The phase current I in amps (A) is equal to the power P in watts (W), divided by 3 times the power factor PF times the line to neutral RMS voltage VL-N in volts (V): I(A) = P(W) 3 × PF × VL-N(V) The power factor of resistive impedance load is equal to 1. Environmental Science Energy Production What Are Amps, Watts, Volts and Ohms? By: Dave Roos | Updated: Oct 3, 2022 Some pylons near a power transform station at sunrise. More voltage in an electrical system makes more current flow. dowell/Getty Images
Volts, Amps, & Watts Explained! YouTube
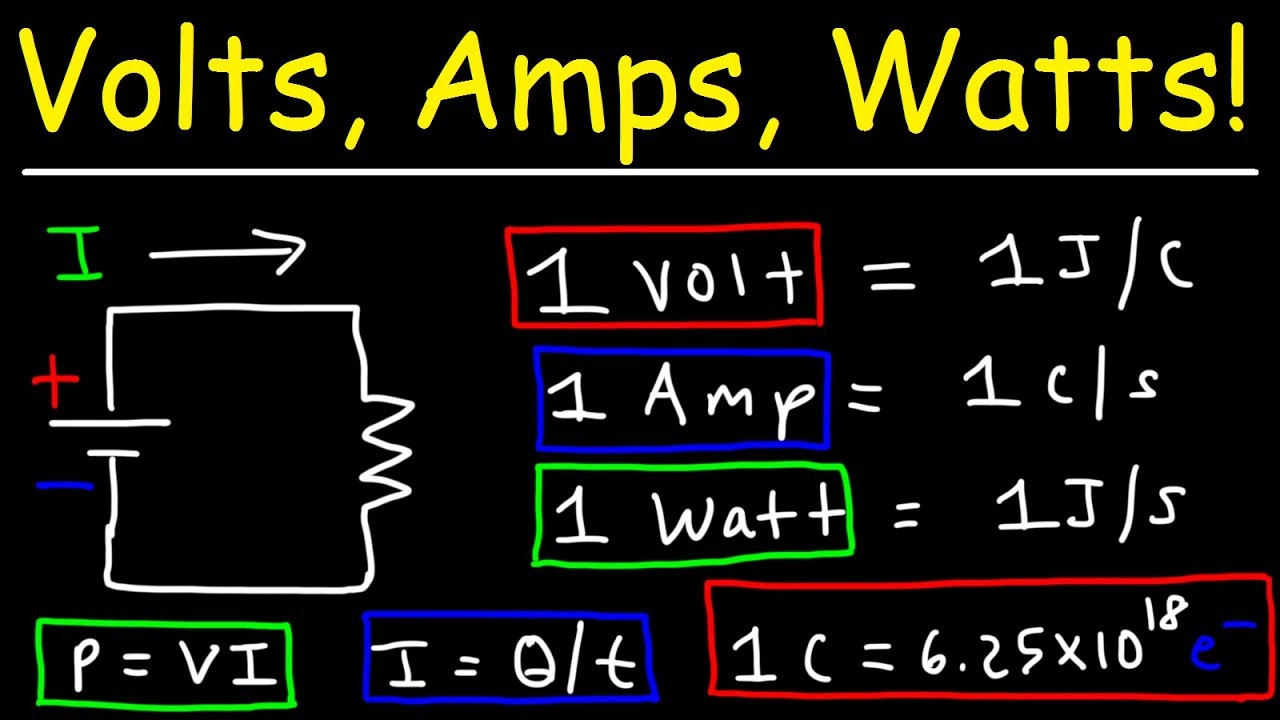
Volts are the unit of measure for electrical voltage and are represented by the letter "V" in electrical equations. Voltage is the difference in electrical potential, or the number of electrons, between any two points in an electrical circuit. In our water analogy, voltage is equivalent to water pressure. To convert watts (electrical power) to amps (electrical current) at a fixed voltage, you can use a variation of Watt's Law formula: Power = Current × Voltage (P = IV). By working backwards, we get the equation: amps = watts ÷ volts, which can be used to convert watts to amps. Example calculation To convert amps (electrical current) to watts (electrical power) at a fixed voltage, you can use the equation: watts = amps × volts. Simply multiply your amps figure by the voltage. Example calculations 15 amps × 120 volts = 1800 watts 20 amps × 120 volts = 2400 watts Amps to watts at 120V (AC) Amps to watts at 12V (DC) 1W = 1V * 1A So what is power? Power, in an electric circuit, is the rate of transferring electrical energy per unit of time. Learn more in the electrical power calculator. Ohm's law: volts, amps, and ohms Our watt calculator uses a second formula - Ohm's law. It states that: Voltage = Current * Resistance, or V = I * R
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-difference-between-watts-vs-volts-4767057_V3-9bb4bdf5c97d4f758cbc185d40376e89.png)
Watts Vs Volts Understand The Difference Riset
What Is a Volt? Voltage is the pressure that forces electric current to flow though a wire. In North America, utility systems typically deliver electricity to your home's service panel at 240 and 120 volts. The Watt is the SI unit of power -- Volts times Amperes in direct-current systems, but when dealing with alternating current, if you introduce a reactive (non-resistive) load, Volts and Amps are. Formal definitions of the standard electrical units: ampere, coulomb, charge on an electron, and the volt. Written by Willy McAllister. Electrical units can be described in a formal manner, and that's what we do here. The standard electrical units are defined in a specific order. The ampere is defined first. Volt Ampere to Kilojoule/minute. Instant free online tool for volt ampere to watt conversion or vice versa. The volt ampere [V*A] to watt [W] conversion table and conversion steps are also listed. Also, explore tools to convert volt ampere or watt to other power units or learn more about power conversions.
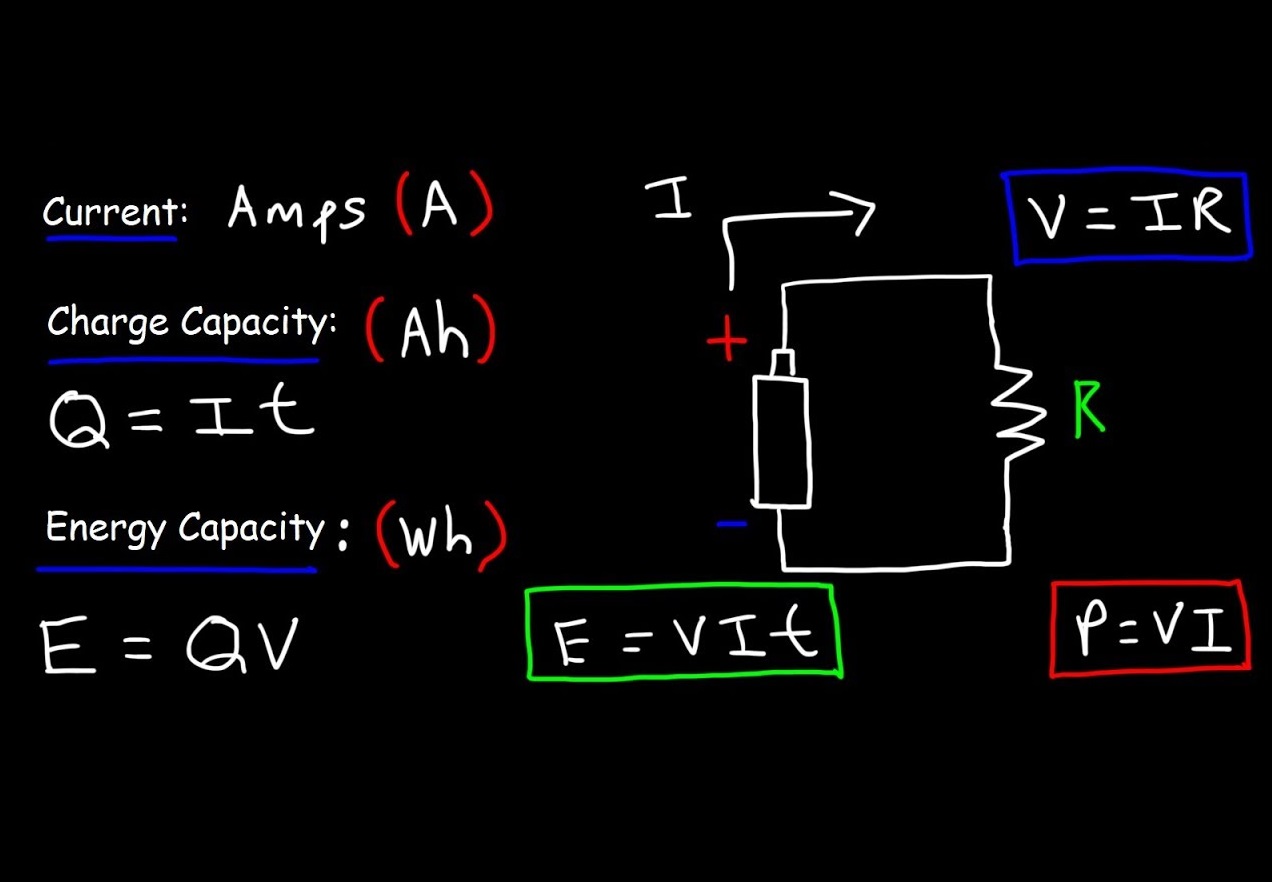
What Does Volts, Watts, Ampere and Amp Hours Mean?
The SI unit of voltage is a volt, the unit of amperage is an ampere (usually shortened to amp), and the unit of power is a watt. All of these units from volts and amps to watts describe the voltage, amperage, and power respectively since they are shorter and easier to be pronounced. You have a 12 Volt power supply that delivers 1 Amp of current. Fill in the Volts and Amps fields to find the Watts. Example 2. The AC24-40 power supply is a 24V AC power supply that can power up to 40 VA. Enter 24 under volts; Enter 40 under watts; Click calculate; You get 1.66 in this example. Thus, the AC24-40 can supply up to 1.6 Amps at.
Watts = Amps * Volts. To calculate watts, we need both the amperage and voltage (usually either 120V or 220V). LearnMetrics has prepared handy amps to watts calculator you can freely use. Below the A to W calculator you will also find a table with calculated watts from amps for 120V and 220V voltage systems. To illustrate how amps to watts. The volt-ampere (SI symbol: VA, sometimes V⋅A or V A) is the unit of measurement for apparent power in an electrical circuit.It is the product of the root mean square voltage (in volts) and the root mean square current (in amperes). Volt-amperes are usually used for analyzing alternating current (AC) circuits. In direct current (DC) circuits, this product is equal to the real power, measured.
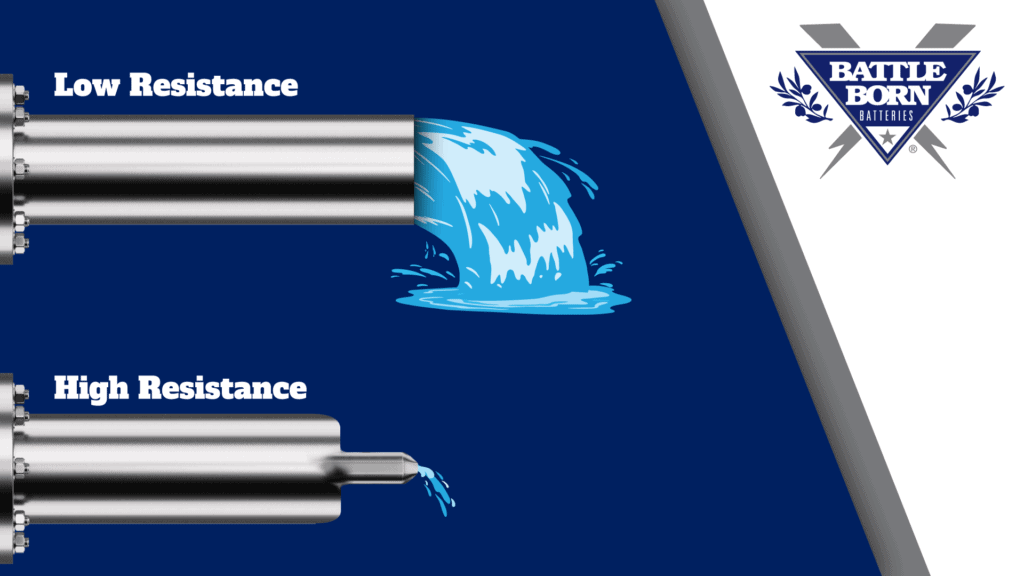
Amps, Volts, Watts Differences Explained In Simple Terms
For three-phase AC circuits where the line-to-neutral voltage is known, the formula to convert watts to amps is: I (A) = P (W) V L-N (V) × PF × 3. The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, the power factor PF, and 3. This formula calculates the current for all three. Basic Guide to Electricity Welcome to your guide to the basics of electricity. The four most basic physical quantities in electricity are: Voltage (V) Current (I) Resistance (R) Power (P) Each of these quantities is measured using different units: Voltage is measured in volts (V) Current is measured in amps (A) Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-difference-between-watts-vs-volts-4767057_V3-9bb4bdf5c97d4f758cbc185d40376e89.png)


