the wind. Starre Vartan Updated August 13, 2021 Fact checked by Elizabeth MacLennan Treehugger / Hilary Allison In This Article Definition Wind Energy Basics Types How Does Wind Energy Work? What. A wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades, which work like an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade. When wind flows across the blade, the air pressure on one side of the blade decreases. The difference in air pressure across the two sides of the blade creates both lift and drag.
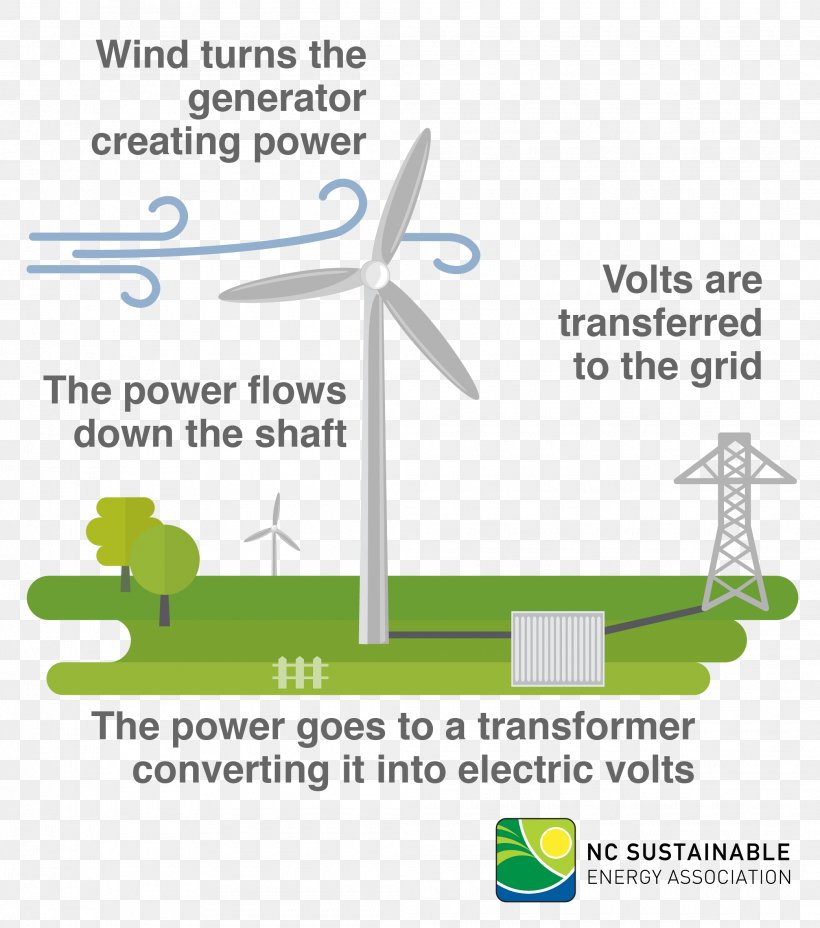
Diagram Of Wind Power
Dec. 27, 2023, 9:50 AM ET (AP) wind turbine Components of a wind turbine. wind power, form of energy conversion in which turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical or electrical energy that can be used for power. Wind power is considered a renewable energy source. Wind energy is actually a byproduct of the sun. The sun's uneven heating of the atmosphere, the earth's irregular surfaces (mountains and valleys), and the planet's revolution around the sun all combine to create wind. Since wind is in plentiful supply, it's a sustainable resource for as long as the sun's rays heat the planet. Energy from moving air. Wind is caused by uneven heating of the earth's surface by the sun. Because the earth's surface is made up of different types of land and water, the earth absorbs the sun's heat at different rates. One example of this uneven heating is the daily wind cycle. How uneven heating of water and land causes wind. Wind Resource and Potential Approximately 2% of the solar energy striking the Earth's surface is converted into kinetic energy in wind. Wind turbines convert the wind's kinetic energy to electricity without emissions.1 The distribution of wind energy is heterogeneous, both across the surface of the Earth and vertically through the atmosphere. Average annual wind speeds of 6.5m/s or greater.

Schematic diagram of wind turbine system. Download Scientific Diagram
Wind Energy Maps and Data. Find maps and charts showing wind energy data and trends. Filter by Turbine Hub Height. 30-Meter Residential 40-Meter Wind Speed 50-Meter Community 60-Meter Wind Speed 80-Meter Land-Based 100-Meter Land-Based 100-Meter Offshore 110. The fraction of the year the turbine generator is operating at rated (peak) power. Capacity Factor = Average Output / Peak Output ≈ 30%. CF is based on both the characteristics of the turbine and the site characteristics (typically 0.3 or above for a good site) Power Curve of 1500 kW Turbine. wind speed (m/s)
500 mi The Global Wind Atlas is a free, web-based application developed to help policymakers, planners, and investors identify high-wind areas for wind power generation virtually anywhere in the world, and then perform preliminary calculations. Dec. 27, 2023, 9:50 AM ET (AP) The year in clean energy: Wind, solar and batteries grow despite economic challenges wind turbine, apparatus used to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity.

Wind Power Wind Power Diagram
The nacelle is the 'head' of the wind turbine, and it is mounted on top of the support tower. The rotor blade assembly is attached to the front of the nacelle. The nacelle of a standard 2MW onshore wind turbine assembly weighs approximately 72 tons. Housed inside the nacelle are five major components (see diagram): a. Gearbox assembly b. Energy in wind comes from the uneven solar heating of the atmosphere. The use of wind for energy goes back to the earliest sailing ships. On land, windmills applied the principle of sails to a rotary shaft, to harvest the mechanical energy of wind for providing mechanical power. Small windmills on farms power water pumps, and some were coupled.



