How does the immune system work? - InformedHealth.org - NCBI Bookshelf The immune system has a vital role: It protects your body from harmful substances, germs and cell changes that could make you ill. It is made up of various organs, cells and proteins. The function of the immune system is to protect the host from pathogens and other causes of disease such as tumor cells. To function properly, the immune system must be able to detect a wide variety of pathogens. It also must be able to distinguish the cells of pathogens from the host's own cells and also to distinguish cancerous or damaged.
NLRP3 and STING enhance immune attack on cancer Cancer Biology
Metrics Abstract The human immune system is composed of a distributed network of cells circulating throughout the body, which must dynamically form physical associations and communicate using. Contents Introduction to the immune system Vaccinations Osmosis High-Yield Notes This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Immune System essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. 11.1: Immune System Concept Map Description A concept map of chapter 11.1 notes taken on 4-14-16 displaying the relationships between and in the specific and nonspecific immune systems. immune system specific immune system nonspecific immune system phagocytes lymphocytes use descriptive tags to organise your content what is immune system Immunity is a biological term that describes a state of having sufficient biological defences to avoid infection, disease, or other unwanted biological invasion. Innate, or nonspecific, immunity is the natural resistance with which a person is born. It provides resistance through several physical, chemical, and cellular approaches.

Immune System Concept Map Template EdrawMind
immune system is a network of cells, tissues*, and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks by "foreign" invaders. These are primarily microbes (germs)—tiny, infection-causing organisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi. Because the human body provides an ideal environment for many microbes, they try to. immune system, the complex group of defense responses found in humans and other advanced vertebrates that helps repel disease-causing organisms (pathogens). Immunity from disease is actually conferred by two cooperative defense systems, called nonspecific, innate immunity and specific, acquired immunity. The immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies. Antibodies attach to an antigen and attract cells that will engulf and destroy the pathogen. The main cells of the immune system are lymphocytes known as B cells and T cells. Concept maps are graphical representations of knowledge that connect concepts, ideas, and relationships. The present study aims at assessing the perception of medical students in utilization of concept maps as a tool to foster their lifelong learning skills in immunology. Methods:

Immune system group 5
• PART 1 o Identify the main organs and cells of the immune system, and explain how they work together. o Describe the origin of the immune cells that might appear in a medical report. • PART 2 o Compare and contrast the innate and adaptive immune responses, and explain how they interact. Complete this concept map to summarize the key concepts concerning the body's defenses. Verified Solution. 2m.. Immune System, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #45. CrashCourse. 636. 04:44. The Immune System. Medical Research Council. 358. 08:56. Immune System. Amoeba Sisters. 230. 05:23.
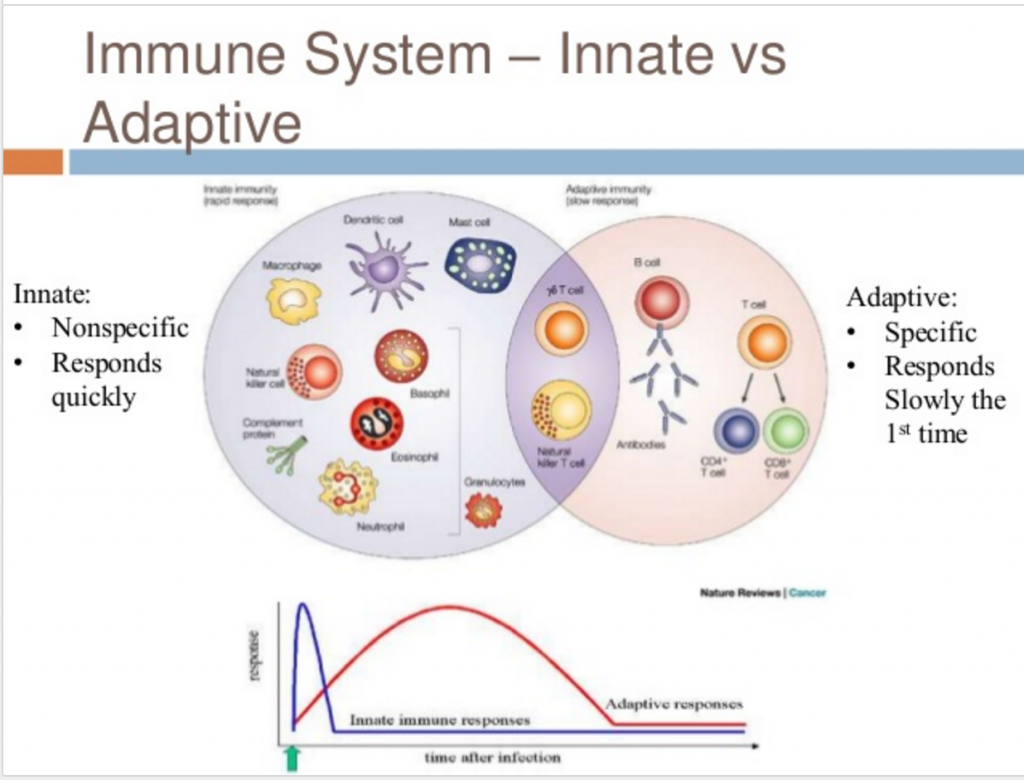
Scientists create first full map of human immune system connectivity. By using advanced screening methods to tune into the communications taking place between individual cells, scientists have. In all, the innate immune system is thought to recognize approximately 10 3 of these microbial molecular patterns. For More Information: Leukocytes from Unit 5 Examples of innate immunity include anatomical barriers, mechanical removal, bacterial antagonism, antigen-nonspecific defense chemicals, the complement pathways, phagocytosis, inflammation, fever, and the acute-phase response.

Ch 21 Immune System Group 4
"The immune system includes primary lymphoid tissue, such as the thymus and bone marrow, secondary lymphoid tissue, like the lymph nodes and spleen, and immunocytes in non-lymphoid tissues such as lung, skin and gut," says Dr. Teichmann. Keywords: active learning, concept maps, immunology education, just-in-time teaching, student-centered learning, technology in education, undergraduate.. The American Society of Microbiology (ASM) podcasts describe many pathogens and their interactions with the immune system, and also include a dedicated "Immune" podcast devoted to.


