Witteveen-Kolk syndrome is caused by specific changes (known as pathogenic variants) to, or a deletion of, a gene called SIN3A (SIN3A is an abbreviation of the gene's full name, switch-insensitive 3 transcription regulator family member A). The SIN3A gene is located on the long 'q' arm of chromosome 15 in a region called 15q24.2 (see below). Witteveen-Kolk syndrome, also known as WITKOS and 15q24 microdeletion syndrome, is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay/intellectual disability, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature. The syndrome is caused by loss of function of switch‐insensitive 3 transcription regulator family member A ( SIN3A ).

WITTEVEENKOLK SYNDROME Semantic Scholar
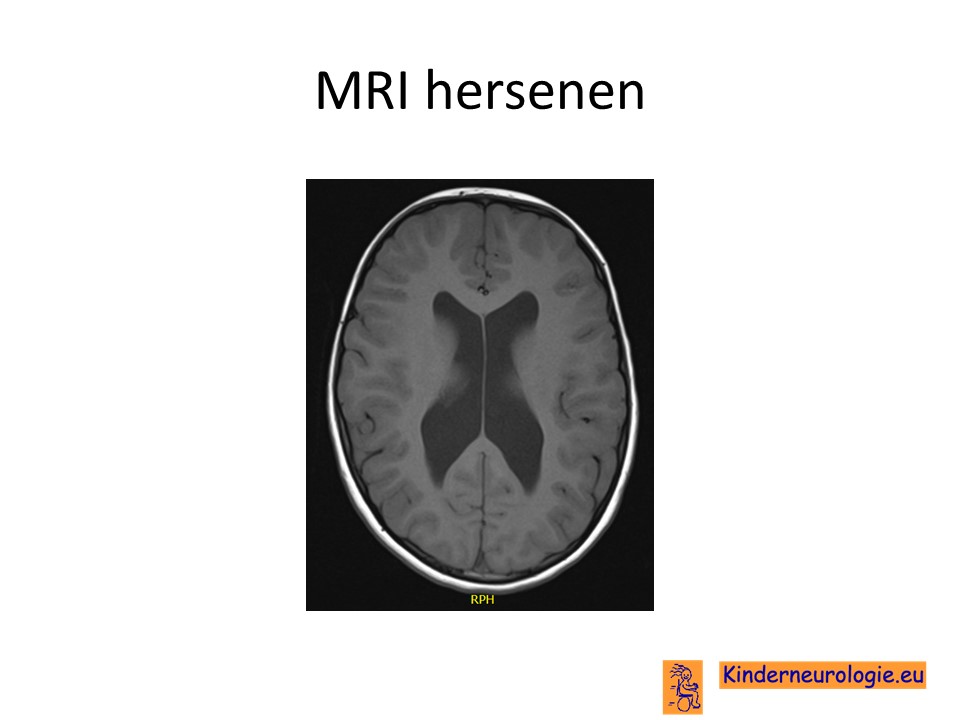
Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is an autosomal dominant disorder with characteristic distinctive facial features, microcephaly, short stature, and mildly impaired intellectual development with delayed cognitive and motor development and subtle anomalies on MRI-brain imaging (summary by Balasubramanian et al., 2021 ). Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (OMIM 613406) is a recently defined neurodevelopmental syndrome caused by heterozygous loss-of-function variants in SIN3A. We define the clinical and neurodevelopmental. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is an autosomal dominant disorder with characteristic distinctive facial features, microcephaly, short stature, and mildly impaired intellectual development with delayed cognitive and motor development and subtle anomalies on MRI-brain imaging (summary by Balasubramanian et al., 2021). Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay/intellectual disability, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature. The syndrome is caused by loss of function of switch-insensitive 3 transcription regulator family member A (SIN3A). Regarding behavioral functioning, Autism Spectrum.
Kinderneurologie.eu
Witteveen-Kolk syndrome. Disease definition A rare genetic neurodevelopmental syndrome characterized by mild intellectual disability, developmental delay, dysmorphic facial features, growth- and feeding problems, hypotonia, epilepsy, behavioral problems and a variety of congenital abnormalities. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (OMIM 613406) is a recently defined neurodevelopmental syndrome caused by heterozygous loss-of-function variants in SIN3A. We define the clinical and neurodevelopmental phenotypes related to SIN3A-haploinsufficiency in 28 unreported patients. Patients with SIN3A variants adversely affecting protein function have mild. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (OMIM 613406) is a recently defined neurodevelopmental syndrome caused by heterozygous loss-of-function variants in SIN3A.We define the clinical and neurodevelopmental phenotypes related to SIN3A-haploinsufficiency in 28 unreported patients.Patients with SIN3A variants adversely affecting protein function have mild intellectual disability, growth and feeding difficulties. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay/intellectual disability, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature. The syndrome is.

WITKOS (WitteveenKolk Syndrome) and what it is YouTube
Purpose: Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare, autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder caused by heterozygous loss-of-function alterations in the SIN3A gene. WITKOS has variable expressivity that commonly overlaps with other neurodevelopmental disorders. In this study, we characterized a distinct DNA methylation epigenetic signature (episignature) distinguishing WITKOS from. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay/intellectual disability, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature. The syndrome is caused by loss of function of switch-insensitive 3 transcription regulator family member A (SIN3A). Regarding behavioral functioning, Autism Spectrum.
Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a neurodevelopmental condition, the first case described in 2016, and is characterized by distinctive facial traits, microcephaly, small height, modest intellectual delay, delayed development, ventriculomegaly, corpus callosal atrophy, cerebellar atrophy on MRI-brain imaging. This condition results from frameshift and missense mutations in switch-insensitive. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay/intellectual disability, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature. The syndrome is caused by loss of function of switch‐insensitive 3 transcription regulator family member A ( SIN3A ).

Anterior megalophthalmos in sisters with WitteveenKolk syndrome Journal of American
Witteveen-Kolk syndrome (WITKOS) is a rare, autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder caused by heterozygous loss-of-function alterations in the SIN3A gene. WITKOS has variable expressivity that commonly overlaps with other neurodevelopmental disorders. In this study, we characterized a distinct DNA methylation epigenetic signature (episignature) distinguishing WITKOS from unaffected. Witteveen-Kolk syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by intellectual disability, developmental delay and dysmorphic facial features including a long face with prominent forehead, depressed nasal bridge, long-smooth philtrum and malformed ears. Skeletal abnormalities, microcephaly and malformation of the brain are other findings.




