Whenever you look at an adult elbow x-ray, review: alignment fat pads for effusion bony cortex Alignment Check the anterior humeral line: drawn down the anterior surface of the humerus should intersect the middle 1/3 of the capitellum if it does not, think: distal humeral fracture Check the radiocapitellar line: drawn along the radial neck The sail sign On the lateral radiograph, inspect for the displacement of the anterior and posterior fat pads embedded in the two layers of the joint capsule. The anterior fat pad is normally seen as a faint line running with the distal humerus, whilst the posterior fat pad is not seen in normal radiographs.

Imaging of Elbow Fractures and Dislocations in Adults in 2023 Radiology student, Human anatomy
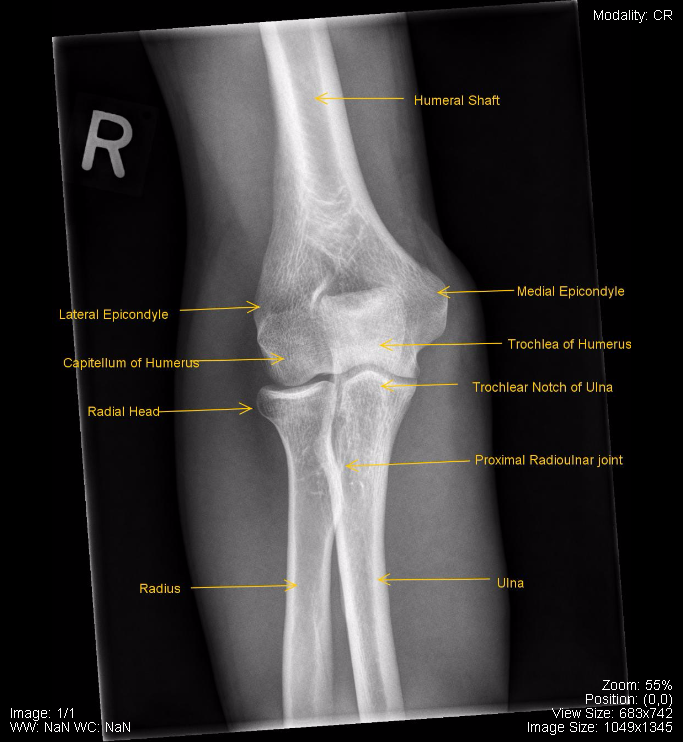
Oblique Elbow. Humerus (shaft) Lateral supraepicondylar ridge. Lateral epicondyle. Capitellum of humerus. Radial fossa. Medial supraepicondylar ridge. Medial epicondyle. Trochlea of humerus. An elbow X-ray is a medical test that produces an image of the inside of your elbow. The image displays the inner structure ( anatomy) of your elbow in black and white. An elbow X-ray shows your soft tissues and elbow bones. Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data The lateral elbow view is part of the two view elbow series, examining the distal humerus, proximal radius and ulna. It is deceptively one of the more technically demanding projections in radiography 1-3. Elbow x-rays are indicated for a variety of settings including: trauma bony tenderness suspected fracture of the proximal radius and ulna suspected fracture of the distal humerus radial head dislocations obvious deformity detecting joint effusions arthritis infection Projections Standard projections AP
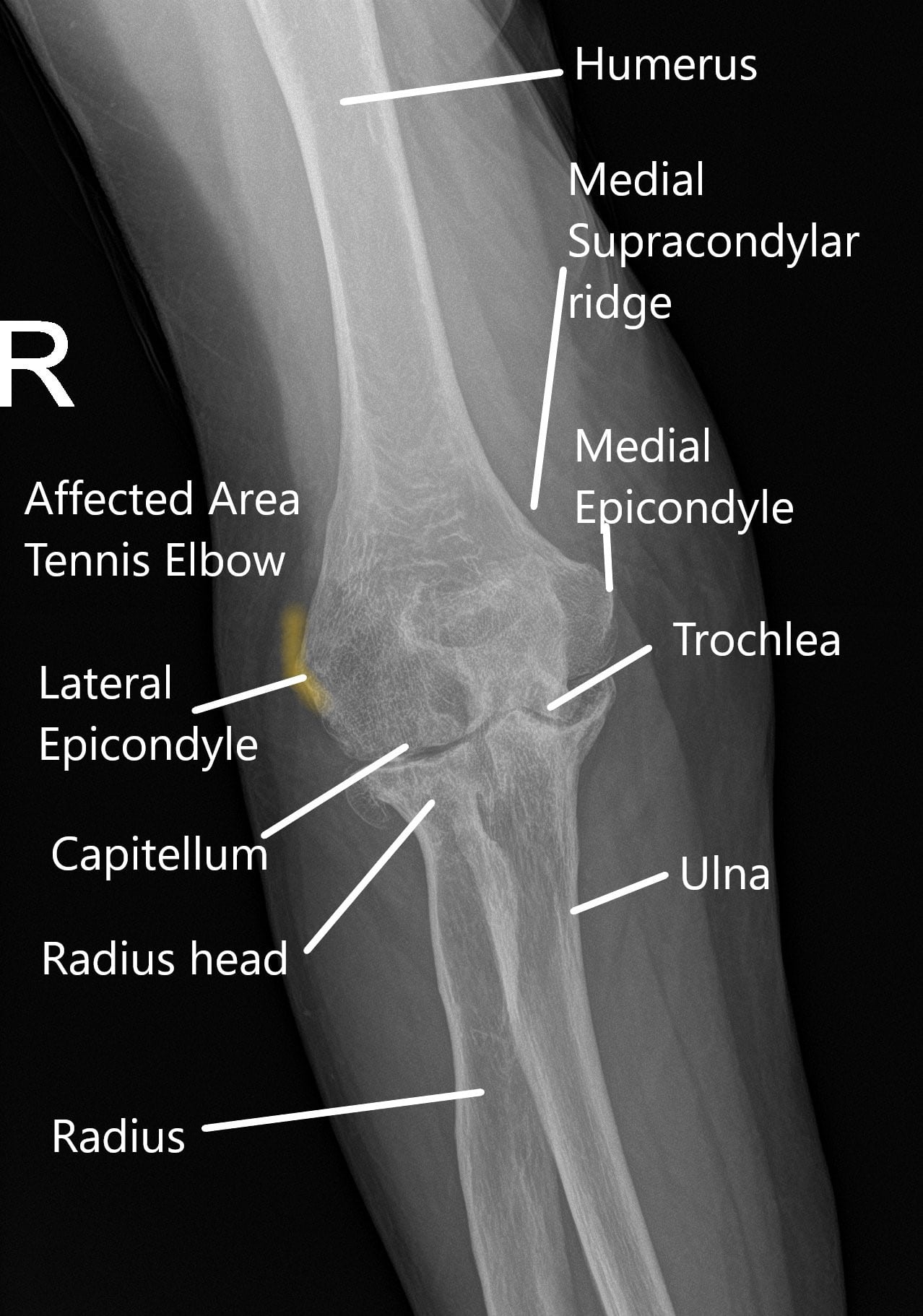
Tennis Elbow Joint Pain, Causes and Management Complete Orthopedics
How to Read Emergency Images How to read an elbow x-ray Fractures lines can be difficult to visualize after acute elbow injury, particularly in children. Below are eight sequential steps to aid in the radiographic recognition of occult signs of injury. An elbow series is the standard series of radiographs that are performed when looking for evidence of fracture, dislocation or elbow joint effusion following trauma. Reference article This is a summary article. For more information, you can read more in-depth reference articles: elbow series (adults), elbow series (pediatrics). Summary indications 7.2K Description Labeled Elbow XRay Anatomy - Lateral View #Anatomy #Radiology #Elbow #XRay #Lateral #Labeled Contributed by Dr. Gerald Diaz @ GeraldMD Board Certified Internal Medicine Hospitalist, GrepMed Editor in Chief 🇵🇭 🇺🇸 - Sign up for an account to like, bookmark and upload images to contribute to our community platform. An approach to the traumatic adult elbow x-ray. 1. Adequacy/Alignment. Check for a "Figure of 8" to ensure that this is a true lateral view. Figure 1: Lateral x-ray of the elbow demonstrating "figure of 8" in blue. Case courtesy of Dr. Craig Hacking, Radiopaedia.org.
EPOS™
Indications This view is clinically indicated for trauma, chronic discomfort or infection of the elbow joint. It aids in visualizing fractures and/or dislocations of the elbow joint, in addition to osteomyelitis and arthritic changes. An X-ray of the elbow is a frequently conducted examination and is mainly used for diagnosing a fracture. Some of the key topics are radial head fracture, supracondylar humeral fracture, anterior/posterior fat pad and elbow luxation. Prior to this module, it is wise to read the Fracture General Principles module.
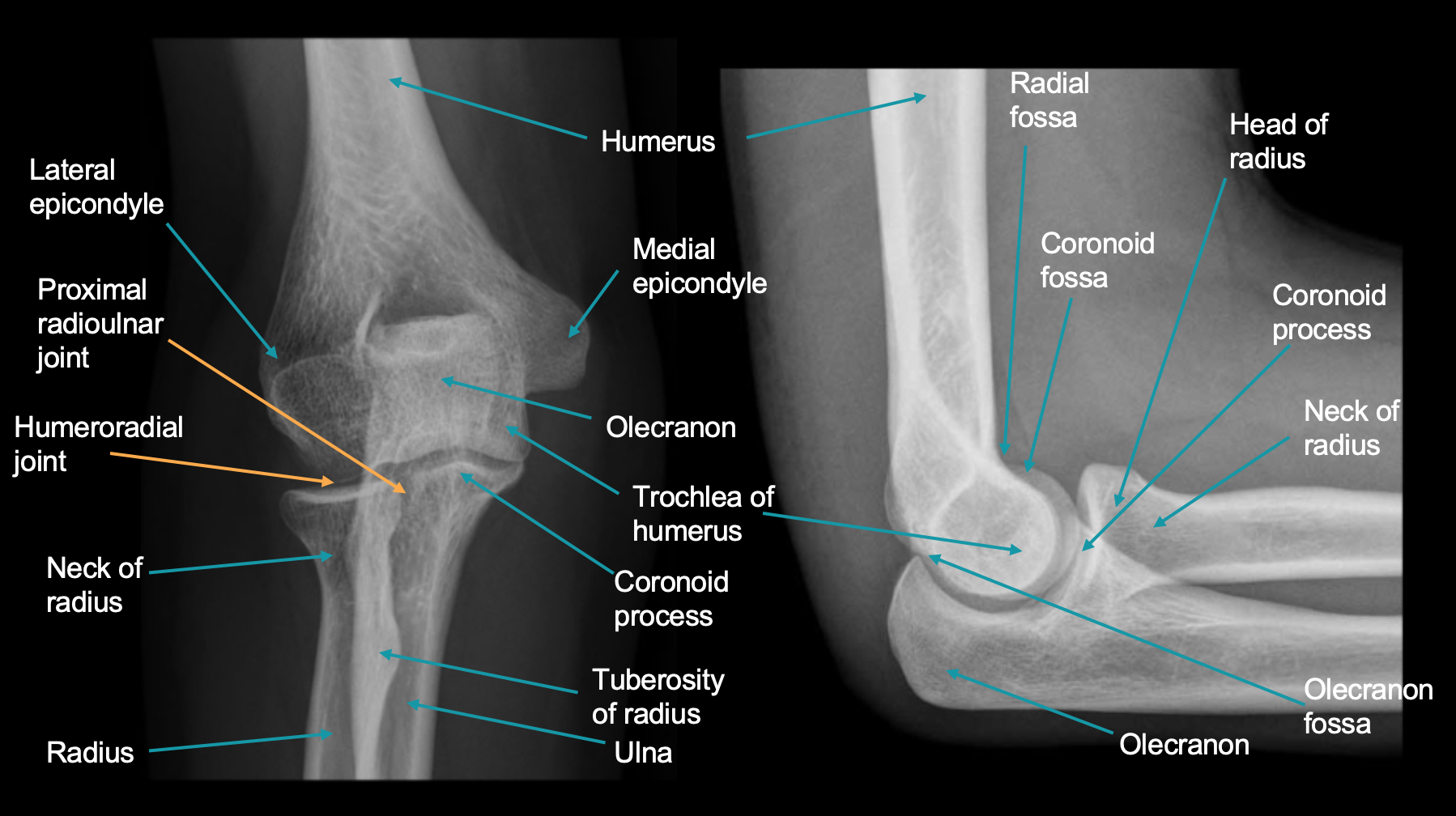
Imaging Imaging of the Elbow By admin On Jan 11, 2023 The elbow joint is a complex structure with three separate intracapsular articulations. These are highly congruent joints with multiplanar, noncollinear surfaces that make imaging difficult. The relatively small amount of overlying soft tissue and the ease of The radioanatomy of the elbow is studied via an AP X-Ray image and one in profile, showing the medial and lateral epicondyles, the olecranon, the head and neck of the radios, the radial and olecranon fossae, the humeral trochlea and the anatomical structures composing the humeroulnar joint, humeroradial joint and proximal radioulnar joint.
elbow x ray anatomy
This is often the only X-ray sign of a bone injury. A post-traumatic effusion without a visible bone fracture usually indicates a radial head fracture in an adult, and a supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus in a child. If there is a joint effusion but no history of trauma, an inflammatory cause should be considered. Adults: Treat as radial head fracture Peds: Be certain that neither an undisplaced supracondylar fracture nor a displaced internal epicondyle fracture is overlooked! Is the radiocapitellar line normal? A line drawn along the longitudinal axis of the radial head and neck should pass through the capitellum




