Low FODMAP is a three-step elimination diet: First, you stop eating certain foods (high FODMAP foods). Next, you slowly reintroduce them to see which ones are troublesome. Once you identify the foods that cause symptoms, you can avoid or limit them while enjoying everything else worry-free. What is a low-FODMAP diet? FODMAP is an acronym for a certain class of carbohydrates, called fermentable short-chain carbohydrates, which are more difficult for people to digest. (The full acronym stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides and Polyols.)
FODMAP Dieta, O Que É, Alimentos — Consultoria Fitness BR
What is the low-FODMAP diet? A team of researchers designed the low-FODMAP diet to relieve symptoms of IBS. The plan helps you determine which FODMAPs are giving you trouble and which ones are your friends. The diet follows three basic steps: Restriction: Limit or eliminate all high-FODMAP foods for two to six weeks. Summary FODMAP stands for fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols. These are small carbs that many people cannot digest — particularly those with IBS. What happens when you eat. What is the Low-FODMAP diet? What effects do FODMAPS have on the digestive system? When is a Low-FODMAP diet recommended? How does the low FODMAP diet work? Examples of Low and High FODMAP foods What foods are suitable, and what should be avoided while on a Low-FODMAP diet? Author (s) and Publication Date (s) Note that the low-FODMAP diet is a therapeutic elimination diet that should be completed under the supervision of a medical professional. Meal planning can help keep you on track, no matter what your nutrition goal is. Prepping and planning doesn't have to be time-intensive and complicated.
Low Fodmap Diet What it Is, Uses & How to Follow
Monash University, which first proposed the diet, describes them as follows: Step 1: Low FODMAP: In this phase, the person swaps all high FODMAP foods for low FODMAP options for 2-6 weeks. Some. The low-FODMAP diet addresses four types of fermentable carbohydrates: oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (collectively referred to as FODMAPs). While the names sound somewhat abstract, the foods found within these groups are often too familiar to those with digestive woes. Oligosaccharides are present in foods like. The low-FODMAP diet can help identify which foods trigger your IBS symptoms. Avoiding these foods may help you manage your condition. How to Follow a LOW FODMAP Diet A low FODMAP diet should only be used by people who have been diagnosed with IBS by a health care provider. It is an elimination diet used to help find which foods cause IBS symptoms. The best foods to eat on a low FODMAP diet include high-protein foods, like meat, fish, poultry, firm tofu, tempeh, or eggs; and fatty foods like oil, butter, and hard cheeses (e.g., cheddar, gruyere, Emmental, parmesan). Kefir and lactose-free dairy products and grains like quinoa, rice, cornmeal, and gluten-free products may also be consumed.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Low FODMAP Diet
The 3 Phases of a Low FODMAP Diet. It's estimated that 50% of people with IBS may benefit from following a low FODMAPs diet [1] . These benefits include lessened gastrointestinal symptoms such. Polyols are sugar alcohols found in some stone fruits (such as cherries and nectarines), apples and pears; in vegetables such as mushrooms and cauliflower; and in some sugar substitutes containing xylitol or sorbitol. This diet starts with a low-FODMAP period, usually ranging from six to eight weeks.
Understanding the low FODMAP Diet Written by: CDHF Updated: November 17th, 2022 What are FODMAPs? FODMAPs are a group of small carbohydrate (sugar) molecules found in everyday foods. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and provide an important source of energy for the body. Low FODMAP Diet: A Guide for Clinicians and Patients is a comprehensive online book that provides evidence-based information on the role of FODMAPs in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other functional gastrointestinal disorders. It covers the mechanisms, diagnosis, management, and challenges of implementing a low FODMAP diet in clinical practice and in everyday life.
Dieta Low FODMAP Parte II NutriPharm
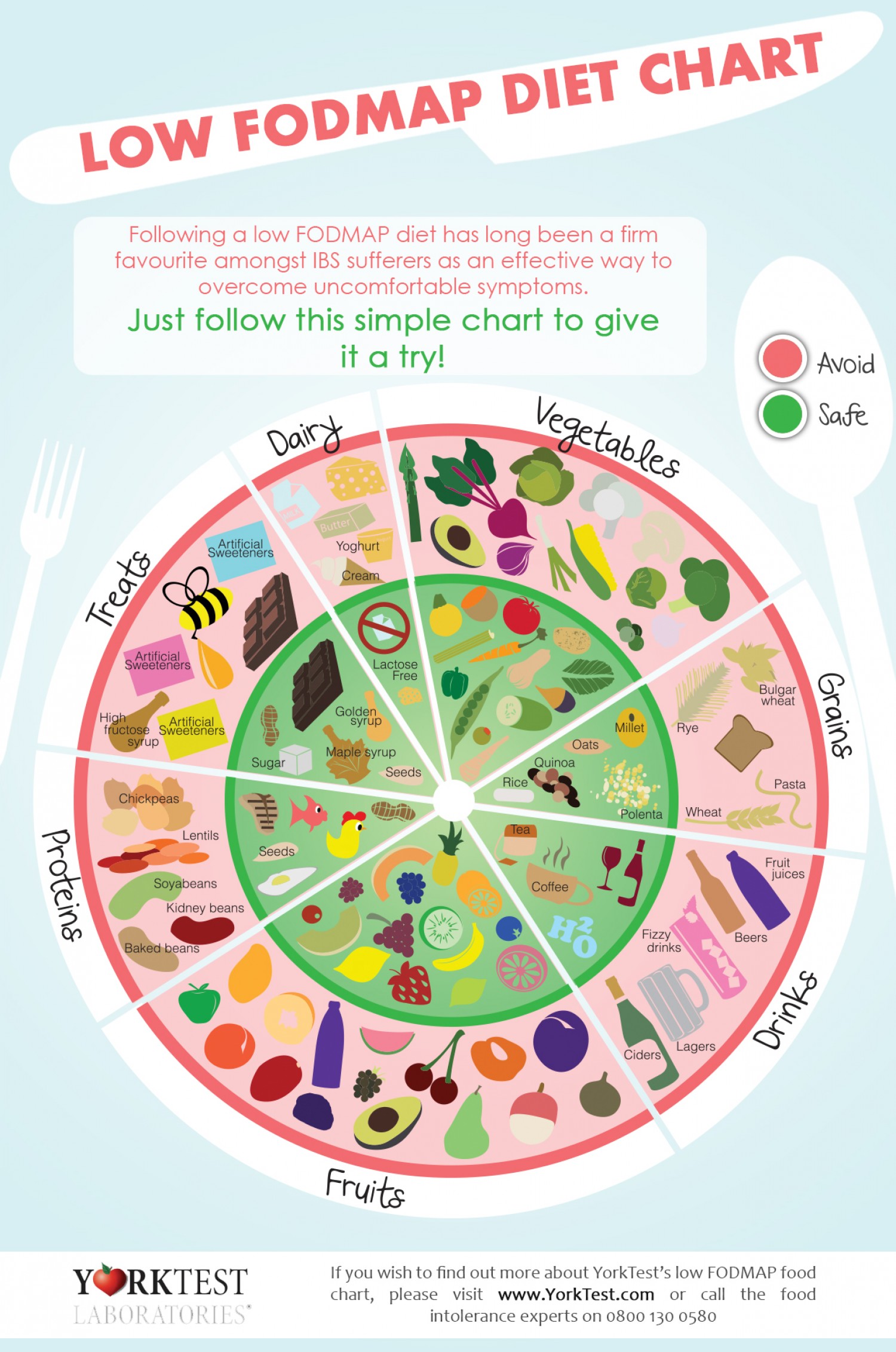
Step 1. In Step 1, follow the Monash University Low FODMAP Diet™ by swapping high FODMAP foods in your diet for low FODMAP alternatives. For example, if you normally eat wheat-based toast with honey for breakfast, you could swap to sourdough spelt toast with jam. The Food Guide of the Monash FODMAP App is very useful in this step of the diet. Elimination Phase: During this phase, you avoid high FODMAP foods for 2-3 weeks. The goal of this phase is symptom relief. Reintroduction Phase: In the reintroduction phase, you test one high FODMAP food at a time. The goal in this phase is to identify which FODMAP foods most aggravate your symptoms.




