Alternating current (AC) flows half the time in one direction and half the time in the other, changing its polarity 120 times per second with 60-hertz current. A welder should know the meaning of polarity, and recognize what effect it has on the welding process. Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as the direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tend to be confusing. This section is written in an attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity.

SIMPLY ELECTRICAL STUDY Some Examples with AC Circuits
Does AC Power have Polarity? Ask Question Asked 9 years, 2 months ago Modified 5 months ago Viewed 43k times 16 When I run 24VAC into a full wave bridge rectifier followed by a 220uF electrolytic capacitor to turn it into ~32VDC, the source has two wires. Does it matter in what order I connect the AC wires to the input to the bridge rectifier? It is a constant current. But an alternating current (AC) changes its polarity from every half cycle. For 50Hz current, the waveform changes its polarity at each 10ms. And the polarity changes 100 times in one second. AC Polarity In a DC system, the magnitude and polarity are sufficient to describe. Alternating current ( AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. What is Alternating Current (AC)? PDF Version Most students of electricity begin their study with what is known as direct current (DC), which is electricity flowing in a constant direction, and/or possessing a voltage with constant polarity.
Identifying the Polarity during a AC Supply of current (English) YouTube
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity. When we measure a voltage, we have a choice in how we connect a. Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity. When we measure a voltage, we have a choice in how we connect a. Measurements of AC Magnitude. So far we know that AC voltage alternates in polarity and AC current alternates in direction. We also know that AC can alternate in various ways, and by tracing the alternation over time, we can plot it as a "waveform.". We can measure the rate of alternation by measuring the time it takes for a wave to evolve. Ac Important Polarity In summary, the correct polarity of AC matters because it affects the direction of current flow, which can be important in certain circuits. This is why it is important to connect live to live and neutral to neutral in wall outlets, even though AC itself has no polarity.

Induced AC current and field using a signal excitation coil in... Download Scientific
Being that alternating current has no set "polarity" as direct current does, these polarity markings and their relationship to phase angle tends to be confusing. This section is written in the attempt to clarify some of these issues. Voltage is an inherently relative quantity. AC stands for "Alternating Current," meaning voltage or current that changes polarity or direction, respectively, over time. AC electromechanical generators, known as alternators, are of simpler construction than DC electromechanical generators. AC and DC motor design follows respective generator design principles very closely.
Alternating current, or AC, reverses polarity at a specified period. This polarity switch is a product of the AC power generation process. AC Power Generation An electromechanical device that produces AC power is called an alternator. Chapter 1 Basic AC Theory AC Waveforms PDF Version When an alternator produces AC voltage, the voltage switches polarity over time, but does so in a very particular manner. When graphed over time, the "wave" traced by this voltage of alternating polarity from an alternator takes on a distinct shape, known as a sine wave: Figure below
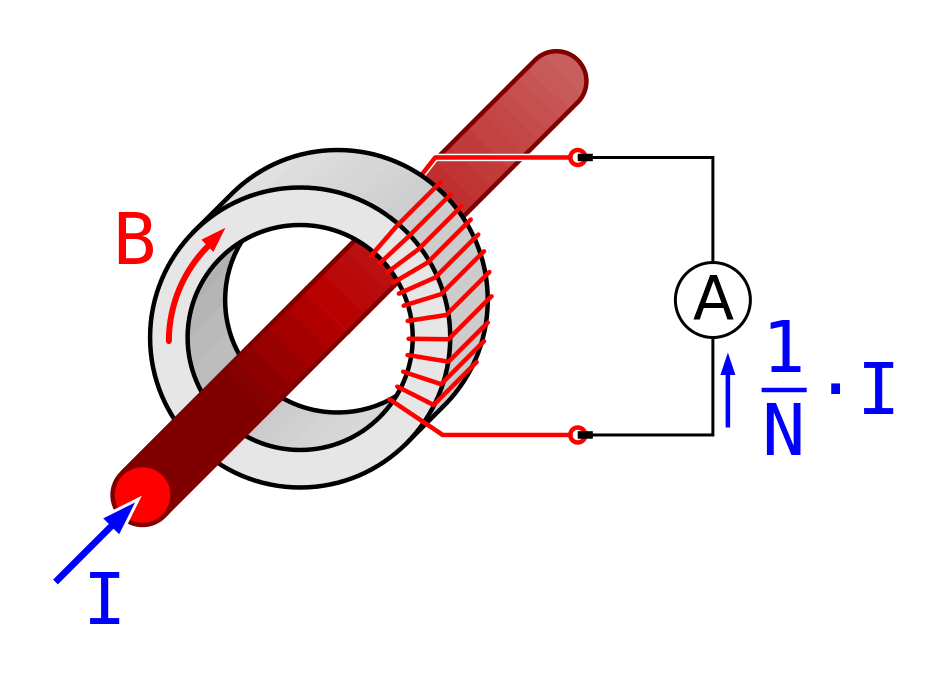
Current Transformer Basics Understanding Ratio, Polarity, and Class
AC, or Alternating Current, is a type of electric current that periodically reverses direction, oscillating between positive and negative values. In an AC circuit, the electric charge flows first in one direction and then in the opposite direction, constantly reversing its direction at a certain frequency. The periodic change in polarity in AC produces a magnetic effect crucial for these devices, lacking in DC.. (DC) power, but the power supplied to the computer from an electrical outlet is alternating current (AC). The power supply unit (PSU) in a computer is responsible for converting the incoming AC power from the wall outlet into the.




