Animal cells Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells. Animal cells have a basic structure. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell, on the left viewed with. Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions.

Animal Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
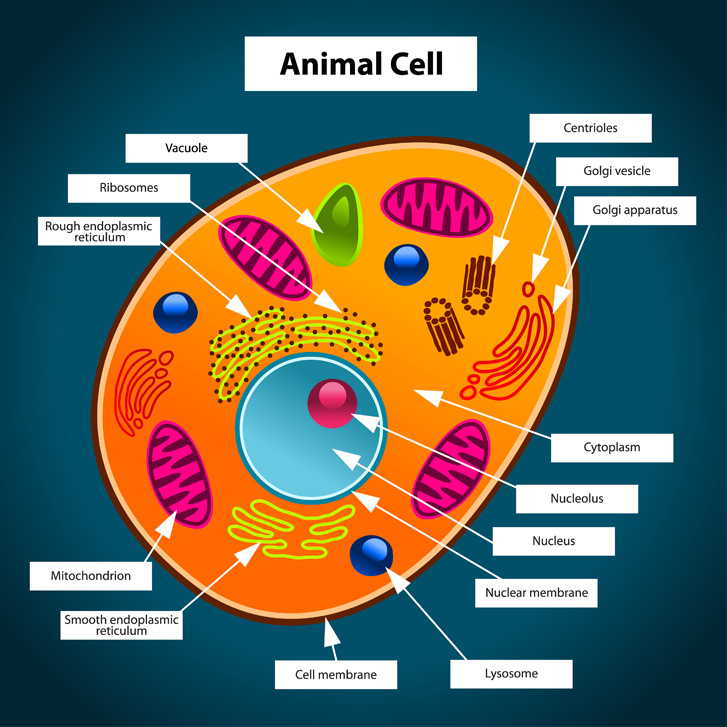
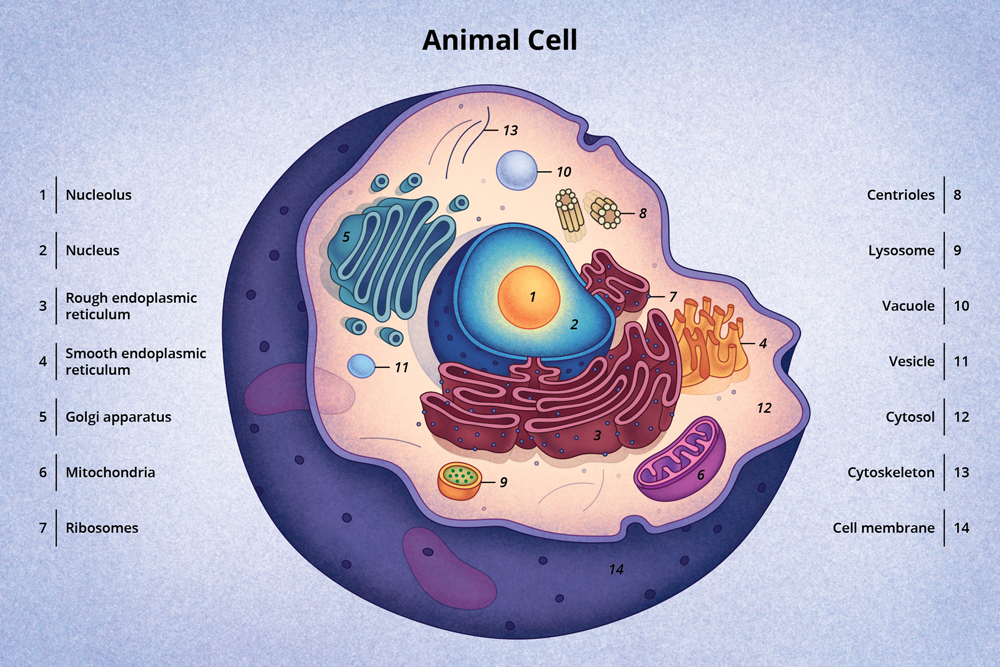
An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall. The nucleus is an organelle that contains a cell's genes. Chloroplasts are organelles that carry out photosynthesis, which makes the food plant cells need to live. This food is in the form of sugars. Plant cells have chloroplasts and a cell wall, but animal cells do not. An animal cell lacks a cell wall or chloroplasts. Its outer coating is a semipermeable cell membrane. Animal cells are the fundamental units of life in protozoa and multicellular animals. Each cell is a wonder in its own right, plus they work together as building blocks for tissues, organs, and organ systems. What are cells? All life on Earth is made from cells. Without cells, there can be no life. Almost all cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. Some organisms, like.
Animal Cell Free printable to label + Color
. This means they have a nucleus and other structures which are surrounded by membranes . A generalised animal cell and its components Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are visible with a. KS3 Specialised animal cells Part of Biology Living organisms Remove from My Bitesize Key points Specialised animal cells have components that allow them to complete a specific purpose.. Animal cells Animals depend upon plants as an energy source. Chemicals in food are broken down in respiration to create energy stores that can be used by the cell. Animal cells have a basic. Animal cells Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell, on the left viewed with the light microscope, and on the right with the.

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Ensure that your students understand the core components of a basic animal cell with this Animal Cell Labelling activity sheet.This resource features a large-scale illustration/diagram of an animal cell, with four arrows pointing to the cell nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane and mitochondria. In order to complete the worksheet, students must correctly label all four components.This labelling. "An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles." Explanation Animal cells range in size from a few microscopic microns to a few millimetres.
Animal Cell Anatomy. The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; in fact, most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Where, prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else.
Discovery and Structure of Cells Biology Visionlearning
Animal Cell Definition. Animal cells are the types of cells that make up most of the tissue cells in animals. Different kinds of animals have different numbers of cells, but most have millions and millions. Human beings, for instance, have over 40 trillion cells. Animal cells are eukaryotic, which means they have a nucleus that holds DNA. The shape of a typical animal cell varies widely from being flat, oval to rod-shaped, while others assume shapes such as curved, spherical, concave, and rectangular. An animal cell ranges in size from 10 to 30 µm. Under the microscope, an animal cell shows many different parts called organelles, that work together to keep the cell functional.




