A comparative analysis of three recognized CSR models—represented graphically as a pyramid, 4 intersecting circles, 5 and concentric circles 6 —might help locate and clarify ambiguities through revealing systematic differences in their underlying assumptions, conceptual structure, methodological tools, and managerial implications. The concentric zone model, also known as the Burgess model or the CCD model, is one of the earliest theoretical models to explain urban social structures. It was created by sociologist Ernest Burgess in 1925. [1] [2] The model
How Do Cities Grow? PropertyMetrics
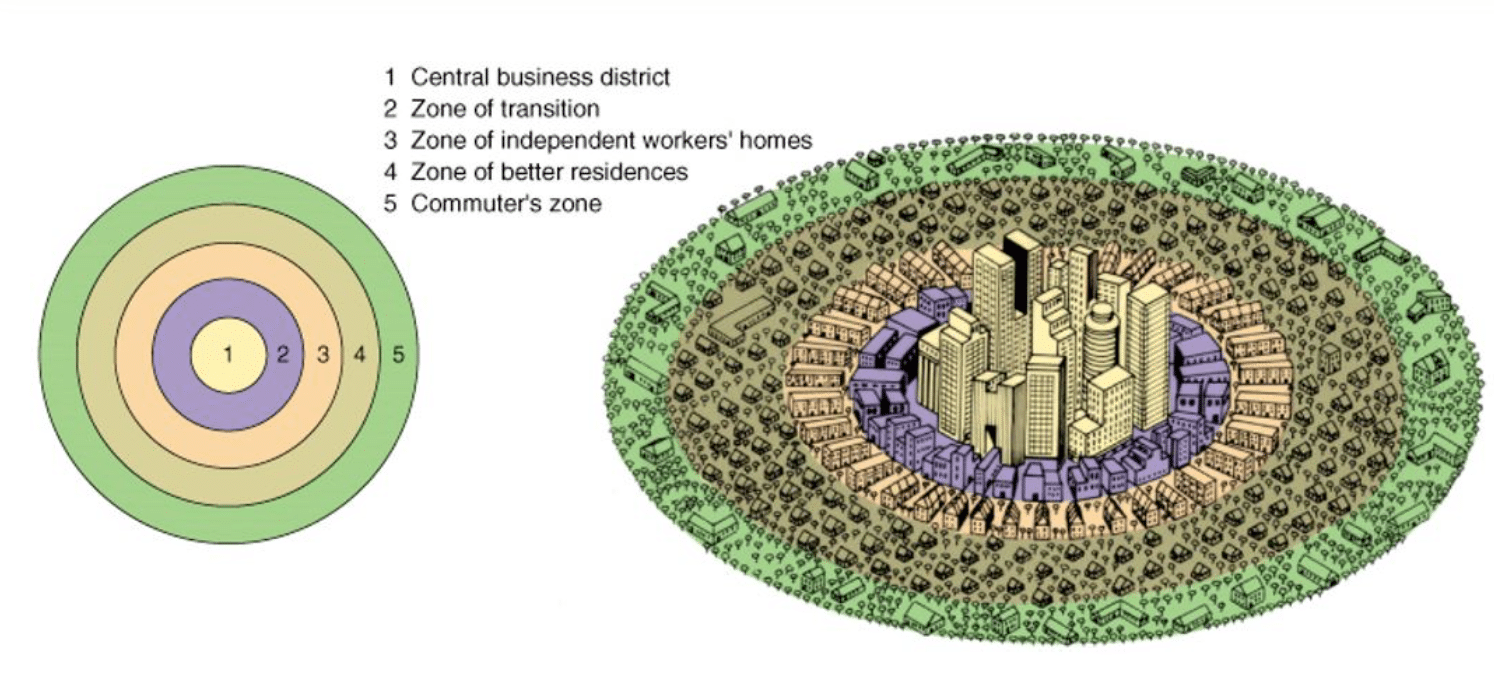
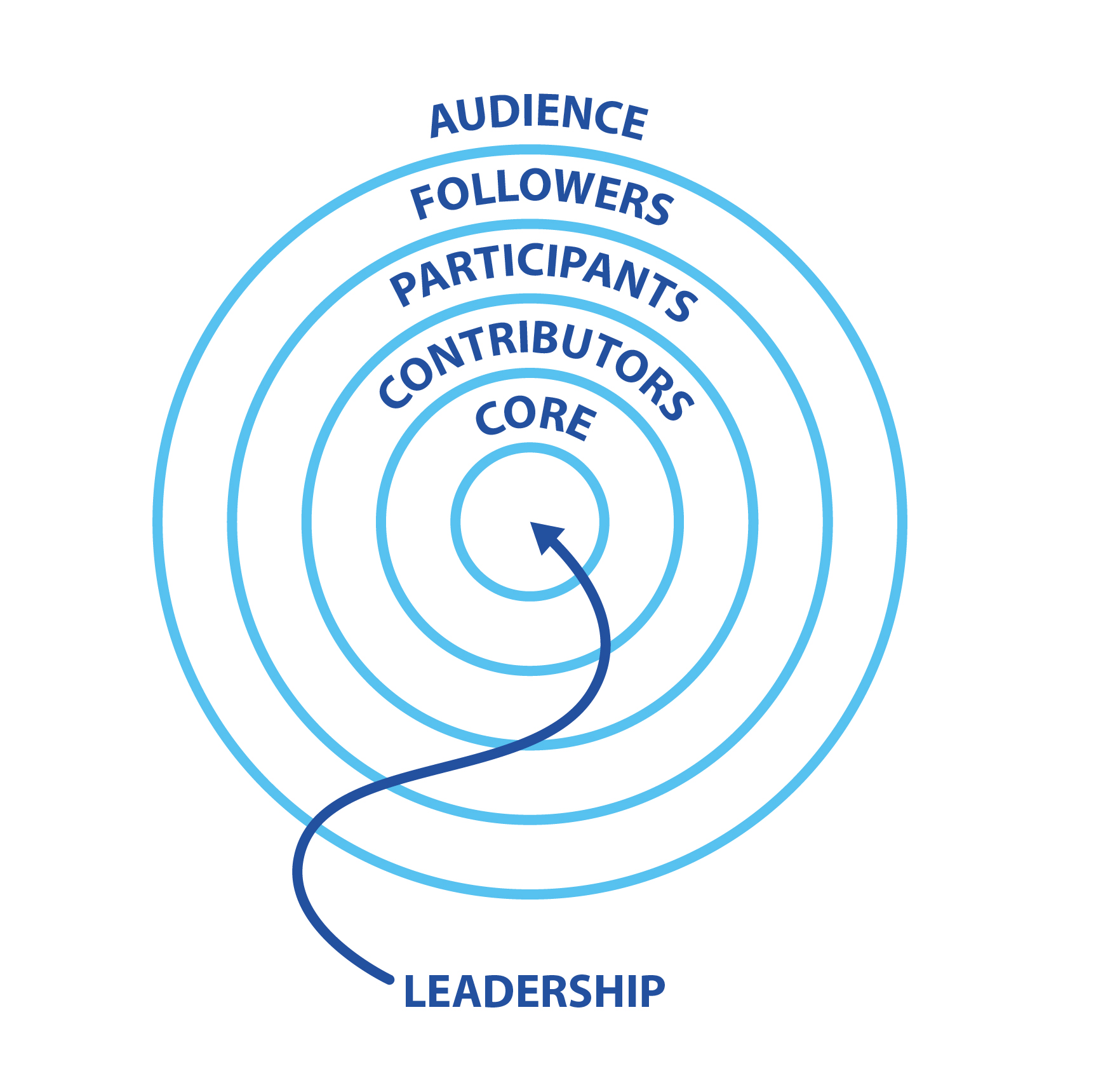
What is the Concentric Circle Model? The concentric zone model, commonly referred to as the Burgess model, explains urban social structures in terms of socioeconomic clusters grouped in concentric circles around the city center. It was proposed by sociologist Ernest Burgess in 1925. The Concentric Circles model | Centre For Effective Altruism When describing the target audience of our projects, it is useful to have labels for different parts of the community. Common language can help us communicate better internally, and so make better decisions. The concentric circles model adopts an assumption that cultural content springs from the incorporation of creative ideas into the production and / or presentation of sound, text and image and. The concentric circles model of the cultural industries. . Characteristics of the cultural workforce: Australia, Canada, New Zealand, UK, USA. . Employment in creative/cultural occupations as a.
Concentric circles clipart 20 free Cliparts Download images on Clipground 2023
I next present the three CSR models beginning with a critical analysis of Carroll's CSR pyramid, a dominant model that has enjoyed wide popularity among business and society scholars; I will then examine the intersecting circles (IC) model, a CSR configuration representing overlapping responsibility areas; I will conclude with the concentric circ. David Throsby. This paper examines the assumptions and structure of the concentric circles model of the cultural industries. Empirical data for Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the UK and the US are used to illustrate the model's key characteristic: the proposition that the cultural content of the output of the cultural industries declines as. Concentric circle model of the three pillars of sustainability | Download Scientific Diagram - uploaded by Content may be subject to copyright. Concentric circle model of the three pillars of. This view of CSR is consistent with what Geva calls "concentric-circle model of CSR", which this researcher identifies as preferable to Archie Carroll's pyramid of CSR and the "intersecting circles model of CSR".Carroll presents a view of CSR according to which it encompasses four categories of responsibilities: economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic.
Concentric Circles and Grid Patterns
The Three-Circle Model of Sustainability The 1987 UN report Our Common Future launched the word "sustainability" into vernacular use. The report defined "sustainable development" as a good thing, meaning "satisfying the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs". The concentric circles model adopts an assumption that cultural content springs from the incor-poration of creative ideas into the production and/or presentation of sound, text and image and that.
Figure 1: The Intersecting Circles Source: Schwartz and Carroll (2003) According to Kanji and Agrawal (2016) CSR is incomplete without the firm's philanthropic acts. In 1971, the Committee for Economic Development issued a statement leading to the growth of the Concentric Circles Model of CSR incorporating the philanthropic circle. The concentric circle model and the future of organizational thinking. The concentric circle model is an organizational way of thinking. It places the residents of your world in a ripple effect.
The Concentric Circles model Centre For Effective Altruism
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a self-regulating business strategy that helps businesses to be socially responsible and accountable, to their stakeholders and to the public. Several CSR models have been formulated over the years. The purpose of these models is to design and execute the CSR process and to enable its monitoring and control. The concentric zone model is a theory used in human geography to explain the patterns of urban land use. The model was first proposed by sociologist Ernest Burgess in 1925 and has since been refined by other researchers. The concentric zone model posits that cities grow outward from a central business district in a series of rings.




