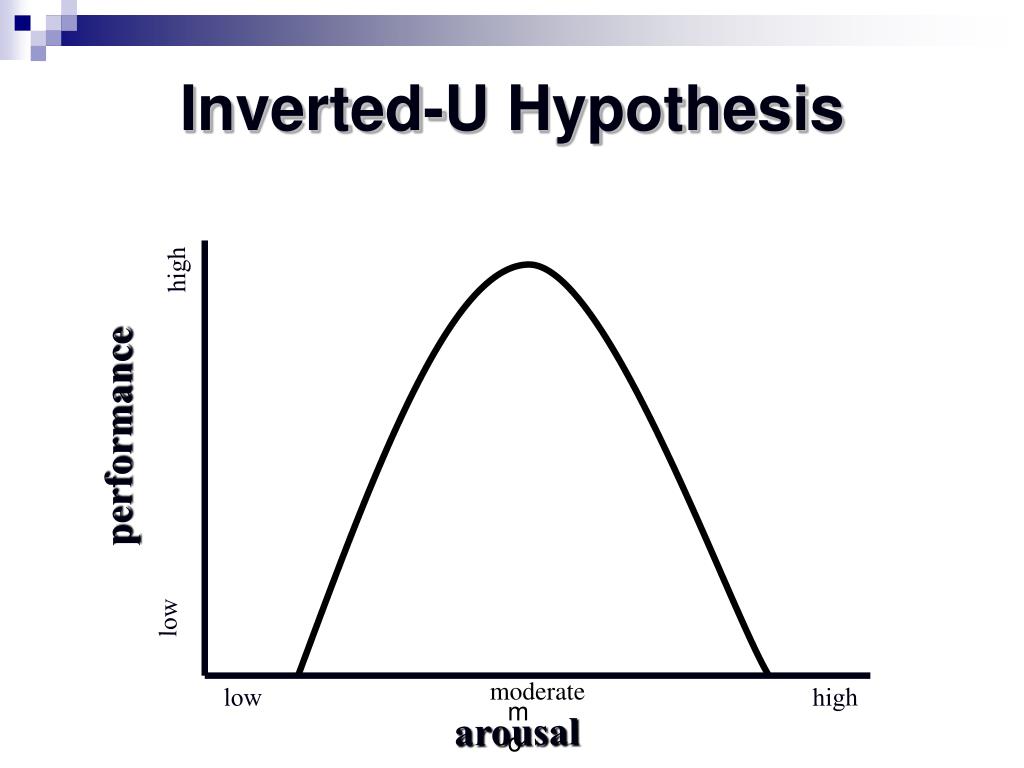
The Inverted U theory in sports aims to explain the relationship between arousal levels and performance. The theory also suggests how different levels of arousal can lead to either an increase or decrease in performance. In 1908, researchers Yerkes and Dodson published a study that forms the foundation of the Inverted U theory. The 'inverted U' theory proposes that sporting performance improves as arousal levels increase but that there is a threshold point. Any increase in arousal beyond the threshold point will.
Inverted U Theory Explained Sport Science Insider
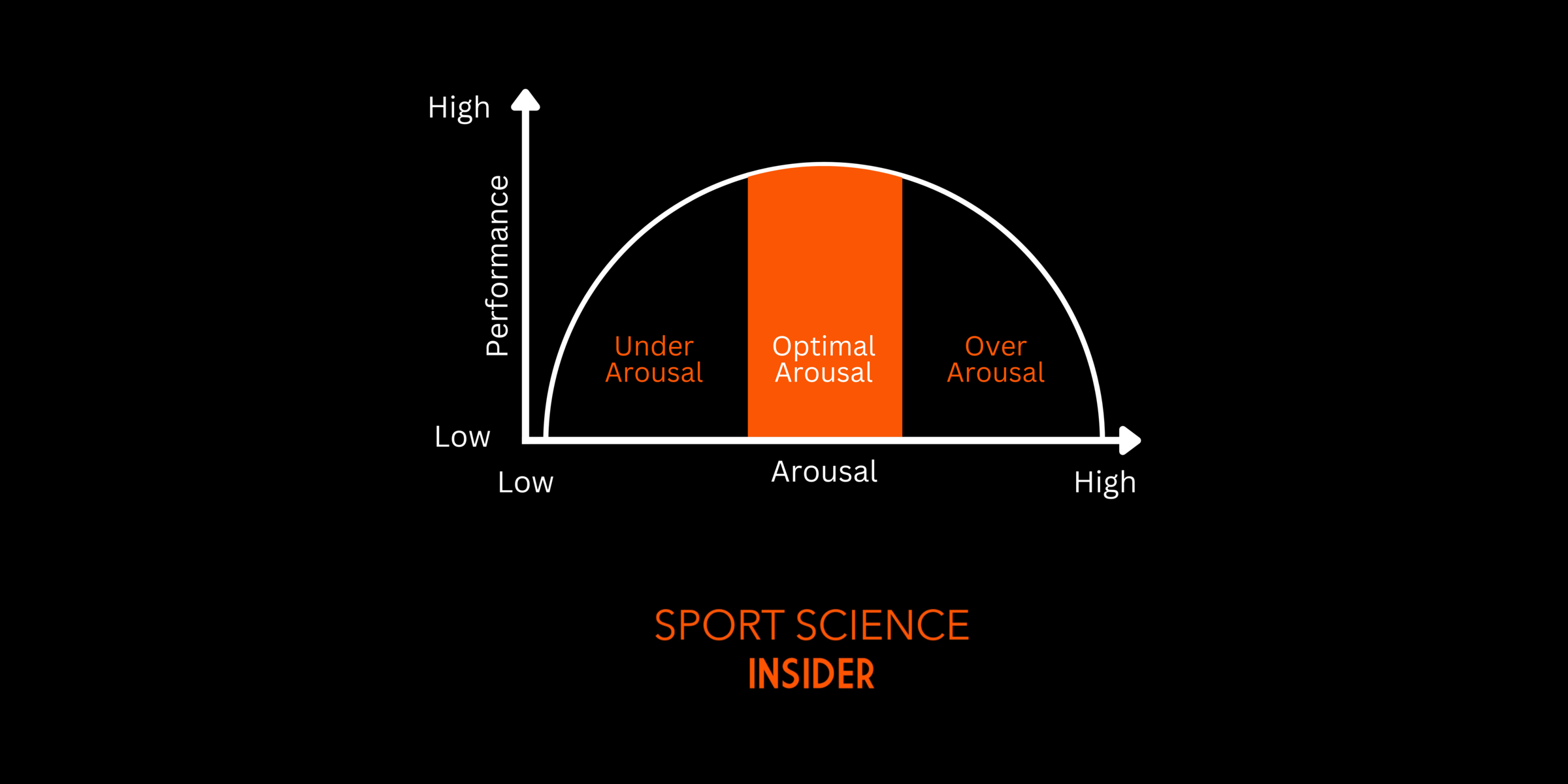
The inverted u theory describes the relationship between arousal and performance. The theory hypotheses that arousal levels that are either too high or too low can result in gradual decreases in performance. In between these high and low arousal levels, is an optimum level of arousal for performance, which can be seen in the inverted u curve below. The approach to seeing stress as a challenge supports a series of strategies that can be used to help control arousal in sport. Keywords cognitive appraisal psychophysiology stress performance challenge threat imagery reappraisal relaxation confidence control approach focus Subjects Sports Psychology The Autonomic Nervous System Until recently, the traditional Inverted-U hypothesis had been the primary model used by sport psychologists to describe the arousal-performance relationship. However, many sport psychology researchers have challenged this relationship, and the current trend is a shift toward a more "multidimensiona. This is unsurprising, as sport psychology researchers have somewhat unanimously agreed that competitive sport has the potential for high levels of stress and anxiety. 1 Equally, practicing and employing a range of psychological strategies to combat potential negative emotional states such as sport-related anxiety has become an integral part of a.
PPT Exercise & Sports Psychology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID506698
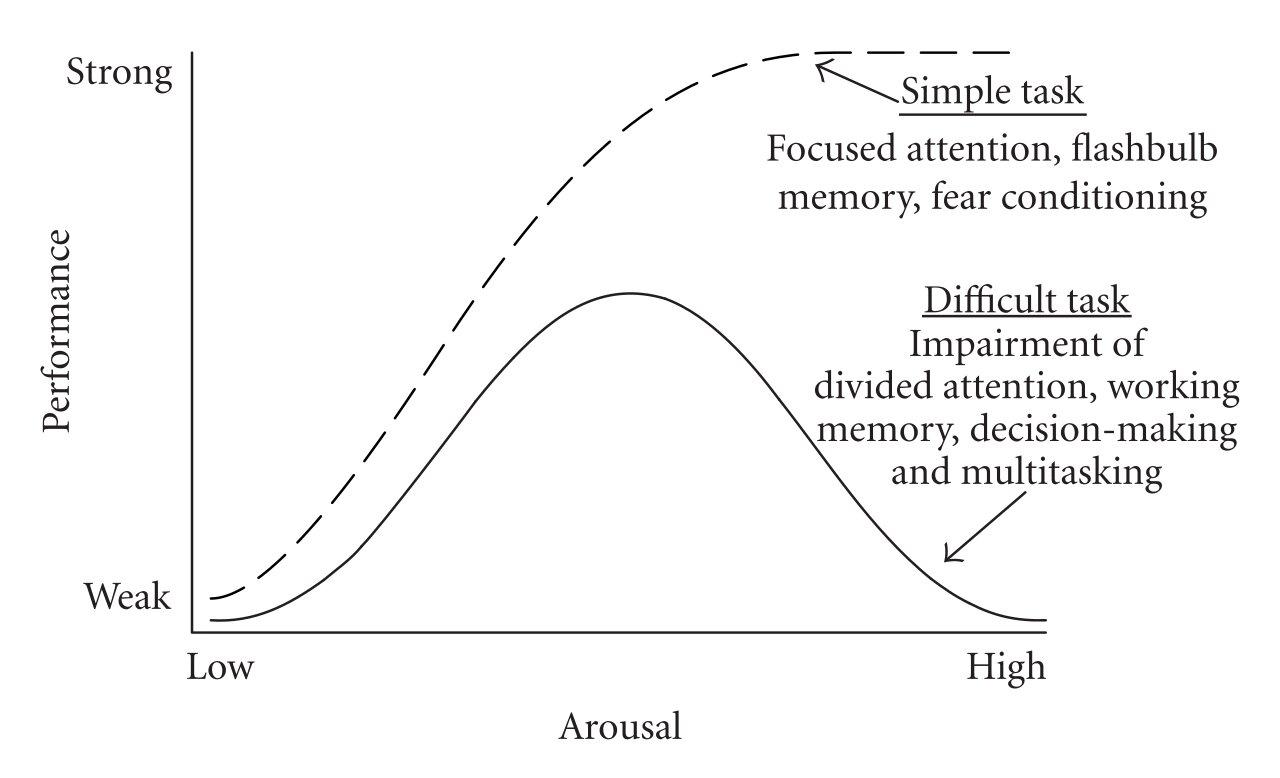
The inverted-U theory was first identified by Yerkes and Dodson (1908). The inverted-U suggests the relation between both arousal and sports performance in a curvilinear relationship.. The Inverted U Hypothesis is an appealing explanation for performance flaws. In many ways this explanation fits into the observations from sport performers but in reality is too simplistic. Sports psychologists have for some time put forward the inverted‐U‐hypothesis as a useful working model of the relationship between arousal and performance. Although some emphasis in the sports psychology literature has been placed on the limitations of the hypothesis, generally the notion of an optimal level of arousal has been well received. According to the multidimensional anxiety theory, cognitive anxiety has a negative linear relationship with sport performance, while somatic anxiety has an inverted-U relationship. By explicitly considering the interaction between the two anxiety components, the catastrophe model of anxiety suggests that the influence of somatic anxiety depends.
The InvertedU Theory Balance Performance & Pressure
The inverted-U theory defines a model that can be used to describe the arousal-performance relationship in terms of sports psychology. Athletes should obtain optimal arousal to exhibit their. Quick Reference. A theory that proposes that the needs and desires directing human behaviour switch back and forth between one state of mind and another during the course of a day. According to reversal theory, motivational states occur in four pairs of alternative states (called metamotivational states): the telic state and paratelic state.
What Is the Inverted-U Theory? The Inverted-U Theory was created by psychologists Robert Yerkes and John Dodson in 1908. Despite its age, it's a model that has stood the test of time. [1] The theory describes a clear relationship between pressure and performance. PMID: 1623887 Abstract From the findings summarized in this review, it appears that there is little evidence in support of the inverted-U hypothesis. Available research indicates that there is considerable variability in the optimal precompetition anxiety responses among athletes, which does not conform to the inverted-U hypothesis.

PPT Sports Coaching PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4675100
The theory suggests that like the inverted U theory, moderate amounts of arousal will provide an athlete with the optimal performance, although once an athlete over arouses themself, there will be a sharp decline in performance (Hardy, 1990).. L. & Fazey, J. (1987). The Inverted-U Hypothesis: A Catastrophe For Sport Psychology? Paper. Theories of Arousal in sport. There are numerous theories that describe different relationships between arousal and performance. Here is a brief overview of each of these theories. Inverted U hypothesis. The Inverted U Theory describes how an optimal level of arousal correlates to peak performance. Deviations from this optimal arousal level.



