The stria medullaris (SM), (Latin, furrow and pith or marrow) is a part of the epithalamus and forms a bilateral white matter tract of the initial segment of the dorsal diencephalic conduction system (DDCS). It contains afferent fibers from the septal nuclei, lateral preoptico- hypothalamic region, and anterior thalamic nuclei to the habenula. The pineal gland, habenular nuclei, and stria medullaris thalami are the principal components of the epithalamus ( Figs. 15.2, 15.4, and 15.15 ). The pineal gland consists of richly vascularized connective tissue containing glial cells and pinealocytes but no true neurons.

The dorsal diencephalic conduction system, with the stria medullaris,... Download Scientific
This nucleus communicates with the rest of the limbic system via the stria medullaris thalami (along the midline of the roof of the third ventricle). Habenula 1/2. Synonyms: none. In addition to connecting the Habenular nucleus to the hypothalamus, it also connects it to nuclei of the septum (septal area). It is the caudal part of the forebrain (prosencephalon) that occupies the central region of the brain. The diencephalon is comprised of the: Epithalamus Thalamus Subthalamus Metathalamus Hypothalamus In the following article, we will explore the anatomy of different parts of the diencephalon as well as their function. Contents Function Stria medullaris thalami - e-Anatomy - IMAIOS Human anatomy 2 Human body Parts of human body Regions of human body Musculoskeletal systems Visceral systems Integrating systems Endocrine glands Cardiovascular system Lymphoid organs Nervous system Central nervous system Gray matter White matter Reticular formation Ependyma Meninges Brain Cerebrum The stria medullaris is a fiber bundle containing efferent fibers from the septal nuclei, lateral preoptico-hypothalamic region, and anterior thalamic nuclei to the habenula. It forms a horizontal ridge on the medial surface of the thalamus. Incoming Links Related articles: Anatomy: Brain (advertising) ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
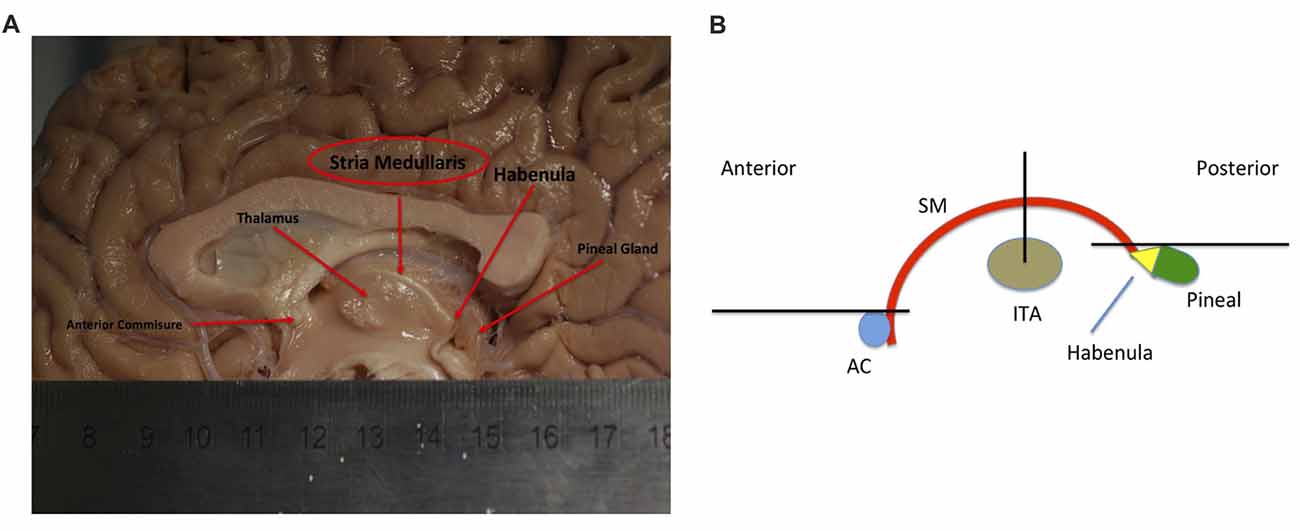
Frontiers Awakening Neuropsychiatric Research Into the Stria Medullaris Development of a
The habenular nuclei receive afferents via the stria medullaris thalami from the septal area (subcallosal area) and pre-optic nuclei (hypothalamus), via stria terminalis from the amygdaloid body and via fornix from the hippocampus (1, 4-8, 25-28). Some stria medullaris thalami fibers pass through the dorsal lamina of the pineal stalk and. The stria medullaris, also known as stria medullaris thalami, is a fiber bundle containing afferent fibers from the septal nuclei, lateral preoptic hypothalamic region, and anterior thalamic nuclei to the habenula. Pineal Gland. The Stria medullaris (SM) Thalami is a discrete white matter tract that directly connects frontolimbic areas to the habenula, allowing the forebrain to influence midbrain monoaminergic output. Habenular dysfunction has been shown in various neuropsychiatric conditions. The main afferent system is composed by olfactory fibers that run within the stria medullaris thalami. The habenular complex receives these fibers, which are derived from the septal region, hypothalamus, and the amygdala. The stria medullaris thalami is a band of fibers arching on the upper part of the medial surface of the thalamus, passing.
/images/library/2065/CY1FbBNvoPm9auinc5GlSw_Thalamus_01.png)
Thalamic Nuclei Connections, Functions & Anatomy Kenhub
The septal area also projects to the habenula nuclei via the stria medullaris thalami and the anterior hypothalamus. Hypothalamus. The hypothalamus lies at the center of the limbic system and is at the confluence of many neural pathways. It is subdivided from anterior to posterior into three zones: the supraoptic region, the tuberal region and. Identification of the stria medullaris thalami using diffusion tensor imaging Identification of the stria medullaris thalami using diffusion tensor imaging Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Oct 26;12:852-857. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.10.018. eCollection 2016. Authors Ryan B Kochanski 1 , Robert Dawe 2 , Daniel B Eddelman 1 , Mehmet Kocak 3 , Sepehr Sani 1
Some of those fibers turn backward to enter the stria medullaris thalami and reach the habenular nuclei. Fibers from the dorsal fornix reach the splenial gyrus and the gyrus cinguli; Learn everything about the fornix anatomy and function with our articles, video tutorials, quizzes and labeled diagrams. It lies most medially and adjacent to the AV but is separated from AV, the stria medullaris thalami, and the ventricular surface of myelinated fibers and a glial lamella. Our results show that the.

Case MU 6664. In section 1900 the extensive demyelination of the stria... Download Scientific
Awakening Neuropsychiatric Research Into the Stria Medullaris: Development of a Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Tractography Protocol of This Key Limbic Structure Front Neuroanat. 2018 May 8;12:39. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00039. eCollection 2018. Authors The Stria medullaris (SM) Thalami is a discrete white matter tract that directly connects frontolimbic areas to the habenula, allowing the forebrain to influence midbrain monoaminergic output. Habenular dysfunction has been shown in various neuropsychiatric conditions.


/images/library/2065/CY1FbBNvoPm9auinc5GlSw_Thalamus_01.png)

