This article will describe the anatomy from the inferior view of the skull base. We will explore the many foramina and projections that enable arteries and nerves to both enter and leave the skull. 7.3 The Skull Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: List and identify the bones of the cranium and facial skull and identify their important features Locate the major suture lines of the skull and name the articulating bones that form them Define the paranasal sinuses and identify the location of each

parietal bone Colouring Pages (page 2) Anatomy bones, Skull anatomy
1/2 Synonyms: none The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( neurocr anium) and the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium ). The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault (Figure 1). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws. creates a bridge-like structure that connects the temporal bone with the zygomatic bone forming part of the zygomatic arch. Above: Markings of the cranium with the following views: (A) anterior view, (B) lateral view of the left side of the skull, (C) posterior view, and (D) lateral view of the right side of the skull. This is the preview of our full video about the bones, structures, foramina and fissures of the skull from an inferior view. Watch the full video on https://.
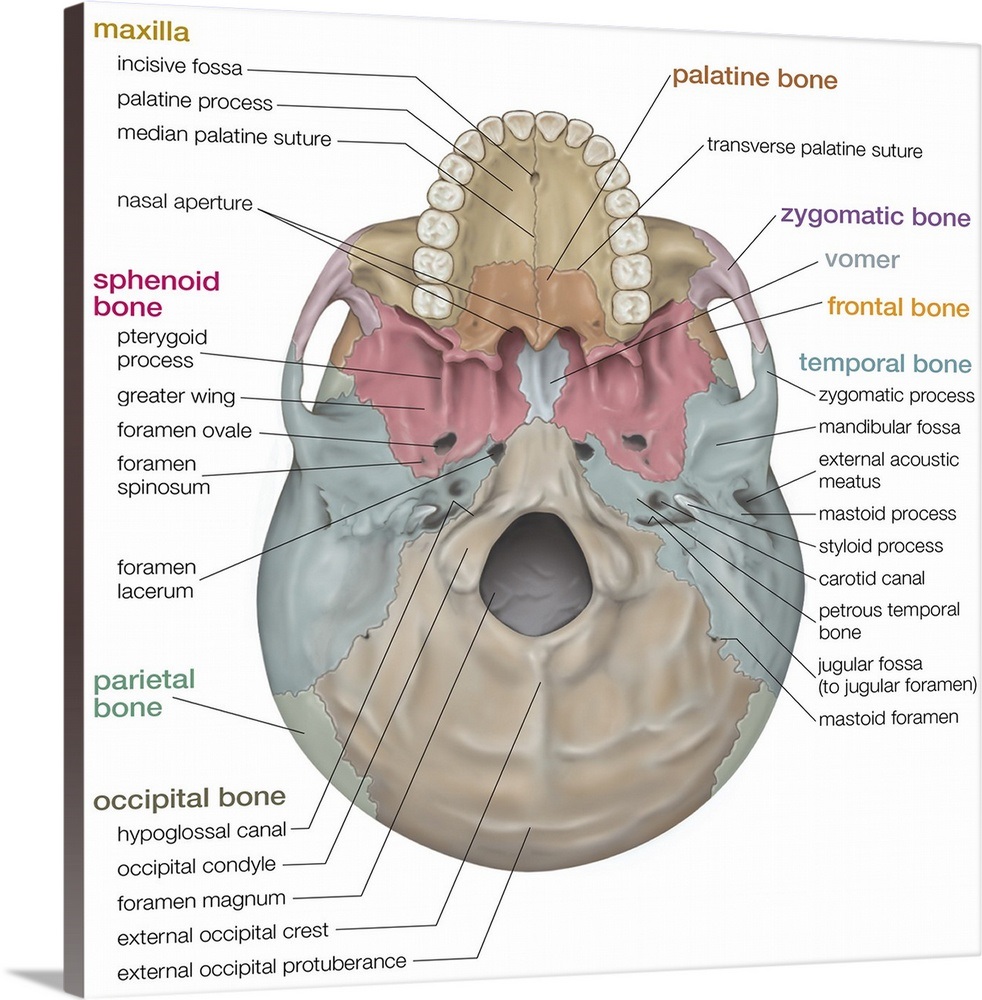
Skull inferior view. skeletal system Wall Art, Canvas Prints, Framed
Facial skeleton Zygomatic arch The zygomatic arch is a ring of flat bone formed by the union of the cheekbone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone.The bone forms the lateral part of the orbital socket and the floor of the orbit as well.. Incisive foramen The incisive foramen is a funnel-shaped opening also known as the anterior palatine foramen. Description: External and Internal Views of Base of Skull. (a) The hard palate is formed anteriorly by the palatine processes of the maxilla bones and posteriorly by the horizontal plate of the palatine bones. (b) The complex floor of the cranial cavity is formed by the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones. The cranium, or skull, is composed of 22 bones anis d divided into two regions: the neurocranium (which protects the brain) and the viscerocranium (which forms the face). Inferior nasal concha (2) Vomer (1) Mandible (1) Here, the hyoid bone, and the ear ossicles (middle ear bones) are also included in the facial bones. The three paired middle ear bones are malleus , incus, and stapes. Apart from forming the face, these bones are responsible for protecting and supporting the soft tissues in the area.

Back Of Skull Anatomy Labeled Multicolored Skull, inferior view
The facial bones of the skull form the upper and lower jaws, the nose, nasal cavity and nasal septum, and the orbit. The facial bones include 14 bones, with six paired bones and two unpaired bones. The paired bones are the maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior nasal conchae bones. The external cranial base (or external surface of cranial base, Latin: basis cranii externa) is the outer or inferior aspect of the skull base.This part of the skull extends from the superior incisor teeth to the superior nuchal lines of the occipital bone.The external cranial base can be subdivided into anterior, middle, posterior and lateral (2) parts.
skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The upper jaw, but not the lower, is part of the skull. The human cranium, the part that contains the brain, is globular and relatively large in comparison with the face. 1/7 Synonyms: none The human skull consists of about 22 to 30 single bones which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( cerebral cranium) and the face ( visceral cranium ). The main task of the skull is the protection of the most important organ in the human body: the brain.
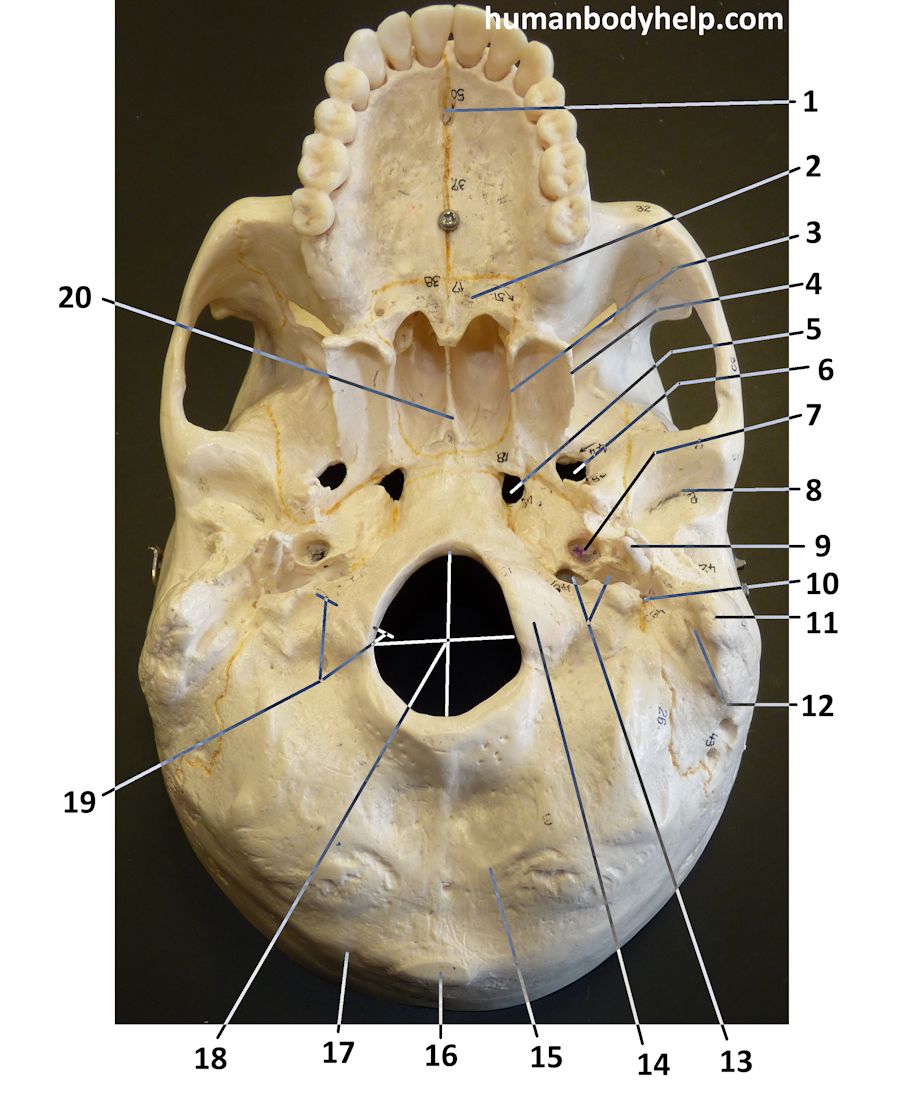
Skull Inferior View Human Body Help
Skeletal System > Skull Bones Review > The Skull Bones Anatomy - Inferior View The Skull Bones Anatomy - Inferior View Author: Scott A. Sheffield MS Last update: Nov 1st, 2022 Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn Start Now In this article, we will review the bones of the skull from an inferior view. Cranial bones and Facial bones: The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault ( Figure 7.3 ). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.




