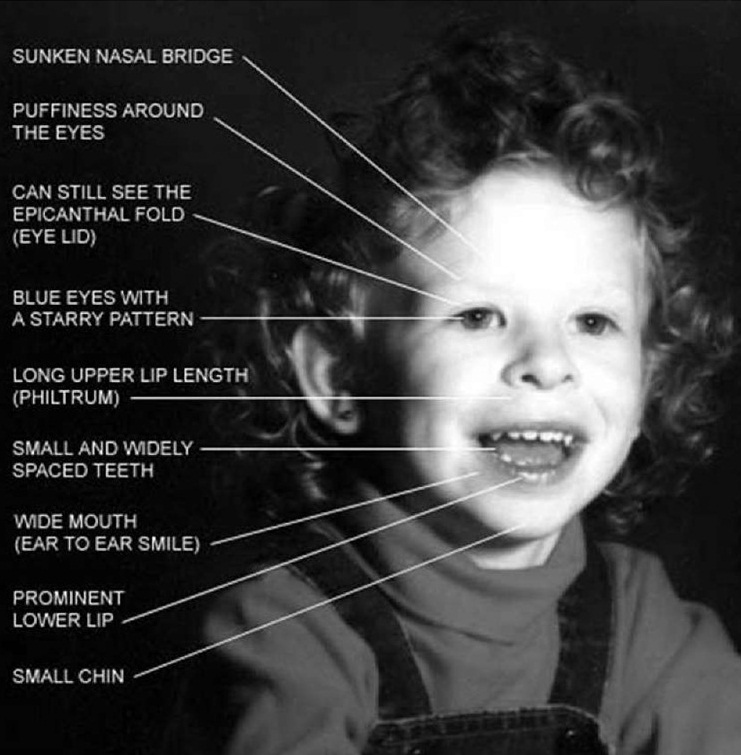
Symptoms of Williams syndrome include: Chronic ear infections and/or hearing loss. Dental abnormalities, such as poor enamel and small or missing teeth. Elevated calcium level in the blood. Endocrine abnormalities: hypothyroidism, early puberty and diabetes in adulthood. Farsightedness. Feeding difficulties in infancy. Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed in people with WS, with particular challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing.
Williams Syndrome Pictures, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Life Expectancy HealthMD
Causes. Symptoms. Facial Features. Heart and Blood Vessels. 4 min read. Williams syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that causes a variety of symptoms and learning issues. Children with this. Musculoskeletal abnormalities associated with Williams syndrome may include depression of the breastbone (pectus excavatum), abnormal side-to-side or front-to-back curvature of the spine (scoliosis or kyphosis), or an awkward gait. In addition, most affected individuals have mild to moderate mental retardation; poor visual-motor integration. Virtually all (98-99%) persons with typical features of Williams syndrome will have a deletion of the elastin gene. In more technical terms: Williams syndrome is the result of a deletion of the 7q11.23 region of chromosome #7 containing 26-28 genes, including the elastin gene. Elastin is the "marker gene" for Williams syndrome. Williams syndrome is a developmental disorder that affects many parts of the body. This condition is characterized by mild to moderate intellectual disability or learning problems, unique personality characteristics, distinctive facial features, and heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) problems. People with Williams syndrome typically have.

Mare (4) heeft het syndroom van WilliamsBeuren Documentaire Familiefotografie
Williams syndrome (WS, OMIM #194050 [ 1 ]), also known as Williams-Beuren syndrome, is a multisystem, contiguous gene deletion syndrome caused by hemizygous deletion of 1.5 to 1.8 Mb on chromosome 7q11.23. The epidemiology, genetics, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of WS are discussed here. Williams syndrome (WS) is a rare genetic disorder. People with WS may have mild to moderate delays in their cognitive development (ability to think and reason) or learning difficulties. They also may have a distinctive facial appearance and a unique personality that combines over-friendliness and high levels of empathy with anxiety. Williams syndrome (WS) is a genetic condition that is present at birth and can affect anyone. It is characterized by medical problems, including cardiovascular disease, developmental delays, and learning challenges. These often occur side by side with striking verbal abilities, highly social personalities, and an affinity for music. WS occurs equally in males and females and in all cultures. Williams-Beuren syndrome, a multisystem disorder caused by the deletion of a chromosome region of 1.5 million to 1.8 million base pairs containing 26 to 28 genes, is a disorder of microdeletion.

Williams Syndroom
Williams syndrome (WS) is a rare genetic and neurodevelopmental disorder. WS often presents at birth when the child is discovered to have supra-vascular aortic stenosis.[1] The child also shows distinctive facies (elfin-like features), hypercalcemia, connective tissue abnormalities, growth abnormalities, intellectual disability, behavior deficits, and a gregarious personality.[2] Introduction. Williams syndrome (WS), also referred to as Williams-Beuren syndrome (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man 194050), is a congenital, multisystem disorder involving the cardiovascular, connective tissue, and central nervous systems. 1 WS occurs in ≈1 in 10 000 live births 2 as a result of the de novo deletion of ≈1.55 to 1.83 Mb.
Ali SM, Shun-Shin GA: Abnormal extraocular muscle anatomy in a case of Williams-Beuren Syndrome. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:196-197. Bela C, Klainguti G: Abnormal extraocular muscle insertion in Williams Beuren syndrome (WBS). Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014; 382-383. Holmström G, Almond G, Temple K, Taylor D, Baraitser M: The iris in Williams syndrome. Williams syndrome (WS) is characterized by developmental delay, intellectual disability (usually mild), a specific cognitive profile, unique personality characteristics, cardiovascular disease (supravalvar aortic stenosis, peripheral pulmonary stenosis, hypertension), connective tissue abnormalities, growth deficiency, endocrine abnormalities (early puberty, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria.

marciano's ziekte.. Williams Syndroom
Williams syndrome is caused by a person missing more than 25 genes from a specific area of chromosome 7 (a "deletion"). The loss of these genes contributes to the characteristic features. Although Williams syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition, most cases are not inherited and occur sporadically in people with no family history of. Contact us. 243 Broadway #9188 Newark, NJ 07104.
[email protected]. 248.244.2229 800.806.1871 248.244.2230 fax



