Die clevere Online-Lernplattform für alle Klassenstufen. Interaktiv und mit Spaß! Anschauliche Lernvideos, vielfältige Übungen, hilfreiche Arbeitsblätter. Jetzt loslernen! Trigonometric functions Trigonometry Outline History Usage Functions ( inverse) Generalized trigonometry Reference Identities Exact constants Tables Unit circle Laws and theorems Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e
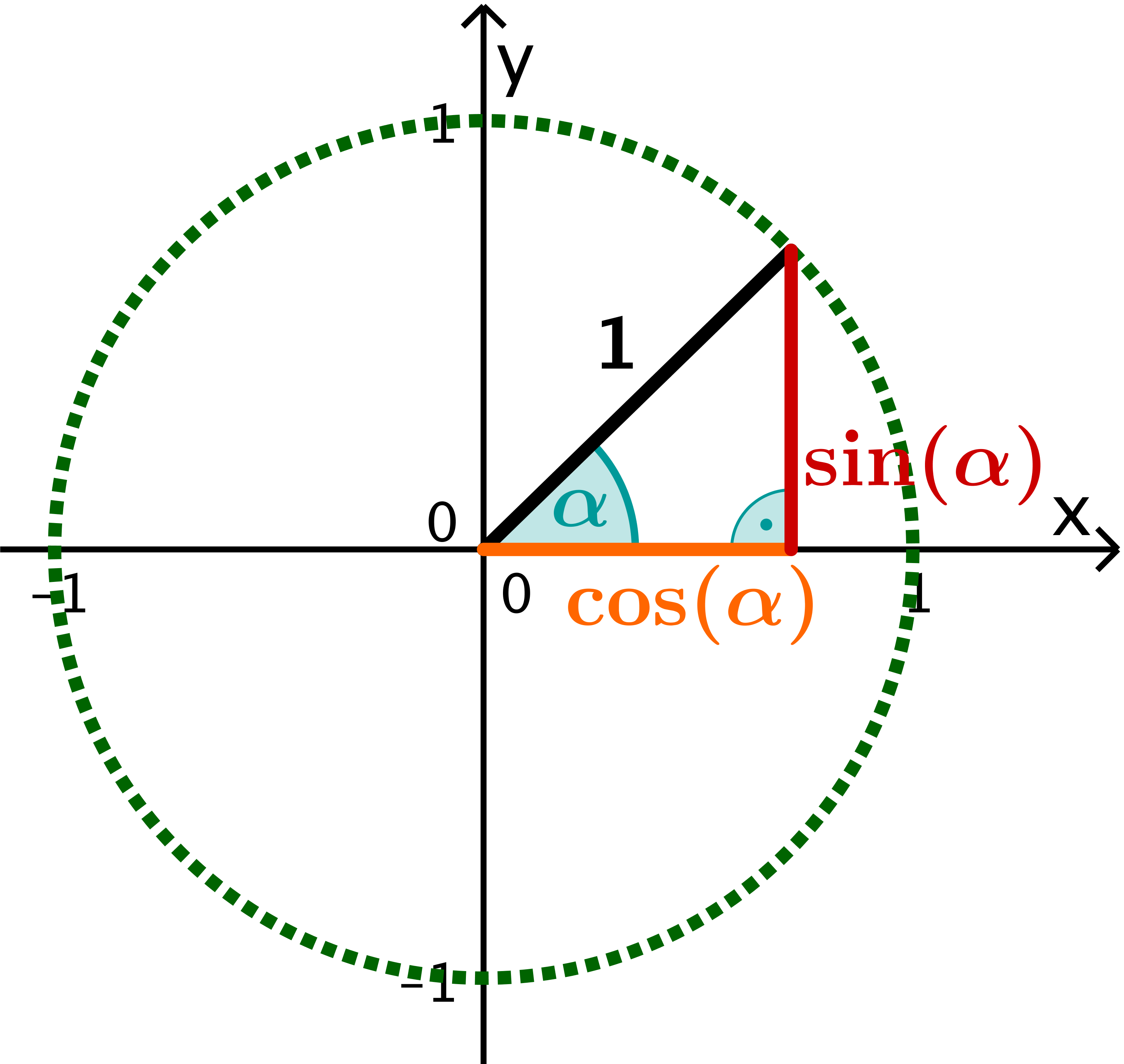
Trigonometrie am Einheitskreis lernen mit Serlo!
Sine, Cosine and Tangent are the main functions used in Trigonometry and are based on a Right-Angled Triangle. Before getting stuck into the functions, it helps to give a name to each side of a right triangle: "Opposite" is opposite to the angle θ "Adjacent" is adjacent to (next to) the angle θ "Hypotenuse" is the long one 🔎 Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) are all ratios. Therefore, you can find the missing terms using nothing else but our ratio calculator! Trigonometry has plenty of applications: from everyday life problems such as calculating the height or distance between objects to the satellite navigation system, astronomy, and geography. A sine wave made by a circle: A sine wave produced naturally by a bouncing spring: Plot of Sine The Sine Function has this beautiful up-down curve (which repeats every 2 π radians, or 360°). It starts at 0, heads up to 1 by π /2 radians (90°) and then heads down to −1. Plot of Cosine Sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. They are often written as sin (x), cos (x), and tan (x), where x is an.
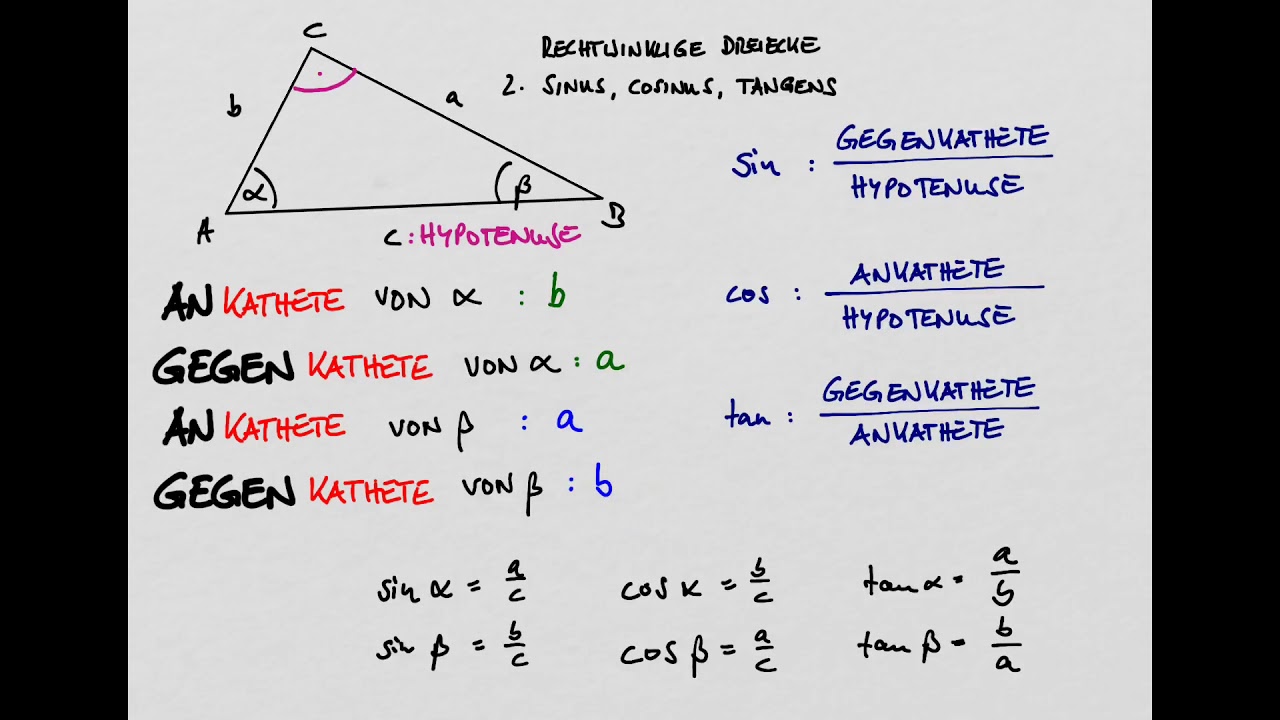
sinus cosinus tangens 2 formeln YouTube
Answer: sine of an angle is always the ratio of the oppositeside hypotenuse o p p o s i t e s i d e h y p o t e n u s e . sine(angle) = opposite side hypotenuse s i n e ( a n g l e) = opposite side hypotenuse Example 1 sin(∠L) = opposite hypotenuse sin(∠L) = 915 s i n ( ∠ L) = o p p o s i t e h y p o t e n u s e s i n ( ∠ L) = 9 15 Example 2 The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle (the hypotenuse ), and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. Trigonometriske funksjoner Funksjonene sinus, cosinus, tangens og cotangens. Defineres enklest for en spiss vinkel i en rettvinklet trekant som forholdet mellom to av sidene i trekanten. trigonometriske funksjonene er: Sinus En trigonometrisk funksjon. To calculate sine, cosine, and tangent in a 3-4-5 triangle, follow these easy steps: Place the triangle in a trigonometric circle with an acute angle in the center. Identify the adjacent and opposite catheti to the angle. Compute the results of the trigonometric functions for that angle using the following formulas: sin (α) = opposite.
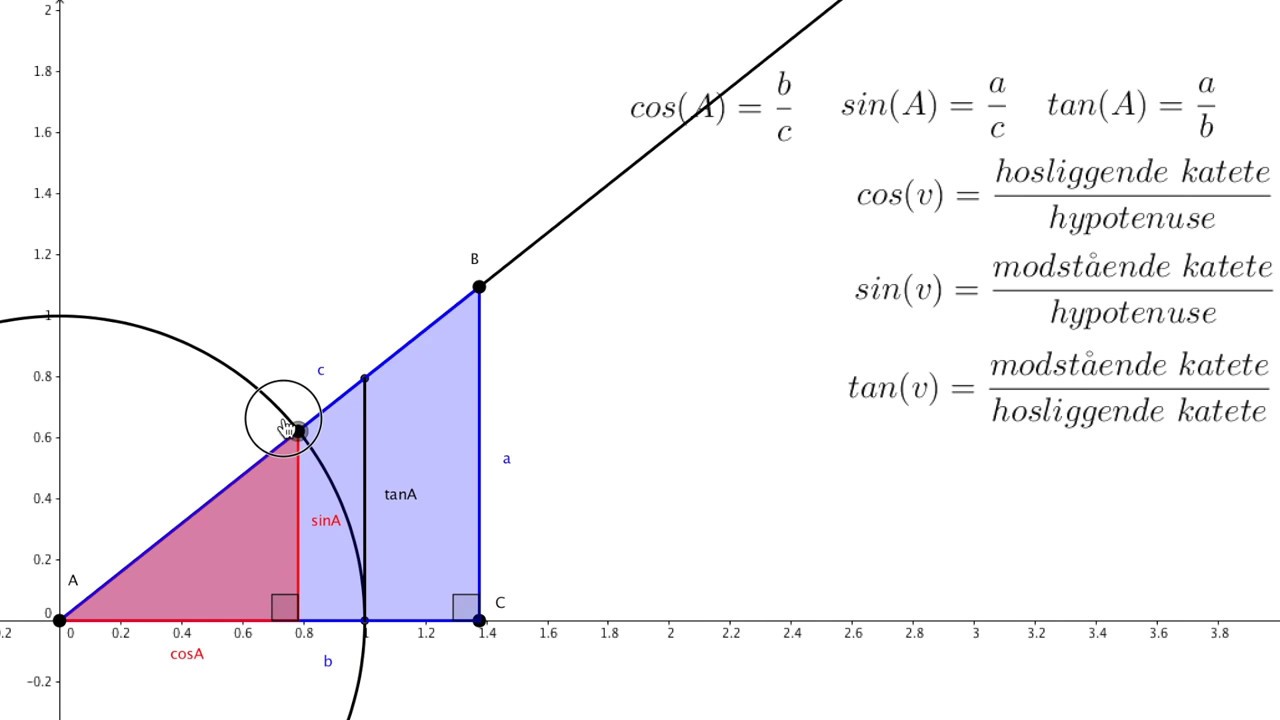
Cosinus Sinus Tangens YouTube
The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change with respect to a variable.For example, the derivative of the sine function is written sin′(a) = cos(a), meaning that the rate of change of sin(x) at a particular angle x = a is given by the cosine of that angle. Die Winkelfunktionen Sinus, Kosinus und Tangens sind die wichtigsten trigonometrischen Funktionen.. Sinus, Kosinus und Tangens beschreiben das Verhältnis von Seitenlängen in einem rechtwinkligen Dreieck in Abhängigkeit von einem der spitzen Winkel.Sie sind folgendermaßen definiert. sin (α) = Gegenkathete Hypotenuse \sin (\alpha )=\frac{\text{Gegenkathete}}{\text{Hypotenuse}} sin (α.
Sinus , Cosinus und Tangens sind trigonometrische Funktionen , mit denen du die Winkel in einem Dreieck berechnen kannst. Beachte, dass du sie nur bei rechtwinkligen Dreiecken anwenden kannst! Sie sind folgendermaßen definiert: Rechtwinkliges Dreieck: sin cos tan In einem rechtwinkligen Dreieck gibt es immer eine lange und zwei kurze Seiten. Vor Tangens und Kotangens sowie Sekans und Kosekans sind sie die wichtigsten trigonometrischen Funktionen. Sinus und Kosinus werden unter anderem in der Geometrie für Dreiecksberechnungen in der ebenen und sphärischen Trigonometrie benötigt.. Die Kreisfunktionen Sinus und Cosinus haben folgende zwei Produktentwicklungen:.
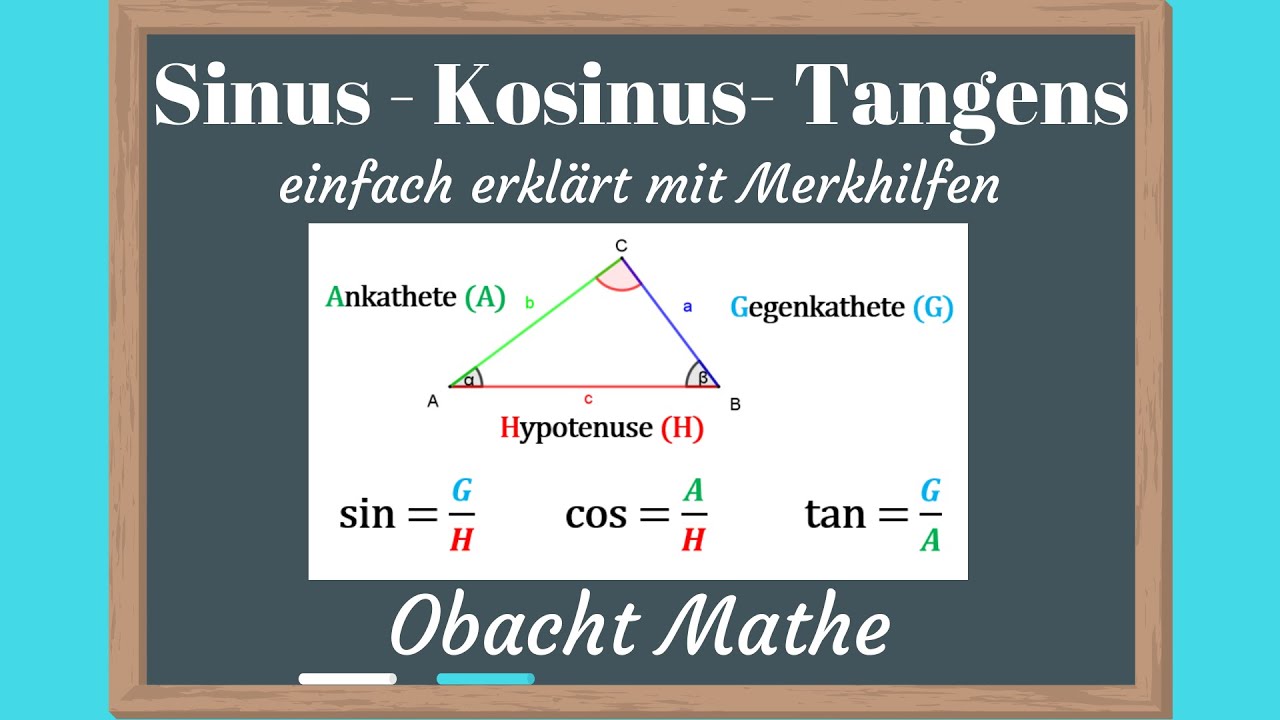
SINUS KOSINUS TANGENS mit Merkhilfen genial einfach&schnell erklärtTrigonometrie
. Par définition, le sinus, le cosinus et la tangente de l'angle aigu de sommet A du triangle rectangle A B C sont : Il faut bien comprendre que les mots hypoténuse, opposé et adjacent désignent les longueurs de l'hypoténuse, du côté opposé ou du côté adjacent à l'angle concerné. SOH-CAH-TOA : un moyen mnémotechnique simple Známe čtyři základní goniometrické funkce — sinus, cosinus, tangens a kotangens. Pusťte si video verzi článku! Základní pojmy o trojúhelníku Goniometrické funkce pracují s úhly v trojúhelníku, proto si v této části zopakujeme pojmy související s trojúhelníkem.




