The anterior triangle is a region located at the front of the neck. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the anterior triangle of the neck - its borders, contents and subdivisions. Note: it is important to note that all triangles mentioned here are paired; they are located on both the left and the right sides of the neck. Borders Contents Anatomical triangles Anterior triangle Muscular triangle Carotid triangle Submandibular (digastric) triangle Submental triangle Posterior triangle Occipital triangle Supraclavicular (omoclavicular) triangle Clinical significance Jugular venous pressure Carotid artery pulsation Cricothyroidotomy Sources + Show all Anatomical triangles

Anterior Triangle of Neck Anatomy QA
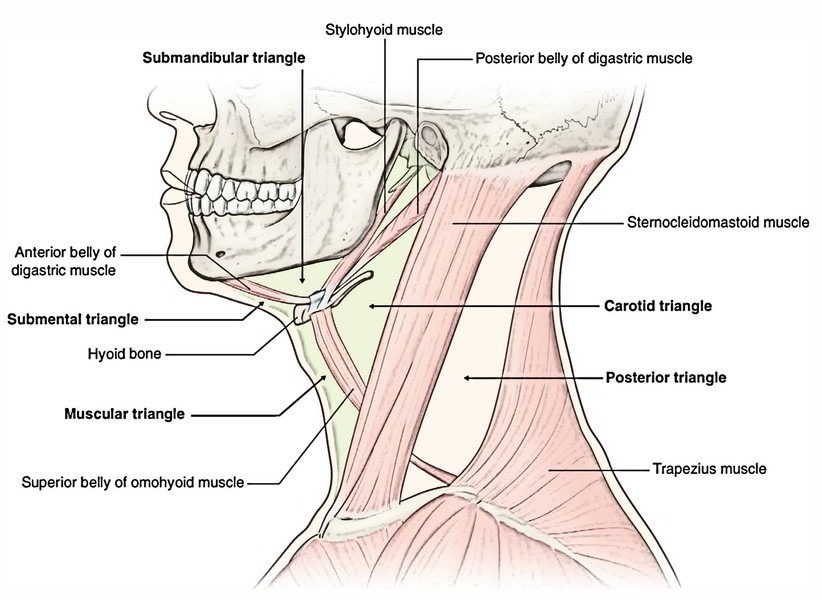
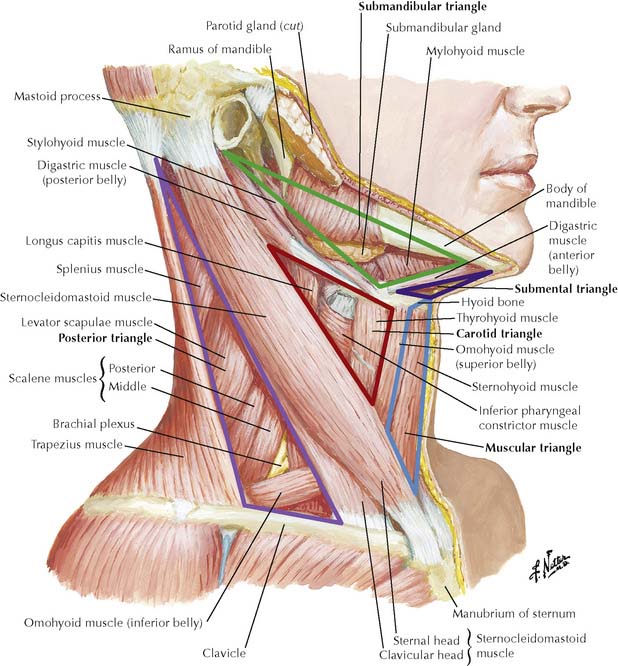
The anterior triangle is bound by the midline of the neck, anterior border of SCM and the inferior border of the mandible. This triangle is further subdivided into four sub-triangles by the hyoid bone, suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles. These sub-triangles are the submandibular, submental, carotid and muscular triangles. Figure 2. The anterior triangle is a region of the neck . Structure The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin. [1] Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor. Anatomy Muscles: Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and Post Belly), mylohyoid, geniohyoid and Stylohyoid. The anterior cervical triangle is bounded by the midline of the neck, the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM), and the inferior border of the mandible [ 3 ]. This triangle is typically subdivided into three paired and one unpaired triangle. The anterior triangles refer to bilateral anatomic subdivisions of the neck comprising the anterior surface of the neck, deep to the superficial cervical fascia and platysma muscle. Laterally, the anterior triangle is bounded by the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Its superior border is the inferior border of the mandible.

Anterior Triangle of Neck Anatomy QA
The neck is divided in two major triangles: anterior and posterior, based mainly on the borders of the sternocleidomastoid, or SCM, and trapezius muscles, as well as other muscular and bony structures found in the neck. These regions provide a clear location regarding the structures, injuries or pathologies involving the neck. The anterior triangle is formed by the inferior border of the mandible, the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid and the sagittal plane in the midline of the neck. It has 4 main subdivisions: The carotid triangle marks the position of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves X & XII. The anterior cervical region or triangle can be topographically located at the anterior portion of the neck. It spans seven levels of cervical vertebrae (C1-7). The anterior triangle is a region bounded superiorly by the inferior border of the mandible, laterally by the anterior median of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and inferiorly by the jugular and clavicular notch of the manubrium. The content of the neck is grouped into 4 neck spaces, called the compartments. Vertebral compartment: contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles.. triangles of the neck. The anterior triangle of the neck is made by the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the inferior border of the mandible and the midline of the neck.
Anterior Triangle of the Neck Earth's Lab
Watch on The sternocleidomastoid muscle obliquely crosses the neck to form the division between the two major neck triangles: anterior triangle and posterior triangle. Both triangles are further divided into sub-triangles. [2] [3] Anterior Triangle Digastric/Submandibular Triangle Carotid Triangle Muscular Triangle Submental Triangle Contain glands, nerves, vessels, and lymph nodes Sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM) divides the neck into the 2 major neck triangles: Anterior triangle: subdivided into smaller triangles Muscular triangle Carotid triangle Submandibular triangle Submental triangle
Contents The anterior triangle is subdivided into three paired triangles and a single midline triangle: Paired triangles: digastric triangle muscular triangle carotid triangle Single midline triangle: submental triangle Boundaries anterior: median line of the neck posterior: anterior margin of sternocleidomastoid muscle Anterior triangle of neck is a large triangular region located on the side on the neck anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Its apex is directed downwards and base upwards. Its boundaries are: Anteriorly: Anterior median line of the neck. Posteriorly: Anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
The Neck Basicmedical Key
The anterior triangle is roofed by the investing layer of deep cervical fascia overlying which is the platysma muscle and subcutaneous fat. The platysma muscle crosses the lower border of the mandible to become continuous with some of the muscles of facial expression. Inferiorly it ends by blending with the thin connective tissue overlying the. The anterior triangle is one of two major neck triangles. It is situated on the front side of the neck. Moreover, it is defined as a triangular-shaped area found anterior to the sternocleidomastoid. The anterior neck triangle has its base directed upward, while its apex faces downward. It is bounded by the following structures:




