Liver Segments (Axial & Coronal) by R. Furman Borst MD; Abdo by Whitney Graff; Anatomía by Diego González; Normals by Noah; ASA 2017 Abdominal anatomy refresher by Craig Hacking Gen Surg by Aaron Ow; Liver Prokop by Stefan Teodoru-Saman; ASA Radiopaedia for sonographers by Craig Hacking Anatomy by Vitalii Rogalskyi; Anatomy by muhammet Segmental anatomy Traditionally, the liver was divided into four anatomical lobes: the right, left, caudate and quadrate lobes.

Couinaud classification of hepatic segments Radiology Reference
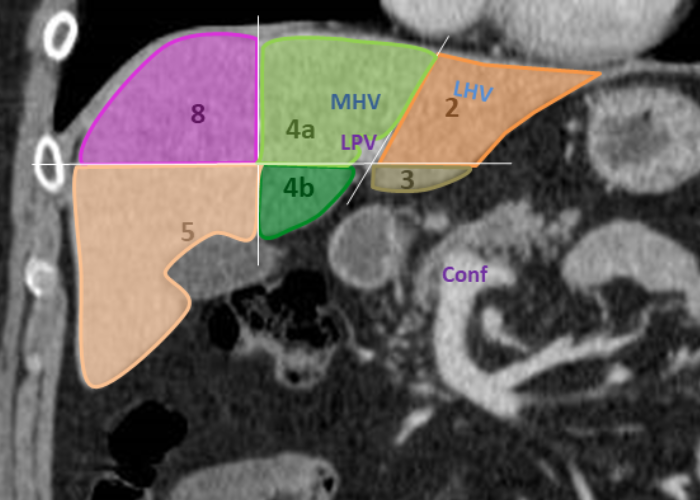
Segments segment 1 (I) is the caudate lobe bounded posterolaterally by the fossa for the inferior vena cava, anteriorly by the ligamentum venosum, and inferiorly by the porta hepatis its inferior portion is subdivided into a lateral caudate process and a medial papillary process 6 may receive its supply from both the right and the left portal vein Segmental anatomy according to Couinaud. Click to enlarge. Couinaud classification The Couinaud classification of liver anatomy divides the liver into eight functionally indepedent segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. 1 case No description provided Article Couinaud classification of hepatic segments The Couinaud classification (French eponym: pronounced kwee-NO) is currently the most widely used system to describe functional liver anatomy. Indications Liver ultrasound is commonly utilized in the evaluation of various hepatic conditions. The most frequent indications include 1,2: screening for hepatic disease in at-risk populations (e.g. hepatocellular cancer screening in cirrhotic patients) investigation of abnormal liver function tests

Couinaud classification of hepatic segments Radiology Reference
Liver volume is assessed primarily via organ segmentation of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. The goal of this paper is to provide an accessible overview of liver segmentation targeted at radiologists and other healthcare professionals. Methods Liver lobules are the basic functional units of the liver. They are classically described ('classic lobules') as hexagonal structures made of six vertically aligned portal canals with a central vein. sectorial branches will separate each sector of the right liver into two segments (5/8 and 6/7, respectively). In practice, it is convened that all these separations (sectorial and segmental) in the right liver occur at the level of the portal bifurcation. In the left liver, the left portal branch describes an arch towards the round ligament. Hepatic segmentation Segmentatio hepatis Definition The hepatic segmentation (lobes, parts, divisions and segments) is the oganization of the liver into parts, divisions and segments.
Radiopaedia CTscan Hepatic segments coronal section labels
In a portal venous phase CT, the right, middle, and left hepatic veins are usually filled with contrast-mixed blood and can be seen emptying into the inferior vena cava, which is found along the back side of the liver. The portal and hepatic veins divide the liver into segmental anatomy that allows radiologists and surgeons to be very specific. The authors developed a simplified description of the segmental anatomy of the liver on the basis of the Couinaud nomenclature. This approach was demonstrated with normal in vivo sonographic images and livers dissected in corresponding planes. The branches of the portal vein, which lead to the center of individual segments, are used as key landmarks in the determination of segmental location.
The most widely accepted model for liver segmental anatomy was first described by Couinaud (Couinaud 1957), and then popularised by Bismuth (Bismuth 1982; Bismuth et al. 1982; Majno et al. 2014), and is now the most commonly used in Europe. According to these authors, the liver is composed of eight anatomical segments, characterised by. A liver segment is one of eight segments of the liver as described in the widely used Couinaud classification (named after Claude Couinaud) in the anatomy of the liver.This system divides the lobes of the liver into eight segments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein, arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the caudate lobe.

Anatomy of the liver segments Liver anatomy, Diagnostic medical
Note the liver segments (labeled in B) and the right portal vein ligation (yellow arrow in A). (C) Illustration of the second stage of ALPPS shows the areas of tumor resection (arrowheads and dashed lines) performed during the first stage in the FLR. Right hepatectomy or right trisectionectomy is performed after 10-20 days (ie, the waiting. 1/4 Synonyms: none The liver is the primary processing facility of the body. The majority of the substances that are ingested, and subsequently digested, are absorbed from the lumen of the small intestines and passed to the liver by way of the hepatic portal vein. This organ is not only special due to its function, but also due to its organization.



