How a Typical Front End Suspension Works (Plus Diagram) - In The Garage with CarParts.com Understand how a typical front end suspension works and what to do in case you need a front end repair in this helpful article. Read more. The job of a car suspension is to maximize the friction between the tires and the road surface, to provide steering stability with good handling and to ensure the comfort of the passengers. In this article, we'll explore how car suspensions work, how they've evolved over the years and where the design of suspensions is headed in the future.
Simple Guide to Automotive Suspension Haynes Manuals
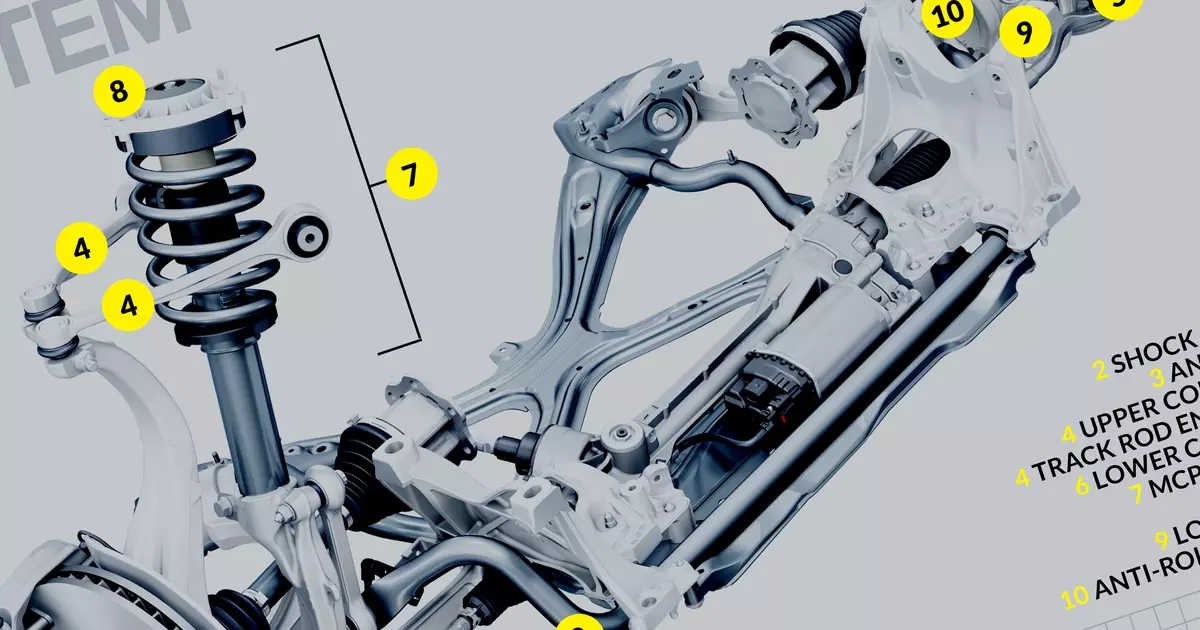
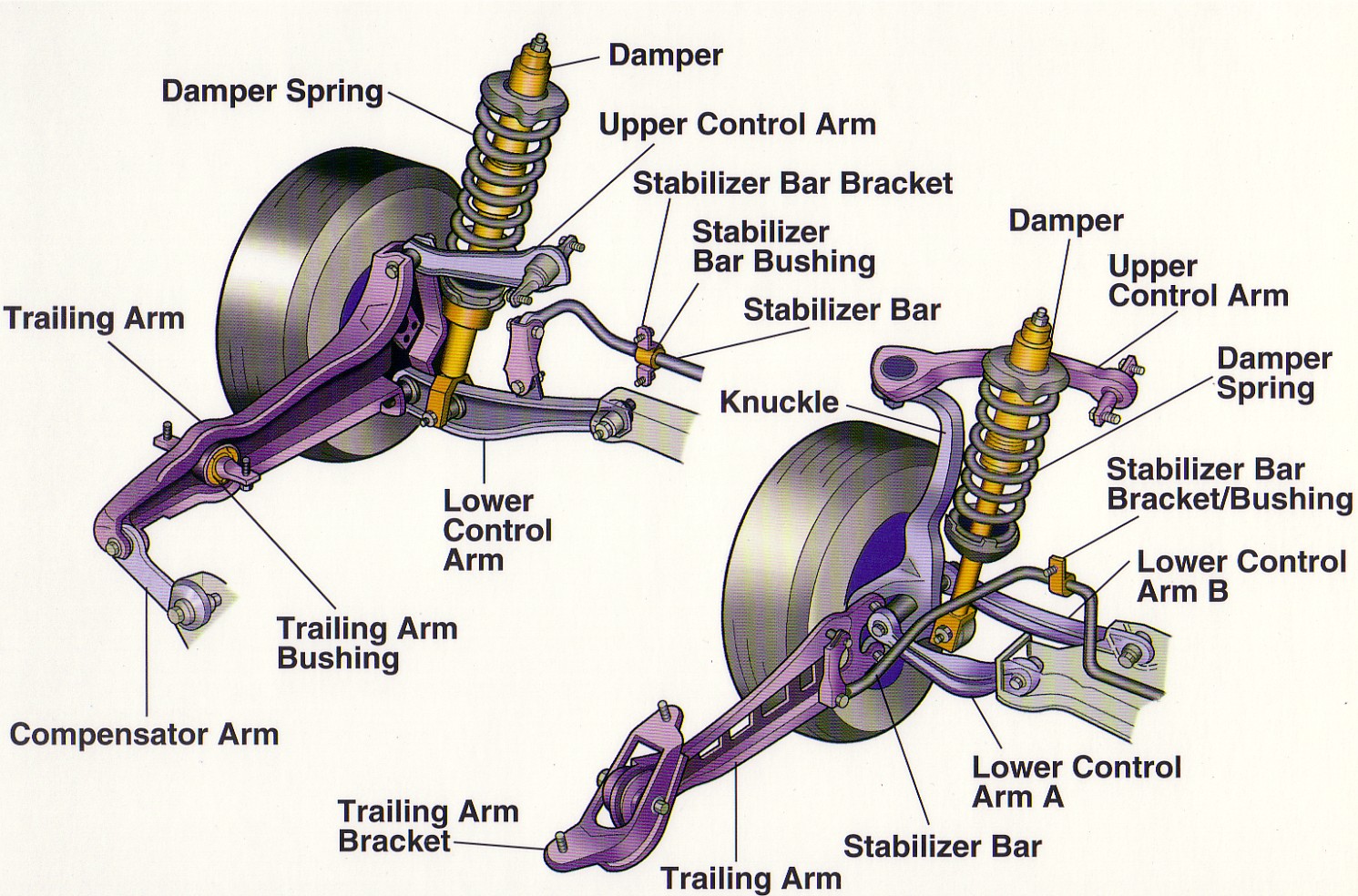
Car Suspension Basic Anatomy Lesson You may not even notice your car suspension and everything it does for you. Because there are many dynamic forces at play and the road is certainly never smooth, your suspension system has to work hard to keep your wheels firmly planted on the pavement and help you maintain control of your vehicle. A car suspension diagram shows the components that help a car maintain stability and absorb shocks. The diagram typically includes parts such as the springs, shocks, control arms, and linkages. These components work together to ensure a smooth and comfortable ride by reducing vibrations and keeping the wheels in contact with the road. A rear-wheel-drive car often has a live axle, a tube containing both the drive shafts (half shafts) and the differential gears . A four-wheel-drive car may have a live front axle as well. A dead axle - a rigid beam - is now used at the front on vans and trucks only. Some front-wheel-drive cars have a dead rear axle. A rigid axle will have springs and links to prevent sideways movement. Understanding the Anatomy of Car Suspension Components: A Detailed Diagram The suspension system of a car is an essential part of its overall construction, as it ensures a smooth and comfortable ride for the driver and passengers.
Automobiles world Suspension System
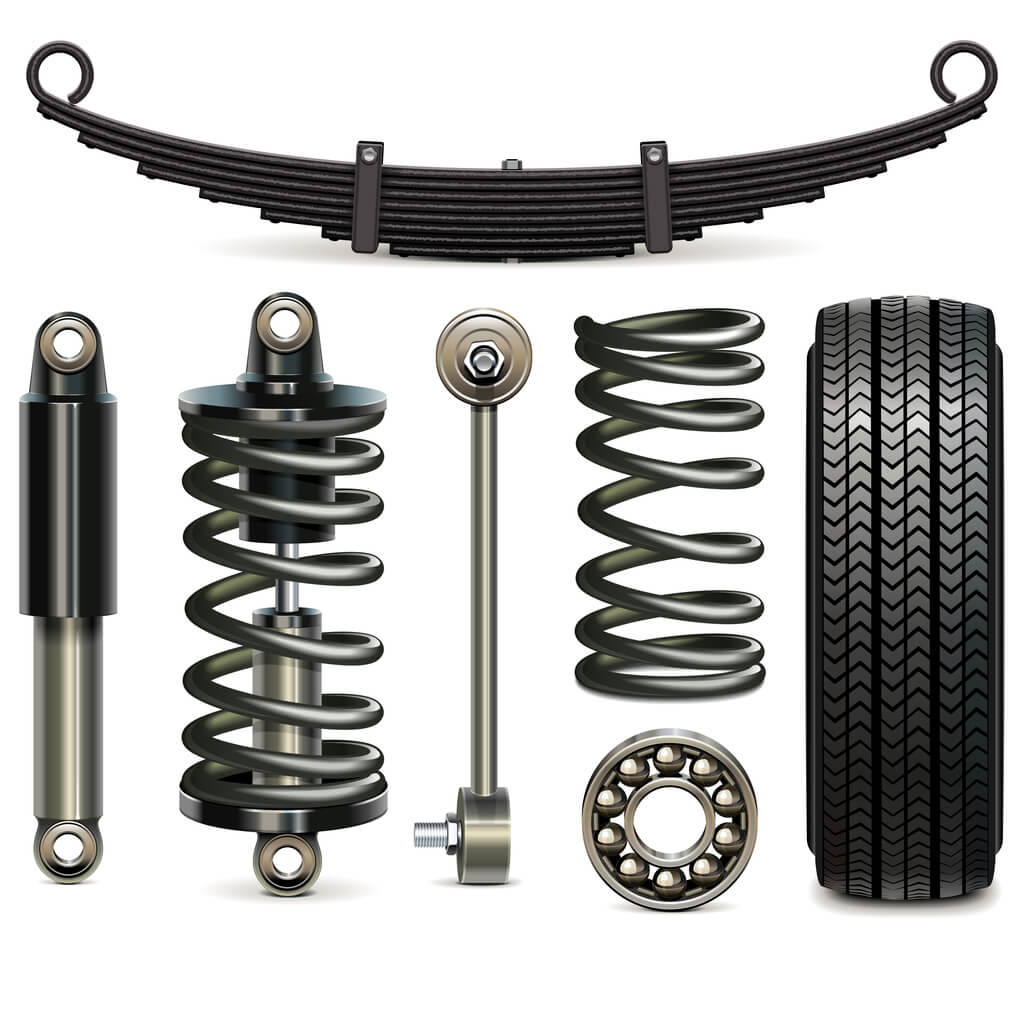
It can be measured as positive or negative. In the case of positive camber, the top of the wheel would pull out from the top of the car. In the case of negative camber, the top would tuck into the car. Take a look at the diagram lower down for a visual explanation. The amount of camber can drastically change the way a car drives. What's in a car's suspension system? Springs Most modern car suspension systems use steel coil springs - one per wheel. However, if you look under an older car or a pick-up truck, instead of springs you'll see narrow strips of metal stacked one on top of the other. These are leaf springs. How Car Suspensions Work | Car Suspension System ExplainedWith car suspension animation in the video, the contents include1) Car suspension components: stee. **Short answer car suspension diagram:** A typical car suspension consists of springs, shock absorbers or dampers, and various linkages to connect the wheels to the chassis. A diagram shows that the main components are arranged in a "double-wishbone" or "McPherson strut" configuration, depending on the type of system used.

Understanding Your Car’s Suspension Tyrepower Wangara
Automotive Suspension Geometry for Dummies The words "suspension" and "geometry" are strung together for a reason. The word "suspension", originates from a Latin verb called suspendere which means "to hang up". It is used in the automotive context because the body of every car is suspended by — you guessed it — the suspension system. Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. [1] Suspension systems must support both road holding/ handling and ride quality, [2] which are at odds with each other.
Diagram KU1. Side and top views of a non-driven upright/knuckle within an independent wishbone suspension. Diagram KU2 shows an example of an independent wishbone suspension for a driven wheel. As with the non-driven version, the upright (Yellow) is attached to the vehicle using the upper and lower wishbones which have ball joints or rod-ends. Car Suspension Basics, How-To & Design Tips. The suspension on a vehicle serves multiple purposes:. Diagram B6 below shows a drum brake in a hydraulic system. The driver presses the brake pedal, which forces a piston in the master cylinder to compress the brake fluid (Yellow). The fluid runs inside a brake line to slave cylinder (Blue) which.
Different Front Car Suspension Diagram
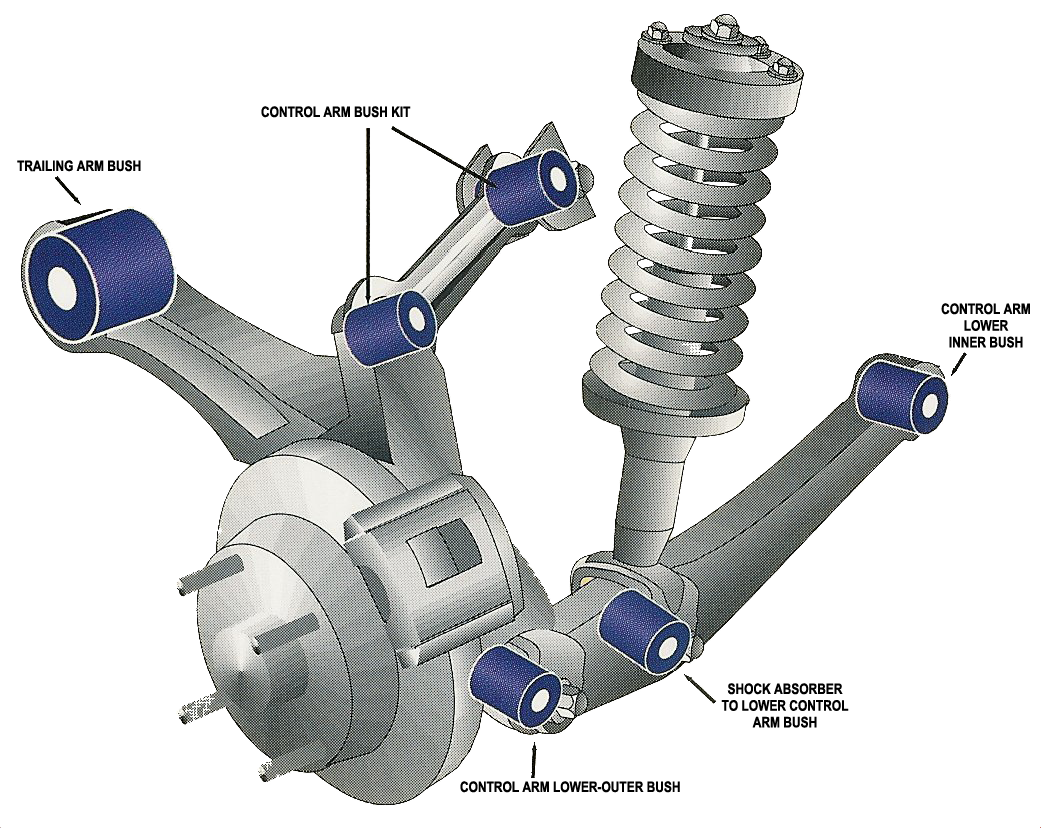
It includes tires, springs, shafts, linkages, struts, joints, bushings, arms, and shock absorbers that connect your vehicle to the wheels creating a relative motion between them. The system neutralizes the forces received by the vehicle while driving on the road making sure it does not lift off from the road. To simplify the car suspension diagram, we will model 2 masses and 2 sets of springs and dampers Fig. 1a and analyze ¼ of an entire car. Fig. 1a and 1b. Model of active suspension system. . Car Mass 2500 kg Body Mass (m1) 650 kg Wheel and suspension mass (m2) 150 kg.




