The scapula, alternatively known as the shoulder blade, is a thin, flat, roughly triangular-shaped bone placed on either side of the upper back. This bone, along with the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum, composes the pectoral (shoulder) girdle, connecting the upper limb of the appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton. Fill in the sentences describing the parts of the humerus with the appropriate feature. Then place the structures in order from proximal to distal. Complete each sentence regarding the bones of the upper extremity. Then place the sentences in order, based on the bones, from proximal to distal.
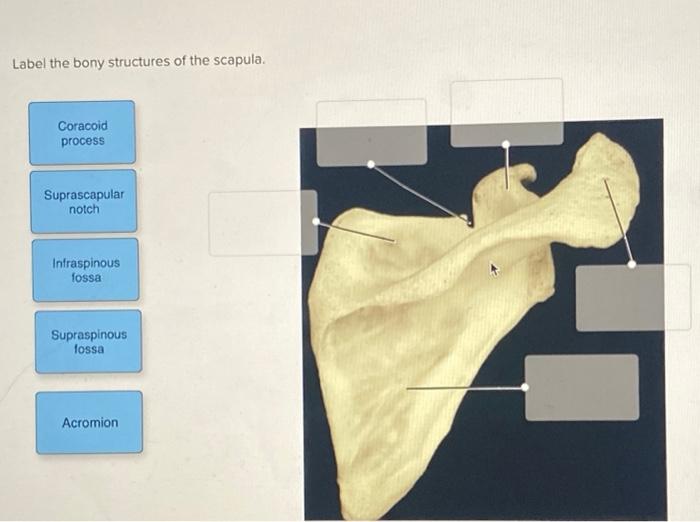
Solved Label the bony structures of the scapula. Coracoid
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a flat triangular bone located at the back of the trunk and resides over the posterior surface of ribs two to seven. Label the bony structures of the scapula. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. The scapula (AKA: the shoulder blade) is a flat, triangular shaped bone connecting the upper limb with the trunk. Along with the clavicle and manubrium of the sternum, it makes up one of three parts of the pectoral (shoulder) girdle. The scapula or shoulder blade is the bone that connects the clavicle to the humerus. The scapula forms the posterior of the shoulder girdle. It is a sturdy, flat, triangular bone. The scapula provides attachment to several groups of muscles. The intrinsic muscles of the scapula include the rotator cuff muscles, teres major, subscapularis, teres minor, and infraspinatus. These muscles attach.
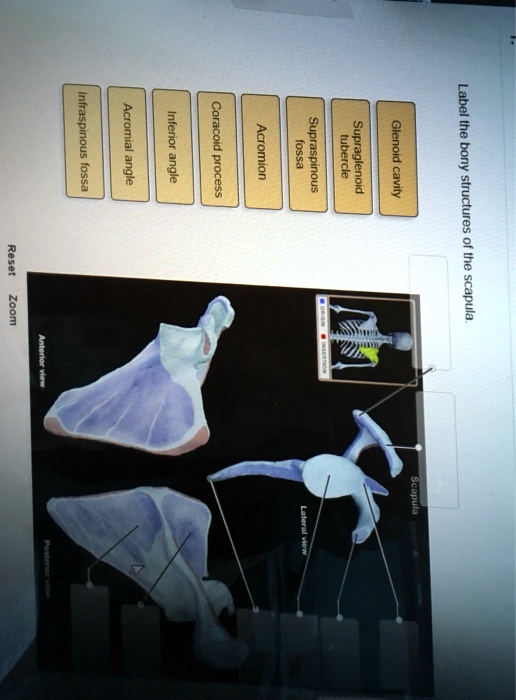
SOLVED Infraspinous fossa Acromial angle Inferior angle Coracoid
The scapula is a flat, triangular-shaped bone (colloquially as the "shoulder blade"). It is located in the upper thoracic region on the dorsal surface of the rib cage. It connects with the humerus at the glenohumeral joint as well as the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint to form the shoulder joint. In total, 17 different muscles attach to the scapula, which makes it difficult to fracture. The scapula stabilizes the arm and neck. The scapula, better known as the shoulder blade, is a triangular bone that serves as a joining force between the clavicle and the humerus. This bone is located posteriorly (on the back half of the body). The scapula plays an important role in stabilizing the other bones involved in the rhythm of shoulder. Structure. The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrinsic, extrinsic, and stabilizing and rotating muscles. The intrinsic muscles of the scapula include the muscles of the rotator cuff—the subscapularis, teres minor, supraspinatus, and infraspinatus. Also called: scapula, either of two large bones of the shoulder girdle in vertebrates. In humans they are triangular and lie on the upper back between the levels of the second and eighth ribs. A scapula's posterior surface is crossed obliquely by a prominent ridge, the spine, which divides the bone into two concave areas, the supraspinous and.
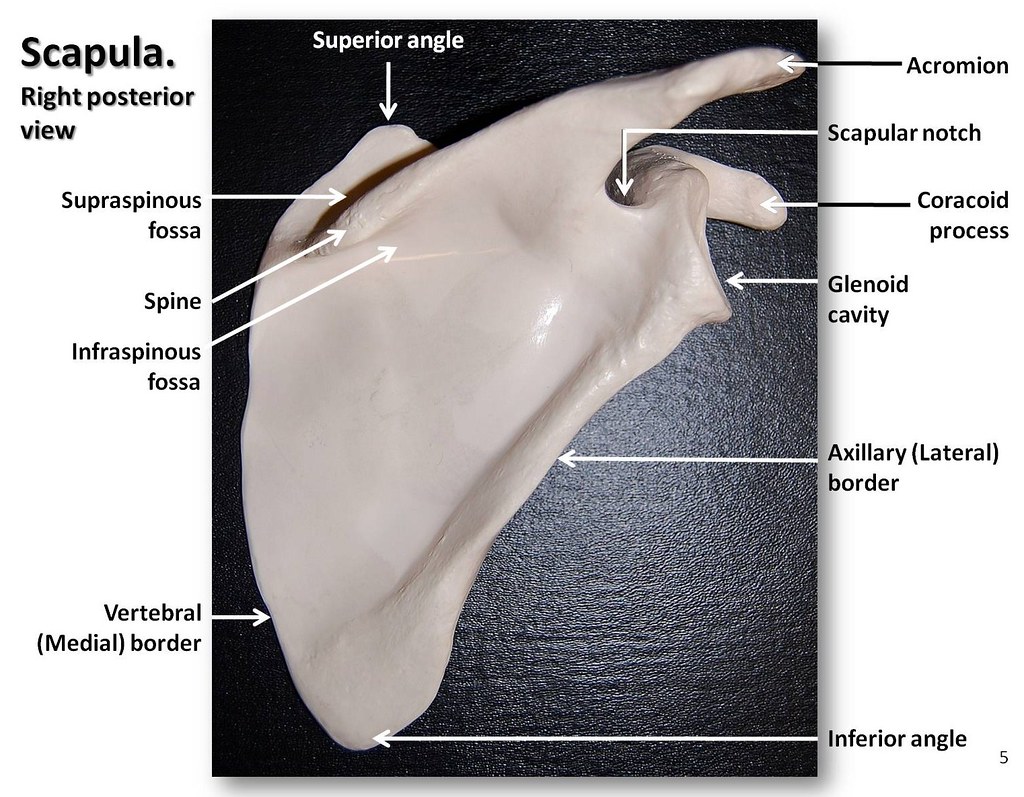
Scapula, posterior view with labels Appendicular Skeleto… Flickr
label the specific bony features of the skull in lateral view: label the bony structures of the shoulder and upper limb: label the bony structures of the thoracic cage: label the structures of the bone: Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like label the structures of a typical cervical vertebra:, label the structures of. It is comprised of two bones - the clavicle and scapula. The scapula is a triangular, flat bone, which serves as a site for attachment for numerous muscles. Anteriorly, the clavicle articulates with the sternum, thereby attaching the upper limb to the axial skeleton. The humerus provides skeletal support for the arm. It articulates proximally.
The scapula or shoulder blade is a flat, triangular upper limb bone that lies on the posterior surface of the thorax, over the ribs 2-7. It is a part of the pectoral (shoulder) girdle, together with the clavicle and sternum. The scapula articulates with the humerus, forming the shoulder (glenohumeral) joint. The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a flat, triangular bone located on the upper back of the body. It forms the posterior part of the shoulder girdle, along with the clavicle and humerus, and provides attachment sites for muscles that enable movement and stability of the shoulder joint. In this article, we will explore the anatomy.

the right scapula Human bones anatomy, Medical anatomy, Basic anatomy
Author: Scott A. Sheffield MS Last update: Nov 7th, 2022 Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn Start Now This 2-part quiz tests your knowledge on the anatomical markings of the scapula. You'll be required to identify all the structures, angles, and borders, as well as telling the difference between the left and right scapula. Basic Role and Anatomy of the Scapula. Humans have two scapula bones. Commonly known as the shoulder blade, the scapula is a relatively flat bone that articulates with both the humerus of the upper arm, forming the glenohumeral joint and the clavicle (collar bone) forming the acromioclavicular joint. Commonly forgotten, however, is the glide.




